S15: Protocol Interface: I2C - CAN Bridge
Contents
- 1 Serial Protocol Convertor
- 2 Abstract
- 3 Objectives & Introduction
- 4 Team Members & Responsibilities
- 5 Schedule
- 6 Parts List & Cost
- 7 Design & Implementation
- 8 Hardware Design
- 9 Hardware Interface
- 10 Software Design
- 11 Implementation
- 12 Testing & Technical Challenges
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Project Video
- 15 Project Source Code
- 16 References
Serial Protocol Convertor
Abstract
This project is aimed at developing a device, which is able to convert the incoming data from one protocol to another (I2C, UART, SPI, CAN). In a system operating over a CAN architecture, there is a need of an inbuilt CAN peripheral interface in every controller. Because of hardware limitations, many controllers do not support the CAN peripherals; therefore they are restricted to communicate over the limited number of protocols. This device provides a flexibility to the designers so that they can choose any communication protocol at the input, and convert the data to the desired protocol.
Objectives & Introduction
Basically, this device will convert the incoming data from one protocol to the other desired protocol. Considering the problems faced in an industry, the main goal of this project is to enable the designers to use a controller, that supports any serial protocol, to the system using CAN bus.
For designing a protocol converter, there are some aspects such as speed synchronization and bi-directional communication, which are necessary to make this device useful. A practical example would be connecting an I2C device to the CAN system. Since the I2C protocol consists of a master - slave approach, it is not possible to control the I2C master by I2C slave. In this project, these conditions are handled using hardware interrupts. Also speed synchronization is a crucial aspect, as every protocol supports different data speed. The concept of Queues and Mailboxes is used to handle the speed limitations. FreeRTOS is used for designing the software of this system.
Team Members & Responsibilities
| S.R. | Team Member's Name | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ishan Bhavsar |
|
| 2 | Tej Kogekar | |
| 3 | Rutwik Kulkarni |
|
| 4 | Mitesh Sanghvi |
Schedule
| S.R. | Start Date | End Date | Task | Status | Actual Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 03/08/2015 | 03/14/2015 | Develop driver for interrupt based I2C acting as a Slave Device | Completed | 03/14/2015 |
| 2 | 03/15/2015 | 03/21/2015 | Exploring CAN API and building CAN bus for communication | Completed | 03/21/2015 |
| 3 | 03/22/2015 | 03/28/2015 | Study and Design mailbox system for CAN messages | Completed | 03/28/2015 |
| 4 | 03/29/2015 | 04/04/2015 | Develop program for configuring the Protocol Interface by I2C Master | Completed | 04/04/2015 |
| 5 | 04/05/2015 | 04/11/2015 | Create task for storing CAN messages in mailboxes | Completed | 04/11/2015 |
| 6 | 04/12/2015 | 04/18/2015 | Create task for giving interrupt to I2C Master | Completed | 04/18/2015 |
| 7 | 04/19/2015 | 04/25/2015 | Create task for sending message on CAN recieved from I2C Master | Completed | 04/25/2015 |
| 8 | 04/26/2015 | 05/02/2015 | Design of Status Register for Protocol Interface | Completed | 05/02/2015 |
| 9 | 05/03/2015 | 05/09/2015 | Finalizing appropriate addresses for all registers | Completed | 05/09/2015 |
| 10 | 05/10/2015 | 05/16/2015 | Testing of Protocol Interface for various conditions | Completed | 05/12/2015 |
| 11 | 05/17/2015 | 05/23/2015 | Adding a feature of Bit-Masked CAN IDs | Completed | 05/22/2015 |
Parts List & Cost
| S.R. | Description | Manufacturer | Part Number | Qty | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SJOne Board | - | - | 1 | $80.00 |
| 2 | Ultrasonic Sensor (Optional) | Parallax | 28015 | 1 | $23.00 |
| 3 | CAN Transceiver (Free Samples) | Microchip | MCP2551 | 1 | $0.00 |
| 4 | Linear Voltage Regulator (Free Sample) | LT | LT1083-5 | 1 | $0.00 |
| Total | $103.00 |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
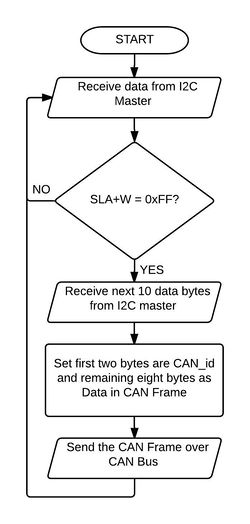
Software Design
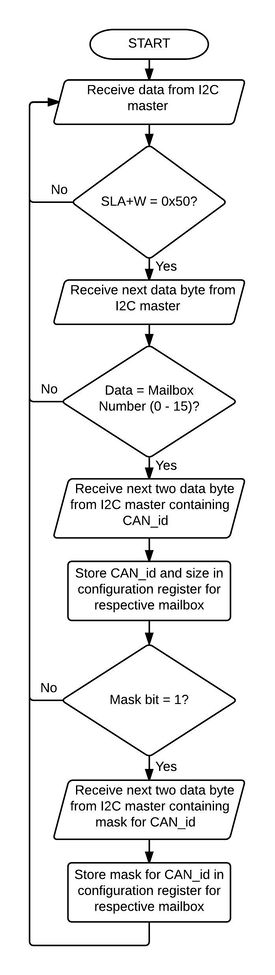
Configure Mailbox
|
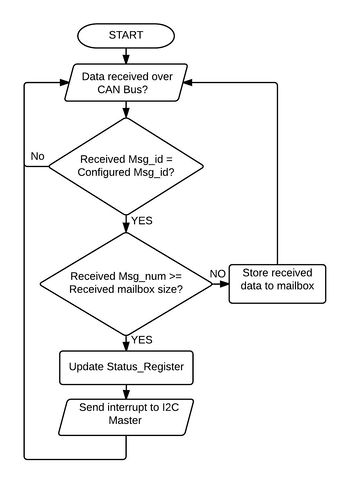
CAN to Mailbox
|
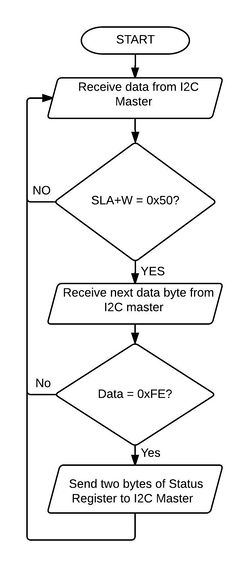
Read Status Register
|
Read Mailbox Data
|
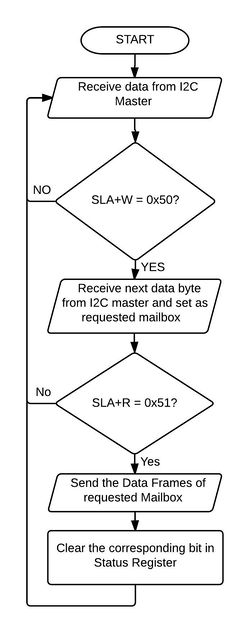
Send Data over CAN
|
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
My Issue #1
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
- LPC_USER_MANUAL
- Ultrasonic Sensor
- GLCD with Touchscreen
- CAN Transceiver
- Linear Voltage Regulator
- Socialledge Embedded Systems Wiki
- Preetpal Kang, Lecture notes of CMPE 243, Computer Engineering, Charles W. Davidson College of Engineering, San Jose State University, Aug-Dec 2014.
- en.wikipedia.org/