Difference between revisions of "S22: Firebolt"
Proj user9 (talk | contribs) (→Parts List & Cost) |
Proj user9 (talk | contribs) (→Parts List & Cost) |
||
| Line 487: | Line 487: | ||
! scope="row"| 13 | ! scope="row"| 13 | ||
| Traxxas Battery and Charger | | Traxxas Battery and Charger | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 4 April 2022
Contents
FireBolt RC Car
Abstract
Firebolt is battery powered autonomous RC car. The car uses four microcontrollers for communication between the nodes- driver node, motor node, bridge & sensor node, and geological node over the CAN bus. It is interfaced to the mobile application which sends GPS coordinates for the destination location to the driver node and reaches the destination by avoiding any obstacles that comes in the path. For obstacle detection and avoidance it uses Ultrasonic Sensor and makes the decision of steering and maintaining speed based on the bridge and sensor node's input.
Objectives & Introduction
Objectives
- RC car can communicate with an Android application to:
- Receive new coordinates to travel to
- Send diagnostic information to the application
- Emergency stop and start driving
- RC car can travel to received coordinates in an efficient path while avoiding obstacles
- RC car can maintain speed when driving on sloped ground
- Design printed circuit board (PCB) to neatly connect all SJ2 boards
- Design and 3D print sensor mounts for the ultrasonic sensors
- Design a simple and intuitive user interface for the Android application
- Design a DBC file
Introduction
The Firebolt RC car uses 4 SJ2 boards as nodes on the CAN bus
- Driver Node
- GEO Node
- Sensors and Bridge Node
- Motor Node
- Mobile Application
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Priyanka Rai
- Geo Controller
- Bridge and Sensor Controller
- Wiki Page Update
- Ritu Patil
- Motor Controller
- Android Application
- Integration Testing
- Ritika Beniwal
- Master Controller
- PCB Designing
- Wiki Page Update
- Utsav Savaliya
- Sensor Controller
- Dhanush Babu
- Hardware Integration
Schedule
| Week# | Start Date | End Date | Task | Actual Completion | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1
02/28 to 03/06 Start of Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2
03/07 to 03/13 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3
03/14 to 03/20 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 4
03/21 to 03/27 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 5
03/28 to 04/03 End of Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 6
04/04 to 04/10 Start of Phase 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 7
04/11 to 04/17 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 8
04/18 to 04/24 End of Phase 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 9
04/25 to 05/01 Start of Phase 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 10
05/02 to 05/10 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11
05/11 to 05/15 End of Phase 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 12
02/28 to 03/06 End of the Project |
|
|
|
|
|
Parts List & Cost
| Item# | Part Desciption | Vendor | Qty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RC Car | Traxxas [1] | 1 | $250.00 |
| 2 | CAN Transceivers MCP2551-I/P | Comimark [2] | 5 | $7.00 |
| 3 | Ultrasonic Sensors | Max Botix[3] | 5 | $150.00 |
| 4 | GPS and Antenna | Adafruit[4] | 1 | $60.00 |
| 5 | HC05 bluetooth RF Transreceiver | HiLetgo[5] | 1 | $12.59 |
| 6 | Triple-axis Accelerometer | Adafruit[6] | 1 | $21.40 |
| 7 | Traxxas RPM Sensor | Traxxas[7] | 1 | $12 |
| 8 | Discrete Electronic Components | Generic[8] | 1 | $28.75 |
| 9 | Buck-Boost Voltage Regulator | Generic[9] | 1 | $11.99 |
| 10 | Traxxas Telemetry Trigger magnet & holder | Traxxas[10] | 1 | $6.35 |
| 11 | Acrylic Sheet | Tap Plastic | 1 | $12 |
| 12 | Battery | |||
| 13 | Traxxas Battery and Charger |
Printed Circuit Board
PCB Schematic
PCB Design
CAN Communication
We use controller area network to broadcast data between the 4 nodes. All nodes are connected to each other through a physically conventional two wire bus. The wires are a twisted pair with 120 Ω resistors at each ends of the bus. 1s and 0s are transmitted as CAN High(0V difference) and Can Low(2v difference). A CAN frame has the following contents:
- Data Length Code (4bits)
- Remote Transmission Request.
- ID extend bit.
- Message ID (11 bit or 29 bit)
- Data bytes( depends on DLC)
- CRC
Arbitration: No two nodes will transmit at the same time because if arbitration. A lower Message-ID has a Higher priority on the CAN bus since 0 is the dominant bit.
Bit Stuffing: CAN bus stuffs extra bits when a long chain of multiple 1's or 0's occur to improve CAN integrity.
| Sr. No | Message ID | Message function | Receivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driver Controller | |||
| 1 | 300 | speed and steering direction for the motor. | Motor |
| 2 | 310 | Destination reached | Sensor |
| Sensor Controller | |||
| 1 | 200 | Sensor sonars from front, back, left ,right sensor | Driver |
| Motor Controller | |||
| 8 | 700 | motor speed, motor direction | Driver |
| Geo and Bridge Controller | |||
| 1 | 400 | Bearing, Heading and Distance | Driver |
| Debug messages | |||
| 1 | 851 | Driver Debug | SENSOR,MOTOR,GEO_AND_BRIDGE |
| 1 | 811 | Motor Debug | SENSOR,MOTOR,GEO_AND_BRIDGE |
| 1 | 801 | Sensor Debug | SENSOR,MOTOR,GEO_AND_BRIDGE |
Hardware Design
DBC File
Sensor ECU
Hardware Design
Sensor Controller Schematic
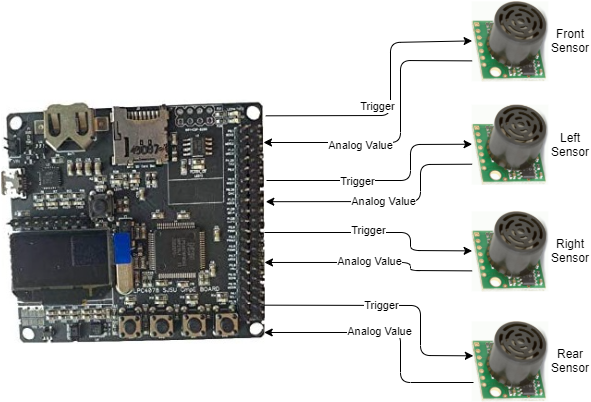
Board Pin Connections
Sensors are interfaced with combination of GPIO, ADC Pins on SJTWo board. Below is the descriptive pin layout:
Software Design
The sensor node mainly does two activity viz. 1) Read sensor values, 2) Transmit obstacle distance over CAN bus. Both of these activities happen in a 20Hz periodic callback.
1. Read Sensor Values
2. Transmit obstacle distance over CAN bus:
Technical Challenges
Neighboring Sensor Interference:
Frequent noisy measurements:
Motor ECU
Hardware Design
The motor node(SJ-2) interfaces primarily interfaces with:
All these three components have 3 pins each. The functionalities of these pins are mentioned in the table below.
Software Design
Technical Challenges
Geographical And Bridge Controller
Hardware Design
Software Design
The GEO controller is divided into 5 parts.
Technical Challenges
Driver Node
Hardware Design
The Driver Node has one peripheral connected to it and that is the LCD screen.
Software Design
- Driver Node Flow Chart
Technical Challenges
Mobile Application
User Interface
Software Design
This app has mainly two activities, The main activity and maps activity.
Maps Activity
Bluetooth/WIFI
Technical Challenges
Conclusion
Project Video
Project Source Code
Advise for Future Students
Acknowledgement
References
http://socialledge.com/sjsu/index.php/Industrial_Application_using_CAN_Bus