F19: Infinity Mirror
Contents
- 1 Infinity Mirror
- 2 Abstract
- 3 Introduction & Objectives
- 4 Team Members & Technical Responsibilities
- 5 Administrative Responsibilities
- 6 Team Deliverables Schedule
- 7 Bill of Materials (General Parts)
- 8 Printed Circuit Board
- 9 Product Enclosure
- 10 RGB LED Matrix
- 11 MP3 Decoder
- 12 Sensors Interface
- 13 OLED Screen
- 14 Android App
- 15 Bluetooth Interface
- 16 Testing and Technical Challenges
- 17 Suggestions for Future Students
- 18 Conclusion
- 19 Project Video
- 20 Project Source Code
- 21 References
Infinity Mirror
Abstract
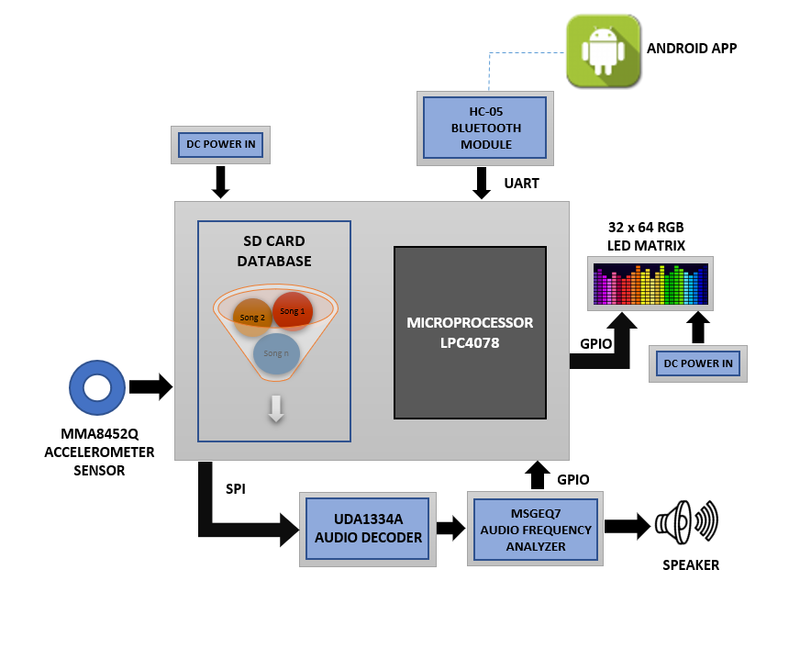
The main aim is to build an embedded system consisting of two entertainment modes - Music and Gaming. On the music mode, the audio frequency spectrum bands based on audio tune are displayed on a LED Matrix. The user can switch to gaming mode with a favorite choice of song being played in the background. The MP3 module reads songs from an SD card and plays the music through a speaker interfaced with the board. It deals with the convergence of various services such as playing a game with background music, gesture recognition, audio decoding, audio saving and retrieving and audio frequency band visualisation etc. This project consists integrating various elements such as 'Audio Codec', '32x64 RGB LED Matrix' and 'HC-05 bluetooth module and android app' along with some other onboard features like 'Gesture detection', 'Ambient Light Sensing' and 'OLED Display' with SJ-two Launch pad.
Introduction & Objectives
The key features support by the system are real-time Gesture recognition & trigger actions in player and display audio Spectrum on LED matrix:
1. Determine the actions of air gesture based on the input received or through a manual key selection of songs from the Songs List (In this prototype, search for the response for recognised gesture from the database & perform actions to other peripherals.)
2. In response, retrieve the data from the SD Card & communicate to the audio decoder for audio streaming.
3. Onboard display will show current playing song information and LED Matrix will show audio spectrum patterns.
4. Interacting with HC-05 bluetooth for communicating with Mobile App.
5. A Game related to accelerometer orientation detection - Fruit Fury - where the player will smash the fruits by tilting the microcontroller board towards the direction of the fruit's appearance on the LED matrix.
Project Objectives
1. Audio Codec - Interacting with Audio Codec for getting the sound samples & generating sound signals from the device
2. Gesture Sensor - Detects the Hand Gesture and send the detected gesture to LED Matrix to navigate LED's.
3. SD Card - Audio data or mp3 files will be retrieved from the SD card based on the user selection.
4. Audio Decoder - Intelligently processing the audio data using audio decoder and sent to the LED Matrix to display spectrum patterns.
5. Bluetooth HC-05 - Interfaces the system using Bluetooth to an Android application.
6. RGB LED Matrix - Display frequency bands on music mode and view the game on the game mode.
Team Objectives
1. Learn each and every module as much as possible, in order to develop an overall product.
2. Understand the proper use of queues and semaphores in order to send/receive the data between multiple tasks.
3. Document and track all the bugs encountered during development and learn to update git repo after every fix.
Team Members & Technical Responsibilities
- Aakash Chitroda
- MP3 Audio Encoder/Decoder
- Audio frequency Analyzer logic
- Vidushi Jain
- Bluetooth Communication
- Interfacing of Gesture & Accelerometer Sensors
- Hardware Designing & PCB Integration
- Ganesh Ram
- Interfacing of LED Matrix and driver design
- Game design
- Audio frequency spectrum logic on LED
- Packaging
- Niket Naidu
- Android & Bluetooth Application
- OLED Interfacing and Designing
Administrative Responsibilities
| Administrative Roles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Aakash Chitroda | |||
|
Niket Naidu | |||
|
Vidushi Jain | |||
|
Vidushi Jain
Ganesh Ram | |||
|
Ganesh Ram | |||
Team Deliverables Schedule
| WEEK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
TASK DETAILS |
STATUS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 Oct 2019 | 22 Oct 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 2 | 23 Oct 2019 | 29 Oct 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 3 | 30 Oct 2019 | 5 Nov 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 4 | 6 Nov 2019 | 12 Nov 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 5 | 13 Nov 2019 | 19 Nov 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 6 | 20 Nov 2019 | 26 Nov 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 8 | 27 Nov 2019 | 3 Dec 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 9 | 4 Dec 2019 | 10 Dec 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 10 | 11 Dec 2019 | 17 Dec 2019 |
|
Completed Completed Completed Completed Completed |
| 11 | 18 Dec 2019 |
|
Completed Completed |
Bill of Materials (General Parts)
| PART NAME |
PART MODEL & SOURCE |
QUANTITY |
COST PER UNIT (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
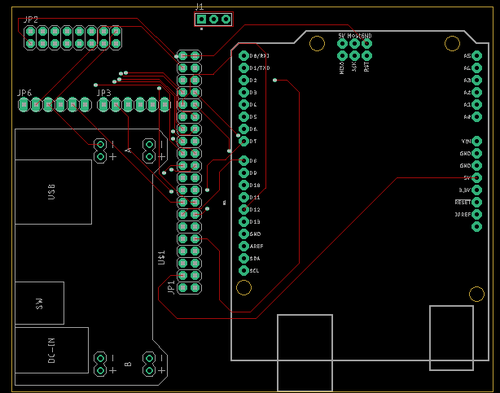
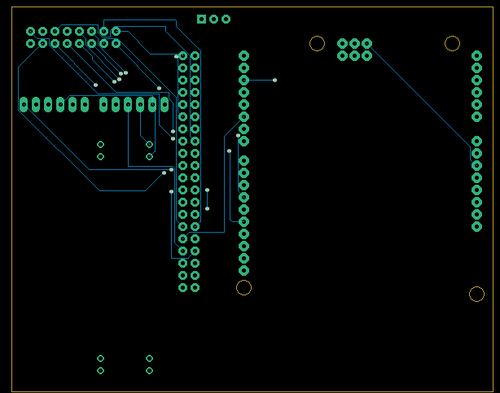
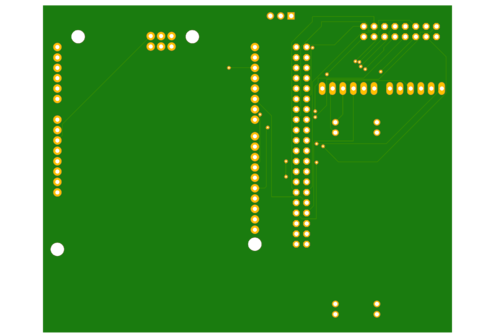
Printed Circuit Board
Design And Architecture
We have designed the custom PCB using Eagle Software and as well as one prototype board in which we have connected all the modules with SJ-Two board. PCB was sent to fabrication to JLCPCB China which provided PCB with lead time of 1 week. We have implemented 2 layers of PCB with all of the parts in top layer.
Components Placements on PCB and on Prototype Board
1. One SJ-Two board is fitted onto the top of the 3D printed lid cover which with a slot opening for 2x40 IDC cable.
2. MP3 Decoder is connected with SJ-Two board and will be place on the right side of PCB and as well as on Prototype board.
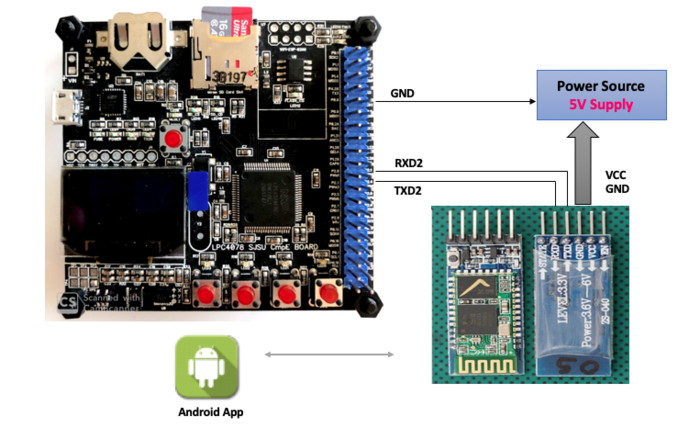
3. Bluetooth Module needs only 4 pins to connect with SJ-Two and goes to UART3 and placed on the top left of the board.
4. LED Matrix is connected using 2x8 IDC cable pins on the top left side of the board.
5. Audio Frequency Analyzer is placed on the bottom side of PCB.
6. Power supply of 5v and 3.3v provisions are made on the bottom left side of PCB.
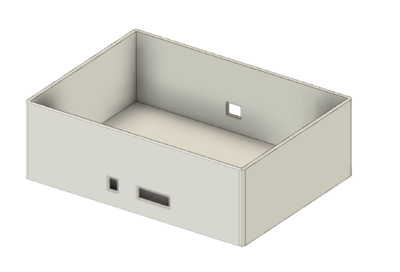
Product Enclosure
To facilitate easy and convenient gaming experience and also act as an effective audio controller, a single 3D printed enclosure was designed which is spacious enough to accommodate the MCU modules like bluetooth, audio frequency analyzer and MP3 decoder on the PCB.
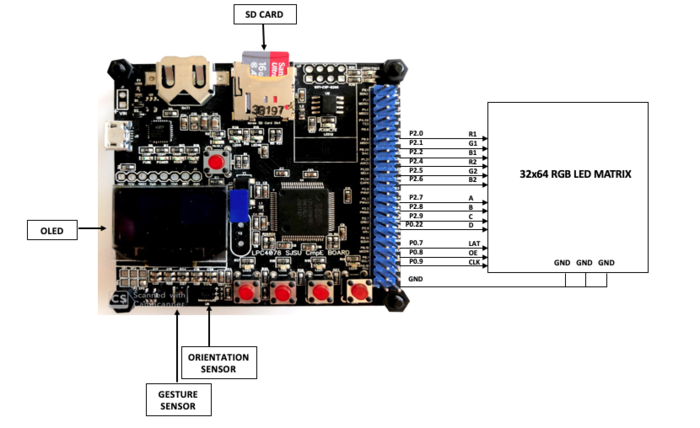
RGB LED Matrix
A 32 x 64 RGB LED Matrix will be powered up through a 5V/4A DC adapter and is interfaced with the board to play the game 'Fruit Fury' with desired background song in the game-mode and to display the frequency bands and other relevant messages such as "Next", "Previous" and "Pause" in the music-mode. Only the INPUT IDC connector will be used because we are not cascading multiple matrices. The matrix has 2 planes (upper and lower), both of which will be programmed separately. In order to set RGB color data for each pixel in plane 1 (top half of the display) we use R1, G1 and B1 pins and for plane 2 we use R2, G2 and B2. By setting and resetting the CLOCK pulse, color data is set for every pixel in the row. Then the LATCH is set to mark end of the row and reset to move to next row. All of these steps are repeated at very less time intervals so that the human eye perceives it as one complete frame (Persistence of Vision).
Below is the description of the pins:
- R1 -> Sets upper panel's Red data
- G1 -> Sets upper panel's Green data
- B1 -> Sets upper panel's Blue data
- R2 -> Sets lower panel's Red data
- G2 -> Sets lower panel's Green data
- B2 -> Sets lower panel's Blue data
- A -> Sets row bit 0
- B -> Sets row bit 1
- C -> Sets row bit 2
- D -> Sets row bit 3
- CLK (Clock) -> Set to access each pixel
- LAT (Latch) -> Set to mark comletion of one row
- nOE (Output Enable) -> Set to switch the LEDs off when transitioning from one row to the next
- GND -> Ground pins to be connected with board's GND.
Below are the technical specifications:
- Pitch -> 4 mm
- Resolution -> 32 x 64 = 2048 dots
- Panel dimensions (l x b x h) in mm -> 256 x 128 x 13
- Working voltage/current rating -> 5v / 4A (max)
- Scan rate - 1/16
- Pixel component configuration (R,G,B) -> 1,1,1
- Weight -> 0.24 kg
LED Matrix Code
GitLab link to LED Matrix Code
Hardware Design
The hardware involves 5V/4A DC power supply adapter, barrel jack connectors and IDC cables to power up the LED matrix and communicate with the board. Below is the pin interfacing diagram.
Software Design
1. Fruit Fury - Game mode
There are 2 tasks involved to ensure functioning of the game.
a) Task 1:
- Display the game's title screen. On pressing the onboard switch (SW1), game begins.
- Also used to display game over screen.
b) Task 2:
- Enter into game mode to play the game.
- Read accelerometer values (board orientation) and render game frame.
- Detect the player's board movement, compare it with fruit's location.
- Display score, lives and smash effects.
- Press another switch (SW0) to stop game and return to title screen or to restart the game once it is over.
Game rules:
a) Game comprises of 3 levels (level 2 on reaching score 15 and level 3 on reaching score 30) and 5 lives in total.
b) Primary objective is to tilt the board to the direction (North West, North East, South West or South East) in which the fruit appears in order to smash it.
c) Score increases by 1 point for smashing each fruit.
d) Bombs start appearing after completion of level 1, which costs a life when hit.
e) Level 3 is faster so make sure you tune your reflexes up.
f) Reach score 50 to win the game.
Bonus:
a) Streaks are rewarding. Smash 10 fruits straight up to win an extra life.
b) Look out for star fruits. Hit them to gain +2 points.
Choose your song to take all the inspiration you can and start smashing!
2. Music mode
a) Press the button to enjoy music-only mode. Graceful audio spectrum bands are displayed that dance to the tune of the chosen song.
b) A display is prompted to the user whenever music is paused or changed to next or previous song.
Implementation
LED Driver
1. Initialize the LED matrix by configuring necessary pin directions.
2. Disable Output Enable (OE) GPIO before feeding matrix data.
3. Select the required row by setting bits on A, B, C, D GPIO pins.
4. Loop through the pixels (columns) in the selected row and set the pixel color on R, G, B GPIO pins.
5. Set zero on R, G, B GPIO pins to mask that particular pixel.
6. Set and Reset the clock for pushing the R, G, B bits for each column.
7. Issue latch to mark the row's completion and reset latch before going to next row.
8. Follow the steps 2 to 7 for other rows.
for (uint8_t row = 0; row < (MAX_ROW / 2); row++) {
disableOE();
set_row(row);
for (uint8_t col = 0; col < MAX_COL; col++) {
LPC_GPIO0->PIN |= (1 << CLK);
set_color_bottom(game_matrix[row + (MAX_ROW / 2)][col]);
set_color_top(game_matrix[row][col]);
LPC_GPIO0->PIN &= ~(1 << CLK);
}
LPC_GPIO0->PIN |= (1 << LAT);
LPC_GPIO0->PIN &= ~(1 << LAT);
enableOE();
vTaskDelay(1);
}
Fruit Fury - Game mode
1. Generate the fruit's initial coordinate using random function (used srand() with time value as seed to get random pattern sets).
2. Construct the LED matrix array by drawing the fruit and borders.
3. Push the entire matrix data to LED driver to display the constructed matrix frame.
4. Then read the player's orientation and match with fruit's direction.
5. Modify game parameters (score, lives and level) based on player's results.
6. Stop game if all lives are over and display game over screen by switching to game init task (Task 1).
/* Push button to exit game */
if (LPC_GPIO0->PIN & (1 << SW0))
is_start_game = false;
if (is_start_game == true) {
/* Generate fruit's initial coordinate position */
get_fruit_begin_coord(&row_pt, &col_pt, &quadrant);
/* Generate final frame by considering fruit object at that position */
construct_game_matrix(row_pt, col_pt);
/* Draw final frame matrix of the game */
draw_final_game_frame();
/* Get the board direction from the user and increment score count */
compute_game_params(row_pt, col_pt, quadrant);
} else
vTaskResume(display_game_init_screen_t);Spectrum display - Music mode
1. Read the audio frequency values from the graphic equalizer task and store it as an array.
2. Based on value of each frequency band, assign a height of the band (in pixels) to be drawn on the LED matrix.
3. Set a unique color for each band.
3. Push the entire matrix data to LED driver to display the constructed matrix frame.
4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 at required intervals to display repeating bands.
for (row = MAX_ROW - 1; row >= 1; row--) {
for (col = 7; col <= 62; col++) {
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[0])) && col >= 7 && col <= 13 &&
band_num <= 0) {
band_matrix[row][col] = RED;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[1])) && col >= 14 && col <= 20 &&
band_num <= 1) {
band_matrix[row][col] = GREEN;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[2])) && col >= 21 && col <= 27 &&
band_num <= 2) {
band_matrix[row][col] = YELLOW;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[3])) && col >= 28 && col <= 34 &&
band_num <= 3) {
band_matrix[row][col] = BLUE;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[4])) && col >= 35 && col <= 41 &&
band_num <= 4) {
band_matrix[row][col] = PURPLE;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[5])) && col >= 42 && col <= 48 &&
band_num <= 5) {
band_matrix[row][col] = CYAN;
}
if ((row >= (MAX_ROW - band_height[6])) && col >= 49 && col <= 55 &&
band_num <= 6) {
band_matrix[row][col] = WHITE;
}
}
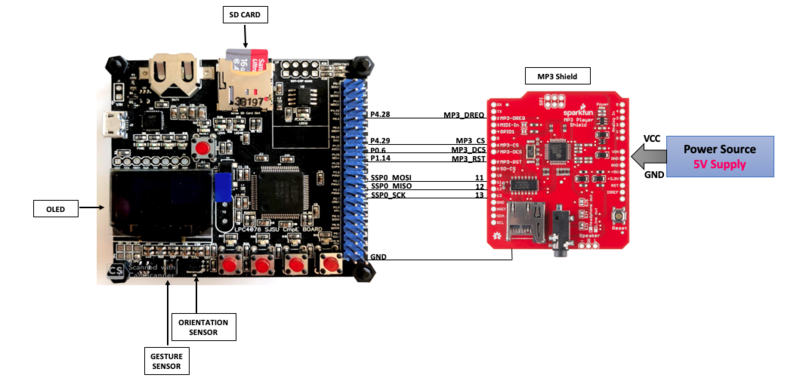
}MP3 Decoder
MP3 Decoder Code
GitLab link to MP3 Decoder Code
Hardware Design
Software Design
Implementation
Sensors Interface
Sensor Code
Hardware Design
Software Design
Implementation
OLED Screen
Software Design
The open source package u8g2 has been used. There are already ready made functions for various OLED Drivers. The indepth setup guide can be found here
Implementation
The u8g2 library is a very robust library which means that this code can be extended for any microcontroller as long as the interface is written properly.
We needed to write 2 main functions, outlined below, i.e byte_cb and gpio_and_delay_cb using the function prototype `uint8_t u8x8_lpc_gpio_and_delay(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr)`.
Since the SJ2 Board is connected to the OLED Screen on the SPI1 Bus we also need to write the SPI1 driver, mainly a method to that sends data over SPI to the Slave device i.e the OLED Screen
Initializing the u8g2 for LPC4078
// Created a file `u8g2_wrapper.h
static gpio_s dc;
static u8g2_t u8g2;
void u8g2_wrapper__init(gpio_s *dc_pin) {
u8g2_Setup_ssd1306_128x64_vcomh0_1(&u8g2, U8G2_R0, u8x8_byte_4wire_hw_spi, u8x8_lpc_gpio_and_delay);
u8g2_InitDisplay(&u8g2);
u8g2_SetPowerSave(&u8g2, 0);
dc.pin_number = dc_pin->pin_number;
dc.port_number = dc_pin->port_number;
}
u8g2_t *u8g2_wrapper__get_instance() { return &u8g2; }
uint8_t u8x8_lpc_gpio_and_delay(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr) {
switch (msg) {
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_AND_DELAY_INIT:
delay__ms(1);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_DELAY_MILLI:
delay__ms(arg_int);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_DC:
// DONE, Write to the GPIO_DC Pin
if (arg_int == 0) {
gpio__reset(dc);
} else {
gpio__set(dc);
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_RESET:
break;
}
return 1;
}
uint8_t u8x8_byte_4wire_hw_spi(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr) {
uint8_t *data;
switch (msg) {
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_SEND:
data = (uint8_t *)arg_ptr;
while (arg_int > 0) {
ussp1__exchange_byte((uint8_t)*data);
data++;
arg_int--;
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_INIT:
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_SET_DC:
if (arg_int == 0) {
gpio__reset(dc);
} else {
gpio__set(dc);
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_START_TRANSFER:
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_END_TRANSFER:
break;
default:
return 0;
}
return 1;
}Android App
Android App Code
Software Design
The Android app has been built using the cross platform framework Flutter
The app is composed of 3 parts, Game Mode, MP3 Mode and MP3 Song List. On the main screen we first connect to the bluetooth before establishing connection with any of the modes. The working of each mode is explained in each subsection below.
A few variables to note in advance ACK = 0x00, sent when successful NACK = 0xFF, sent incase there is any error
Game Mode
To enter the Game Mode screen we first check if the Bluetooth Connection is established. We send in a one byte data 0xa1 over bluetooth to the SJ2 Board and get back the response "a1$ack/nack$##"
We enter the game mode which contains a joystick that can transmit 4 values depending on the quadrant of the joystick.
First Quadrant: 0x71 Second Quadrant: 0x72 Third Quadrant: 0x73 Fourth Quadrant: 0x74
MP3 Mode
To enter the MP3 Mode screen we first check if the Bluetooth Connection is established similar to the Game Mode. We send in one byte of data 0xa2 over bluetooth to the SJ2 Board and get back the response "a2$ack/nack$volumeInfo$currentSong$isPlaying/isPaused$##" where isPlaying is 1 and isPaused is 0.
These values are loaded into the MP3 Mode Screen as initial values for the current song playing.
We can then see a screen where we can control the various aspects of playing songs i.e Playing and Pausing the song, Go to next song and and Go to the previous song. We can also control the volume remotely.
Controlling each part of this interface is the same as sending a single byte of data over bluetooth to the SJ2 Board.
Playing and Pausing Song
We just toggle the state of the Song. We issue this command by sending 0xc1 which is the Toggle State command.
Next Song and Previous Song
Command for the previous song is 0xc0 Command for the next song is 0xc2
Control Volume remotely
For volume we divide the percentage 100 percent in 16 parts. We can send the value between 0xb0 to 0xbf in increments of one ste-p. This is parsed on the SJ2 Board and converted to an equivalent volume signal.
MP3 Song List
To get the MP3 Song List we first check if the Bluetooth Connection is established similar to the Game Mode and MP3 Song mode. We send in one byte of data 0xa3 over bluetooth to the SJ2 Board and get back the response "a3$ack/nack$data$data$...$##".
Bluetooth Interface
Bluetooth Code
Hardware Design
Software Design
Implementation
Testing and Technical Challenges
1. RGB LED Matrix
a) Getting control of the matrix was challenging as it needs to follow specific sequence of pin enabling/disabling at appropriate timing.
b) Setting right delays to avoid flickers and get smooth transitioning between frames.
c) Fixing high CPU utilization.
d) Designing elements of the game (title screen and fruit objects).
Suggestions for Future Students
1. RGB LED Matrix
- To begin with, focus on writing simple driver to get control of 1 pixel at a targeted location and then use appropriate loops to light up entire row / column.
- Make sure all pixels are able to light up with all possible colors to eliminate hardware defects.
- Try with minimum / no delays, print tick counts and then come up with meaningful delay numbers.
- Optimize the code (minimum delays, avoiding repetitive function calls etc.) to bring down the CPU usage level.
- Use the link in the references to draw desired elements and generate the matrix.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
- Git Project Link: [1]
References
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank professor Preet for giving us the opportunity to incorporate the course curriculum into practical model and supporting us whenever needed. Availability of slack channel and weekly reviews ensured us to clarify bottlenecks in the project, keep things organized and track progress of each tasks. We would also extend our gratitude towards ISA members who have taken their time in clearing our queries throughout the course.