S14: Data Acquisition using CAN bus
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Project Title
Abstract
Our project is to implement a high speed data acquisition system using CAN and storing the data into the SD card. Our system will collect data from sensors over multiple nodes and transmit the data over the CAN bus. The CAN packets are received by a single node and stored into the SD card. We will use SPI bus protocol to communicate with SD card. The purpose is to gather all the data simultaneously over the CAN bus.
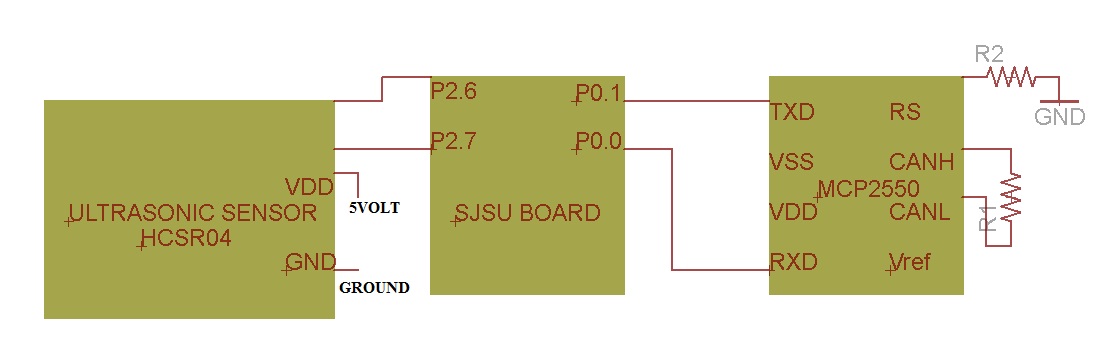
Figure 1 shows the system block diagram:
Objectives & Introduction
Our idea is to use the on board accelerometer and gyroscope together as a motion/gesture sensor to identify the motion then it will send to the other board via CAN bus. We are planning to use 6 degree of freedom MPU-9150 sensor for doing precise movement tracking. Recognized movement will trigger predefined tasks and transmit to Android phone via UART-Bluetooth module. More sensors will also be added to do data acquisition.
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Shweta Bohare
- Can bus Interface
- Mradula Nayak
- Can bus Interface
- Heng Zhang
- Accelometer and sensors
- All Team
- FreeRTOS Software Design
- 3D on the computer
Schedule
Show a simple table or figures that show your scheduled as planned before you started working on the project. Then in another table column, write down the actual schedule so that readers can see the planned vs. actual goals. The point of the schedule is for readers to assess how to pace themselves if they are doing a similar project.
| Week# | Start Date | End Date | Task | Actual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2/25 | 3/18 |
|
Completed.Other parts are ordered. |
| 2 | 3/18 | 3/26 | Self-Loop testing of CAN Bus | Completed. |
| 4 | 3/27 | 4/13 | Write on microSD SPI microSD I/O | Initial write on SD-card is done. |
| 5 | 4/6 | 4/12 | Interfacing ultrasonic sensor with the board. | In process |
| 6 | 4/13 | 4/27 | Accelerometer data transmission between 2-Boards. | In process |
| 7 | 4/22 | 4/27 | Communication between 3 CAN Nodes | |
| 8 | 4/28 | 5/5 | Testing and remove bugs, further enhancements | |
| 9 | 5/8 | 5/8 | Demo |
Parts List & Cost
| Parts | Cost | Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
SJ One Board[1] |
$80.00 x3 |
Each board uses for different functions |
GY 521 board(MPU-6050) |
$5.90 x1 |
6 DOF motion sensor |
</tr>
|
TJA1049TK[2] |
$0.00 x4; free samples |
high-speed CAN transceiver |
|
Total Cost |
$$$$$ |
Keep it low |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
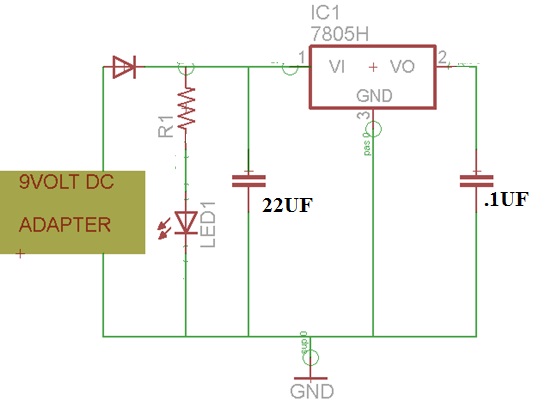
Power Supply : An LM7805 linear regulator IC is used for this purpose. It converts a DC input voltage of range 7-25 V to a stable +5 V. It requires just two external capacitors and is very easy to useThe input DC voltage for LM7805 could be obtained from a 9V DC wall adapter that can supply 1 Amp of load current.We need the 5 volt supply for all the external ICs have been used in this project like MCP2551 and MPU6050.The following schematic is generate the 5Volt regulated power.
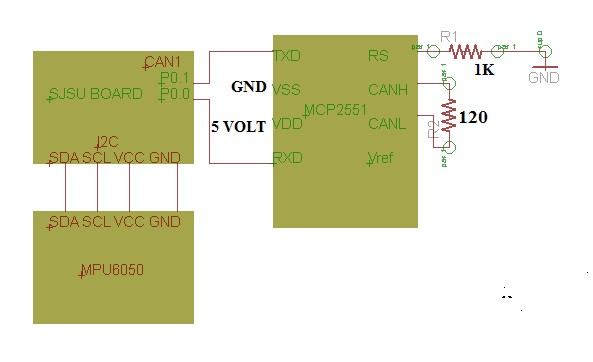
The MCP2551 is a high-speed CAN, fault-tolerant device that serves as the interface between a CAN protocol controller and the physical bus. The MCP2551 device provides differential transmit and receive capability for the CAN protocol controller, and is fully compatible with the ISO-11898 standard, including 24V requirements. It will operate at speeds of up to 1 Mb/s.
It is used for following functions:
1. As a Transmitter: It operates in two states Dominant and Recessive. When differential voltage between CANH and CANL is less than 102 V it operated in dominant mode, and when the voltage difference is less than 1.2 volt it operates in Recessive mode. These both modes are corresponds to the TXD pin .
2. Maximum nodes: allowing a maximum of 112 nodes to be connected
3. Receiver Function: The RXD output pin reflects the differential bus voltage between CANH and CANL. The Low and High states of the RXD output pin correspond to the Dominant and Recessive states of the CAN bus, respectively.
4. Operations.High speed flow control and standby. High-Speed mode is selected by connecting the RS pin to VSS. In this mode, the transmitter output drivers have fast output rise and fall times to support high-speed CAN bus rates. The slope, or slew rate (SR), is controlled by connecting an external resistor (REXT) between RS and VOL (usually ground). The device may be placed in Standby or SLEEP mode by applying a high-level to the RS pin
MCP2551
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design and Implementation
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
File:Node1 File:Node2.jpg File:Node3.jpg
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
My Issue #1
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
Send me your zipped source code and I will upload this to SourceForge and link it for you.
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.