Difference between revisions of "SJ One Board"
(→Board Experiments) |
(→File I/O) |
||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
void file_io() | void file_io() | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | /* Option 1 : C library I/O (less efficient) */ | + | /* Option 1 : C library I/O (less efficient) |
| − | FILE *fd = fopen("myfile.txt", "r"); | + | * 0: is for SPI Flash |
| + | * 1: is for SD Card | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | FILE *fd = fopen("0:myfile.txt", "r"); | ||
char line[128] = { 0 }; | char line[128] = { 0 }; | ||
if (fd) { | if (fd) { | ||
| Line 167: | Line 170: | ||
/* Write "hello" to "myfile.txt" */ | /* Write "hello" to "myfile.txt" */ | ||
| − | Storage::write("myfile.txt", "hello", 5, 0)) | + | Storage::write("0:myfile.txt", "hello", 5, 0)) |
/* Read the size of data array from myfile.txt */ | /* Read the size of data array from myfile.txt */ | ||
Revision as of 00:25, 7 September 2013
Contents
Introduction
This article provides details of the SJ-One Board used by San Jose State University.
Contact Preet if you need to get one of these boards.
LPC1758 User Manual
Board Features :
- LPC1758 CPU - 512K ROM, 64K RAM
- 4 Switches and 4 LEDs (both hard-wired)
- Sensors :
- Temperature, 3-Axis Acceleration, IR (remote control), and Light
- 2-Digit 7-Segment Display
- RTC Crystal with Backup Battery
- Micro SD Card and 1Mb SPI Flash.
- Socket for Xbee or Wifi Module (Uart2 or Uart3)
- Built-in Nordic Wireless (Board-to-Board communication)
- Many GPIOs with two SPI, Multiple UARTs, and I2C availability
- Power from USB or External Power
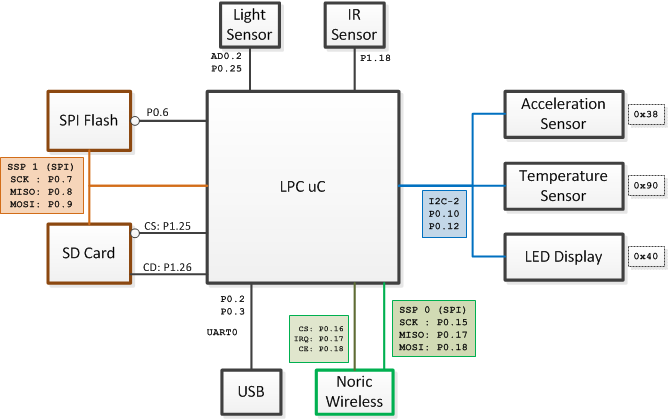
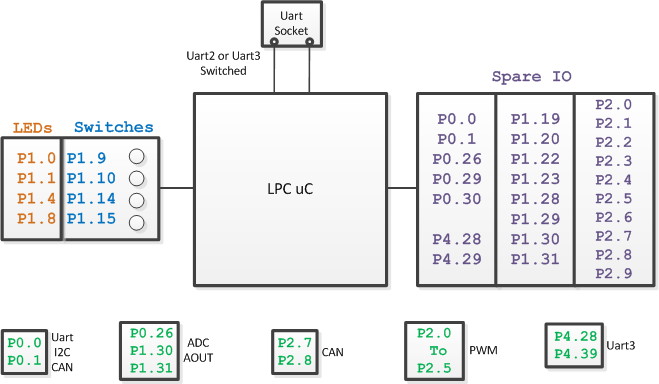
Board Block Diagrams
The block diagrams below show the connectivity to various different chips on the PCB, and also show which GPIOs are available to you. The first diagram shows the pins used for on-board sensors or interfaces. The second diagram shows IOs you can use.
Board Connections
Board IO
Board Schematic
Download the PDF Schematic here:
File:2012SJOneBoardSchematic.pdf
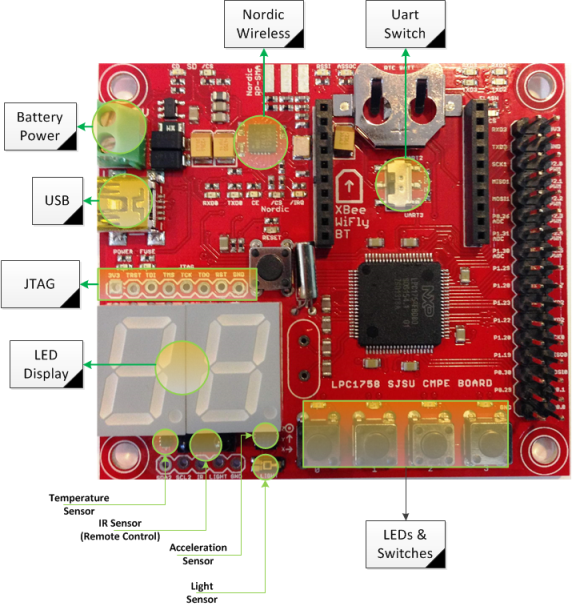
Board Overlay
This board overlay can be compared against diagrams above to get an idea of where the IOs are located.
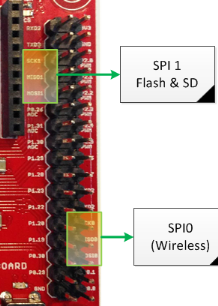
External SPI Devices
To hook up your external SPI device(s), use SPI#1 connections because there is already a driver in SJ-One sample project for this SPI. See the connections below and the sample code:
#include "spi1.h"
void access_my_spi_device()
{
// Send 0xDEAD over to SPI device and get 2 bytes back:
chip_select_my_device(true);
{
char byte_0 = spi1_exchange_byte(0xDE);
char byte_1 = spi1_exchange_byte(0xAD);
}
chip_select_my_device(false);
/**
* You can use any GPIO for CS (chip-select) signal.
* This example assumes CS is done through a function:
* chip_select_my_device(bool);
*/
} |
External I2C Devices
|
I2C#2 is tied to on-board sensors and you should utilize I2C 2's connection to hook up external I2C devices. See the connections below and the sample code: #include "I2C2.hpp"
void send_byte_to_my_i2c_device()
{
const char my_dev_addr = 0xBA; // Your device address
const char my_dev_reg = 0x01; // Write to 1st register of your device
const char my_dev_data = 0xAB; // Write 0xAB to reg 0x01
I2C2::getInstance().writeReg(my_dev_addr, my_dev_reg, my_dev_data);
} |
Board Experiments
LEDs & Switches
There are on-board switches and LEDs you may use. Furthermore, you can interface your board to external LEDs or switches as well.
#include "io.hpp"
void led_sw()
{
/* Check if button 1 or button 4 are pressed */
if (SW.getSwitch(1) || SW.getSwitch(4)) {
LE.on(1);
LE.off(4);
}
else {
LE.setAll(0); /* Turn off all LEDs */
}
}
#include "gpio.hpp"
void external_led()
{
/* You can use any pin defined at gpio.hpp file
* Use "Ctrl+R" and search for "gpio.hpp" file.
*/
GPIO pin20(P1_20); /* Use P1.20 as General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) */
pin20.setAsOutput(); /* Use this pin as OUTPUT */
pin20.setHigh(); /* Turn on voltage to 3.3v */
pin20.setLow(); /* Turn off voltage to 0v */
}
Sensors
This section provides examples of how to read data values from the sensors.
#include "io.hpp"
void sensors()
{
int light_value = LS.getRawValue();
int tilt_x = AS.getX();
int tilt_y = AS.getY();
int tilt_z = AS.getZ();
int temperature_f = TS.getFarenheit();
}
Wireless
This board can communicate to other boards using a very low-powered wireless technology. There are numerous code samples documented at Interactive Wireless Nodes Project article which you can use to get started. The alternative approach is to simply read the documentation of wireless.h file at your project.
File I/O
You can read or write files on the SPI Flash or an SD card. You can open a limited amount of files using standard C libraries. First, at your sys_config.h file, please enable ENABLE_C_FILE_IO
#include "io.hpp"
void file_io()
{
/* Option 1 : C library I/O (less efficient)
* 0: is for SPI Flash
* 1: is for SD Card
*/
FILE *fd = fopen("0:myfile.txt", "r");
char line[128] = { 0 };
if (fd) {
fgets(line, sizeof(line)-1, fd);
fclose(fd);
}
/* Option 2 : Use "storage" object (more efficient)
* This option doesn't require 'ENABLE_C_FILE_IO'
*/
/* Write "hello" to "myfile.txt" */
Storage::write("0:myfile.txt", "hello", 5, 0))
/* Read the size of data array from myfile.txt */
char data[16] = { 0 };
Storage::read("myfile.txt", data, sizeof(data)-1, 0));
}