|
|
| (334 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
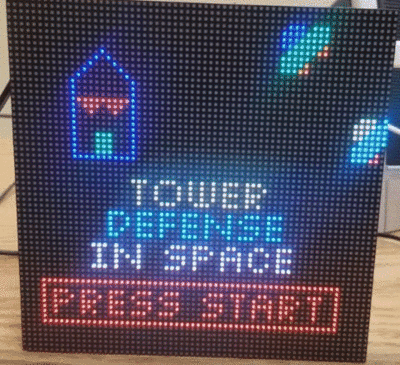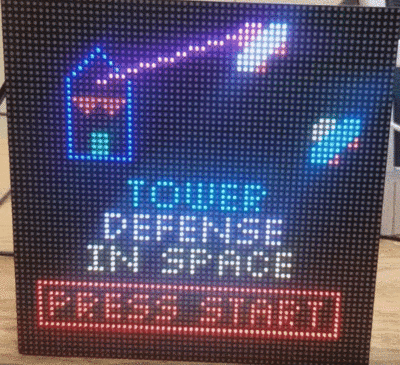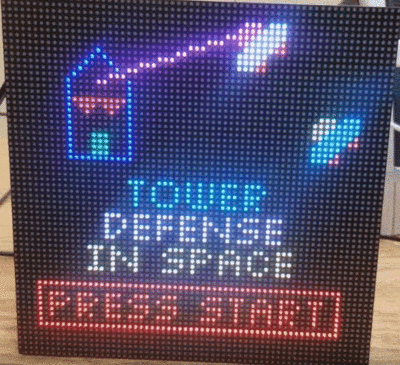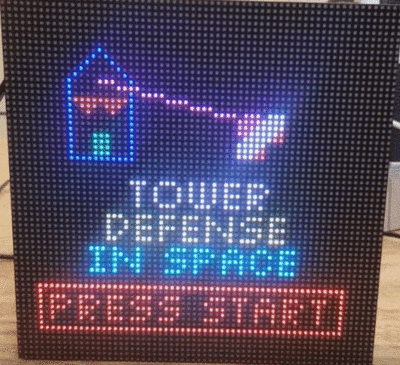
| − | [[File:RunDBC Logo.png|thumb|775px|caption|right|RunDBC Logo]] | + | [[File:start_menu.jpg|thumb|500px|caption|right|Logo]] |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC car pic.jpg|thumb|750px|caption|right|RunDBC Autonomous Car]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | == ABSTRACT == | + | == Abstract== |
| − | The RUN-D.B.C project, involved the design and construction of an autonomously navigating RC car. Development of the R.C car's subsystem modules was divided amongst and performed by seven team members. Each team member lead or significantly contributed to the development of at least one subsystem. The project was an exercise, not only of technical skills, but soft skills such as project management.<br />
| + | This project involves creating and developing a video game where output is displayed on a LED matrix. Development of the relevant hardware/software components and modules was divided among 4 team members. Each team member lead or significantly contributed to the development of multiple components. The project was focused on not only technical skills, but team building as well, and working with others towards a common goal. |
| | + | |
| | + | This project provides us hands-on experience using freeRTOS in a real application. Our objective is to apply what we have learned in class and develop a video game using our SJtwo Board. In this project, we create different tasks for different modules, such as a display task for displaying the game objects on LED matrix, a tower task for detecting nearby enemies and shoot them, a stage task to manage each game stage etc. We need to use both cooperative scheduling and preemptive scheduling technique to make this video game run efficiently. In order to make this game run in a particular sequence, we also need to synchronize and sequentialize each task by setting the task priorities carefully and using binary semaphore correctly. <br /> |
| | <br /> | | <br /> |
| | | | |
| − | == INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVES == | + | == Introduction and Objectives == |
| − | | + | [[File:AlienInvasion.jpeg|300px|thumb|right|Alien Invasion]] |
| − | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;"
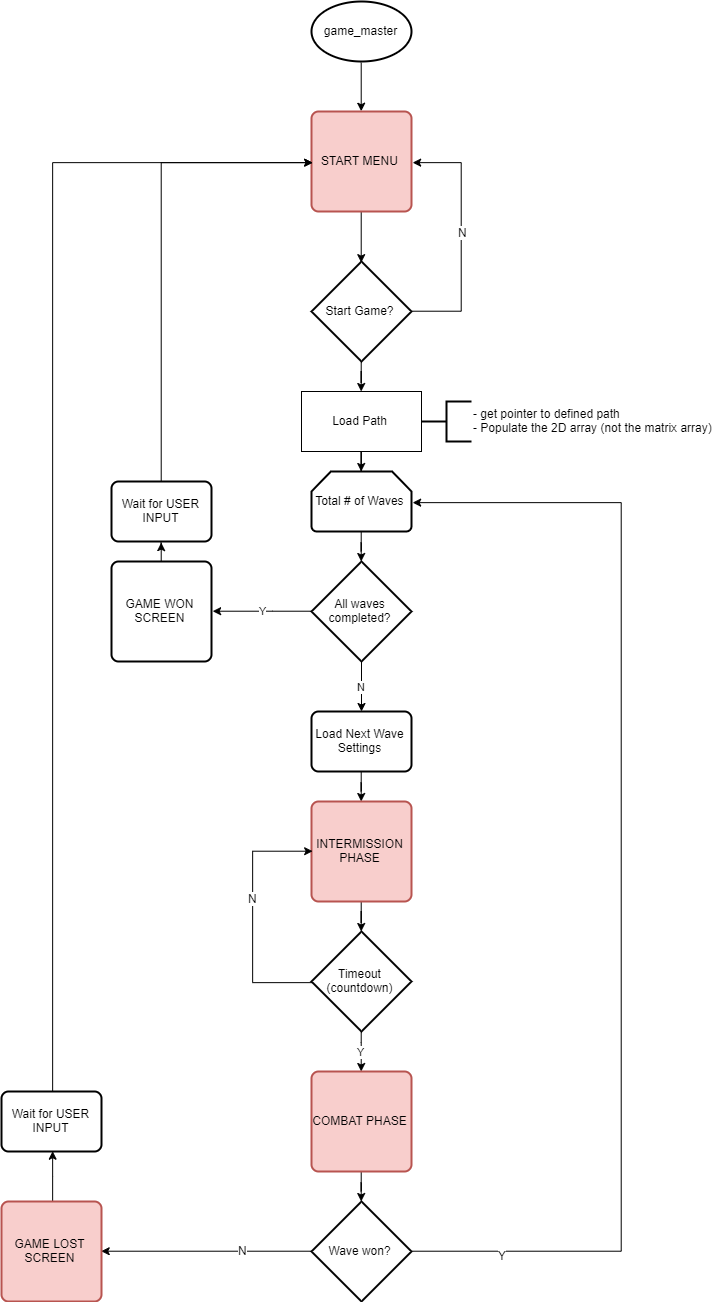
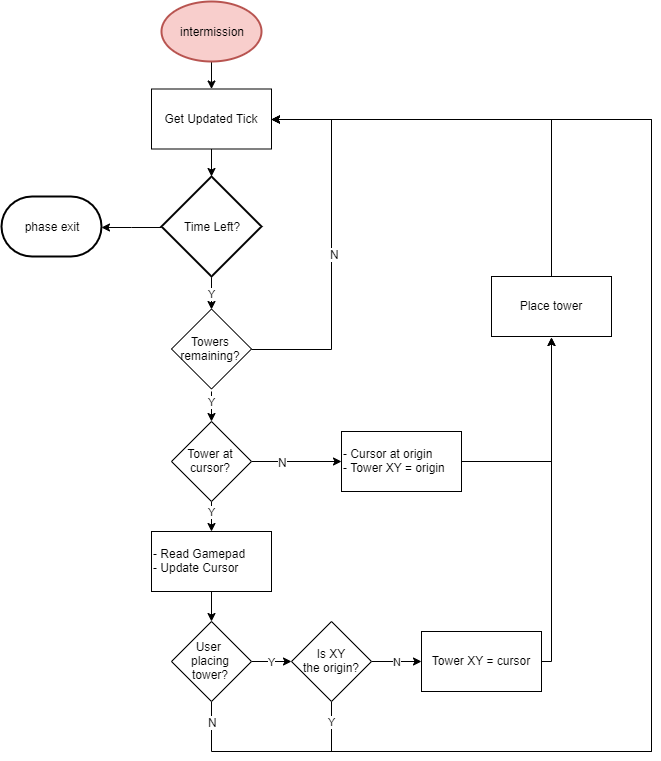
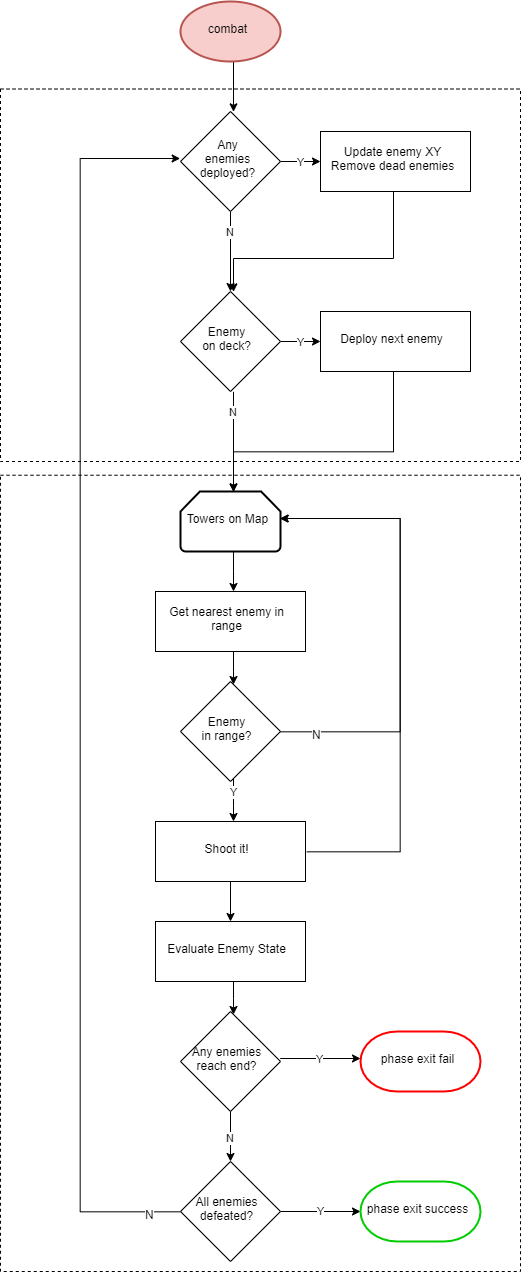
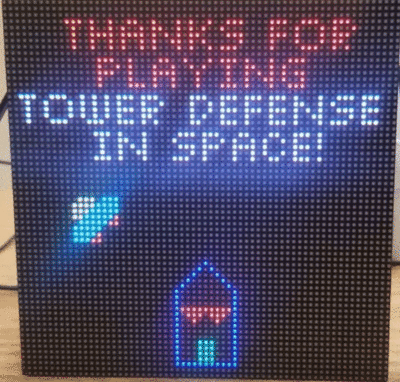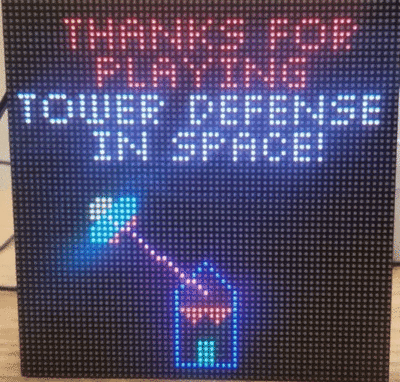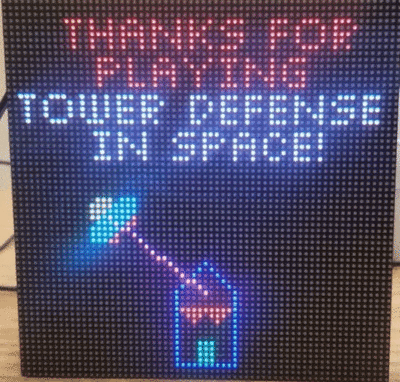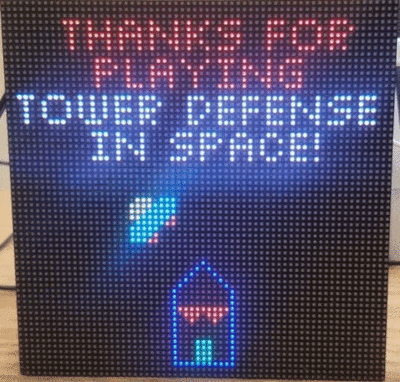
| + | Like most traditional tower defense games, the player needs to defend our planet from the invasion of aliens. The gameplay can be split into 2 phases, <b>Combat Phase</b> and <b>Intermission Phase</b>. During the intermission phase, the player can place different kinds of towers strategically that will attack the invading aliens from entering into our homeland by shooting the enemies. During the combat phase, spaceships follow the path and try to land on our planet. If any enemy spaceship reaches the end of the path, then the player loses. If there are no more spaceships remaining in a wave, the player can build a stronger tower that has a longer attack range and can shoot a more powerful laser to the spaceships in the next wave. The player wins the game after surviving 5 waves of attack. |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> RC CAR OBJECTIVES </span> | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * Successfully detect and avoid obstacles <br />
| |
| − | * Autonomously navigate to a fixed destination, from a fixed starting location; based on feedback from a GPS <br />
| |
| − | * Integrate communication between the RC car's master controller and an Android device, using Bluetooth <br />
| |
| − | * Integrate system hardware communication using a PCB <br />
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| | | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;"
| + | This game can be separated into 4 different modules: |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| + | #<b>Game Logic</b>: SJtwo Board - handles the game logic. (For example: detect and shoot nearby enemies, switch between intermission phase and combat phase) |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" |
| + | #<b>Display</b>: Adafruit 64x64 LED matrix - displays the animation of the game. |
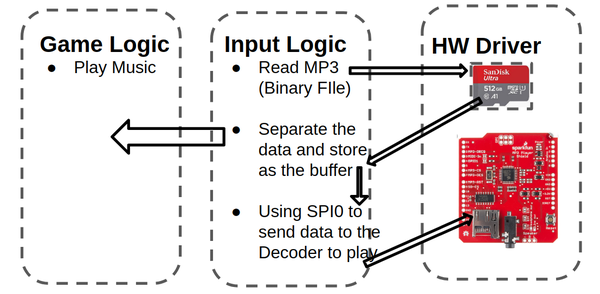
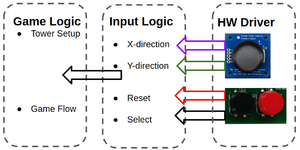
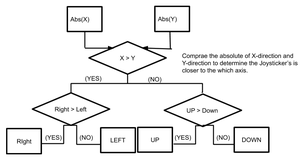
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> TEAM OBJECTIVES </span> | + | #<b>Gamepad Controller</b>: The input of this game. The gamepad controller consists of a joystick and two buttons. The player can use the joystick to move the cursor and decide where to place the towers. After that, the user needs to press the black button to select and confirm the location of the towers. If the player knows that he/she has made a mistake in the middle of the game and will eventually lose the game, the player can press the red button and restart the game. |
| − | |-
| + | #<b>Sound</b>: MP3 Decoder and speaker. Players can enjoy cool music during the game. This is done on an additional SJtwo board, which will play the song on repeat. |
| − | ! style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * Strive to learn as much as possible, in order to develop a professional product
| |
| − | * Establish and enforce professional software design standards <br />
| |
| − | * Establish and enforce professional hardware design standards <br />
| |
| − | * Achieve 100% code coverage, during unit testing <br />
| |
| − | * Carefully document and track all bugs encountered and patched, during development <br />
| |
| − | * Clearly communicate the development of all modules of the RC car <br />
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;"
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> CORE MODULES OF RC CAR</span> | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Android Mobile Application</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Bridge Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Geographic Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Master Controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Motor Controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Sensor Controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969">Hardware Integration PCB</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969">Wiring Harness</span> <br />
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;"
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> PROJECT MANAGEMENT ADMINISTRATION ROLES </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000">Team Lead</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Finance Manager</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Git Repository Manager</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Wiki Report Manager</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Bill of Materials Manager</span> <br />
| |
| − | |}
| |
| | | | |
| | + | == Team Members == |
| | | | |
| | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;" | | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;" |
| Line 82: |
Line 34: |
| | |- style="vertical-align: top;" | | |- style="vertical-align: top;" |
| | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | | | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/tristanfrench/ Tristan French] | + | * [Ryan Zelek] |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * '''Team Lead'''<br />
| + | '''Team Lead'''<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Git Repository Manager</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Finance Manager</span> <br />
| |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Master Controller (Lead)</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:#FF8C00"></span>Game Design Lead<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969">Hardware Integration PCB</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |- style="vertical-align: top;" | | |- style="vertical-align: top;" |
| | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | | | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * Ryan Zelek | + | * [https://www.linkedin.com/feed/ Zach Smith] |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| | + | Git Repo Manager<br /> |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Motor Controller (Lead)</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:#EE82EE"></span>Hardware Design Lead<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Master Controller</span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |- style="vertical-align: top;" | | |- style="vertical-align: top;" |
| | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | | | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/samir-collin-mohammed/ Samir Mohammed] | + | * [Chong Hang Cheong] |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Wiki Report Manager</span> <br />
| + | Wiki Report Manager<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#808080">Bill of Materials Manager</span> <br />
| |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Android Mobile Application & Bridge Controller (Lead)</span> | + | * <span style="color:#008000"></span>LED Matrix API<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969">Hardware Integration PCB</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | |- style="vertical-align: top;" | | |- style="vertical-align: top;" |
| | ! scope="row" style=" text-align: left;" | | | ! scope="row" style=" text-align: left;" | |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/vignesh-kumar-v/ Vignesh Kumar Venkateshwar] | + | * [Polin Chen] |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| | + | Bill of Materials Manager<br /> |
| | | style="text-align: left;" | | | | style="text-align: left;" | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Android Mobile Application & Bridge Controller </span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:#008000"></span>Joy Sticker && Decoder API<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Motor Controller </span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! scope="row" style="; text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/bharath-vyas/ Bharath Vyas Balasubramanyam]
| |
| − | | style=";text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | | style=";text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Geographic Controller (Lead)</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Motor Controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/nuoya-xie-b6988a42/ Nuoya Xie]
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Sensor Controller (Lead)</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Geographic Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| − |
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | ! scope="row" style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * [https://www.linkedin.com/in/chong-hang-cheong-64803095/ Chong Hang Cheong]
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | | style="text-align: left;" |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Sensor Controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Geographic Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#8A2BE2 ">Testing and Integration </span> <br />
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | <br /> | | <br /> |
| | | | |
| − | == SCHEDULE == | + | == Schedule == |
| | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;" | | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: auto;" |
| | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | | | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | |
| Line 172: |
Line 86: |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 1 | | ! scope="row"| 1 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 2/16/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 10/15/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * Share team contact information <br \> | + | * Share team contact information<br> |
| − | * Create Git Repository '''(Tristan)''' <br \> | + | * Create Git Repository<br> |
| − | * Set up Slack <br \> | + | * Set up group Slack channel<br> |
| − | * Invite Preet to Slack <br \> | + | * Invite Preet to Slack<br> |
| − | * Establish Code Guidelines and Standards <br \> | + | * Establish Code Guidelines and Standards<br> |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br> |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 2 | | ! scope="row"| 2 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 2/24/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 10/22/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * (1/2 team) Share research of past projects <br /> | + | * Identify major hardware components (BOM)<br /> |
| − | * Establish ownership of Administrative and Technical Project Modules <br />
| + | * Begin purchasing major items<br /> |
| − | * Establish weekly team meeting time <br />
| + | * Finalize game architecture<br /> |
| − | * Establish Team Slack usage Guidelines and Standards <br />
| + | * Have Git Repo Setup<br/> |
| − | * Received CAN Transceivers <br />
| + | |
| − | * Create Git directory structure '''(Tristan)''' <br />
| |
| − | * Create a Bill of Materials '''(Samir)''' <br /> | |
| − | * Select and order an RC car '''(Bharath)''' <br /> | |
| − | * Push a file to Git Repository <br /> | |
| − | * Conduct research of project modules (based on ownership/sub-team)
| |
| − | * Invite Preet to Gitlab
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 3 | | ! scope="row"| 3 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 3/3/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 10/29/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * (2/2 team) Share research of past projects <br /> | + | * Solidify individual roles and responsibilities<br/> |
| − | * Explore using Splitwise for managing project finances <br />
| + | * Establish baseline software architecture design and guidelines going forward<br/> |
| − | * Explore using Taiga.io for project management '''(Samir/Tristan)''' <br />
| |
| − | * Sub-teams share research and findings with each other and the team<br />
| |
| − | * Start planning what parts need to be ordered and update BoM <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Research which PCB design tools we can use to develop a 4-layer PCB (EAGLE vs. KiCAD) </span> <br /> | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Email Preet regarding LCD screen for Bridge Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Interface with the HC05 Bluetooth module</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Research frameworks for Android App development and decide which to use </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Research GPS modules and decide which to use</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Create a high-level system block diagram and control scheme</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Develop a high-level plan interfacing with speed controller and servo controller</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Test performance/specs of current Ultrasonic sensors and research others</span> <br />
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 4 | | ! scope="row"| 4 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 3/10/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 11/5/19 |
| − | | | + | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000">Each team create a schedule for sub-system development and send to '''Samir'''</span>
| + | '''Kelvin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000">Set up Cygwin on Windows (and configure) Mac machines for auto-formatting</span> | + | * Verify functionality of LED matrix and gather resources for further understanding<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Finalize and purchase LCD screen for Bridge Controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Learn to develop in Android Studio (watch tutorials and begin developing Android App)</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Purchase Adafruit Ultimate GPS module</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Purchase long-range distance sensors and select bump sensors</span> <br />
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 5 | | ! scope="row"| 5 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 3/17/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 11/12/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000">Establish Git Repository Structure ('''Tristan''')</span> | + | '''Kelvin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969">Select PCB manufacturer</span> | + | * Find out feasibility of creating an LED matrix driver in C<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Complete high-level system block diagram </span> <br /> | + | '''Polin''' |
| | + | * Have APIs ready for joystick and buttons<br/> |
| | + | '''Ryan''' |
| | + | * Have basic user interface for the game displayed through serial port<br/> |
| | + | '''Zach''' |
| | + | * First controller PCB design complete<br/> |
| | + | * Specify any remaining hardware components and coordinate purchase<br/> |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span><br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span><br/> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span><br/> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span><br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span><br/> |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 6 | | ! scope="row"| 6 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 3/24/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 11/19/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Select Android mobile phone/OS to load and run Application </span> | + | '''Kelvin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Interface with GPS and compass modules</span> | + | * Complete baseline API for LED matrix<br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Finalize high-level system block diagram and control scheme</span> <br /> | + | '''Polin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Record how servo and DC motors react to RC Transmitter and Receiver feedback</span> <br /> | + | * Determine feasibility of MP3 decoding and integration into system |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Interface with with speed controller and servo controller</span> <br /> | + | '''Ryan''' |
| | + | * Complete first pass at basic tower defense level with straight pathway |
| | + | '''Zach''' |
| | + | * Controller PCB sent out for fabrication<br /> |
| | + | * Design break-out PCB for LED matrix + IO expander /> |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| | + | <br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 7 | | ! scope="row"| 7 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 3/31/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 11/26/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000">'''All parts have been ordered'''</span>
| + | '''Kelvin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Create button to launch mobile application</span> | + | * LED matrix driver should be reviewed and complete<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Integrate Google Maps into mobile application</span>
| + | '''Polin''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Use feedback from GPS and compass to calculate bearing angle</span> | + | * Work with '''Zach''' to identify remaining hardware components and, if applicable, MP3 decoder requirements<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">LPC 1758 responds to feedback from motor speed sensor (reports RPM of wheels, when a PWM signal is applied) | + | '''Ryan''' |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Complete DBC CAN message format</span>
| + | * Work with '''Kelvin''' to integrate his API into the game<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">Complete DBC CAN message format</span> | + | * Game should be running with LED matrix display involvement<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">LPC 1758 responds to feedback from bump sensor</span> | + | * Advanced game logic design/implementation is near feature complete<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33">LPC 1758 responds to feedback from Ultrasonic sensors (reports distance of objects in their detection radius)</span> | + | '''Zach''' |
| | + | * PCB assembled and tested. Problems identified and solutions proposed<br/> |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | <br/> |
| | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 8 | | ! scope="row"| 8 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 4/7/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 12/3/19 |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Successfully get starting and destination coordinates </span> | + | * Complete game testing and validation<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Transmit latitude and longitude coordinates as CAN messages to master controller </span> | + | * Critical bugs (software AND hardware) identified and a clear path towards closure has been identified<br/> |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00"> Master controller can send/receive CAN messages to/from all other controllers on CANbus</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33"> Complete sensor module code and push final revision to GitLab</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Angle wheels left/right/straight based on CAN feedback from master controller</span> <br />
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| | | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="row"| 9 | | ! scope="row"| 9 |
| − | ! scope="row"| 4/14/19 | + | ! scope="row"| 12/10/19 |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Send a message from the Android Mobile Application to the Bridge Controller </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c">Transmit heading and bearing angle as CAN messages to master controller </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00">Completed implementation of speed control algorithm</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE">Implement obstacle avoidance algorithm</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#d33"> Mount and wire sensors to perfboard on car </span> <br />
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 10
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 4/21/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete first indoor vehicle test drive </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Plot CAN signals in Busmaster </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete unit testing code for all modules </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Implement debug messages </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Review PCB Schematics for errors/inconsistencies </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Push final schematics to Google Drive </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Send starting/destination coordinates to bridge controller </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Send starting/destination coordinates as CAN messages from bridge controller to geographic controller</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE"> Design a feed back mechanism to adjust speed of DC motor using RPM sensor values for vehicular movement on the slope</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE"> Mount and solder encoder perfboard </span> <br />
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 11
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 4/28/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Achieve full CAN communication between all subsystems </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete unit testing code for all subsystems </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Complete PCB layout and send board to fabrication house </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Order PCB and components ('''Tristan''') </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Launch a google map fragment on the Android Mobile Application </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Input starting and destination latitude and longitude coordinates in Map </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#36c"> Develop a pathfinding scheme </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#EE82EE"> Use GPS feedback to govern (motor behavior) car movement</span> <br />
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 12
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 5/5/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete indoor test drive of car </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Assemble/solder PCB </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Integrate PCB into car </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#696969"> Confirm that PCB can supply adequate power to car </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Integrate Google Maps into Android Mobile Application</span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Display sensor and compass data on Android Mobile Application </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Transmit destination latitude and longitude coordinates from Android Mobile Application </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#FF8C00"> Complete LCD integration with Master Controller </span>
| |
| − | | |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 13
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 5/12/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Send module summaries to '''Samir''' for Wiki report population </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete outside test drive from start to destination </span>
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br /> | + | * Continuation of previous week activities (bug fixes, etc) |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000">Complete</span> <br />
| + | * Implement any potential optimizations and/or expansions |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 13
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 5/19/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete Wiki Report ('''Samir''') </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete Individual Evaluations </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Schedule time to test car outside on Monday ('''Samir, Nuoya, Tristan''') </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Complete final DBC file </span> | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Integrate pathfinding algorithm with bridge controller ('''Nuoya and Kelvin''') </span>
| |
| | | | | | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span> | + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| + | * <span style="color:green">Complete</span> <br /> |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span> <br /> | |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 14
| |
| − | ! scope="row"| 5/22/19
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Push final code to GIT </span>
| |
| − | * '''DEMO''' <br />
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#000000"> Finalize finances and decide who gets to keep the car... </span>
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| |
| − | * <span style="color:#008000"> Complete </span>
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | <BR/> | | <BR/> |
| | | | |
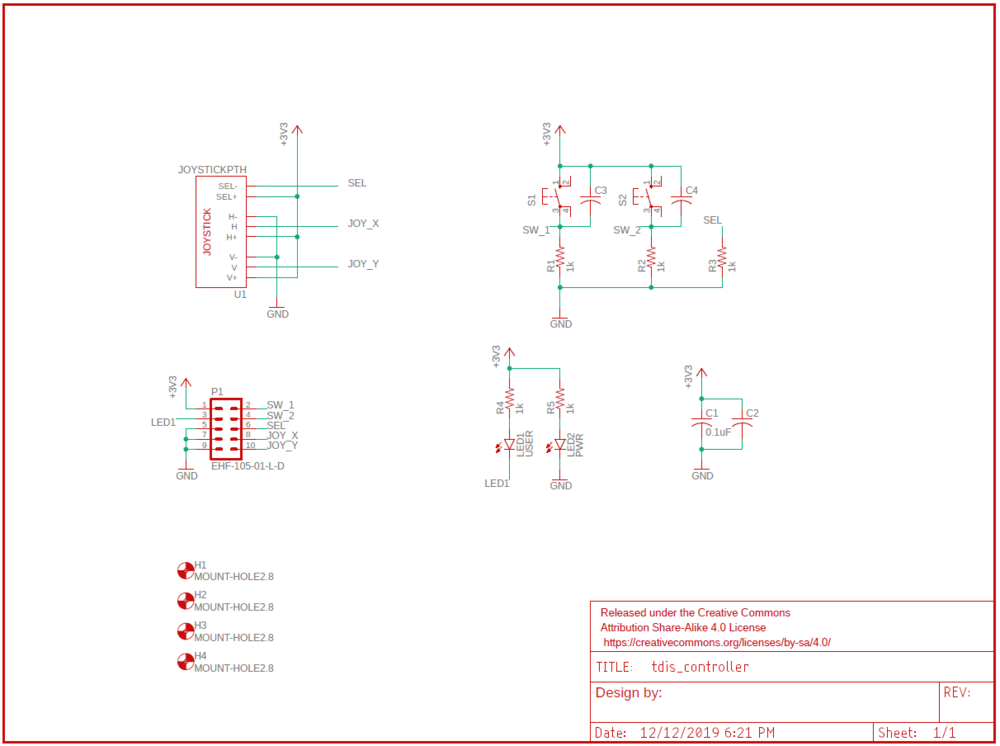
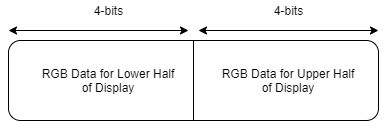
| − | == BILL OF MATERIALS (GENERAL PARTS) == | + | == Bill of Materials == |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | | | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> MICRO-CONTROLLERS </span> | + | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> Top Level </span> |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| Line 473: |
Line 245: |
| | COST PER UNIT (USD) | | COST PER UNIT (USD) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | | <s>'''32x64 RGB LED Matrix'''</s> |
| − | * '''Micro-controller'''
| + | | <s>[https://www.sparkfun.com/products/14718]</s> |
| − | | | + | | <s>2</s> |
| − | * LPC 1758 '''(Purchased from Preet Kang)
| + | | <s>$49.95</s> |
| − | | | + | |- |
| − | * 5 | + | | <s> ''' 64x64 RGB LED Matrix'''</s> |
| − | | | + | | <s> [https://www.sparkfun.com/products/14824 Sparkfun] </s> |
| − | * $80.00
| + | | <s> 1 </s> |
| | + | | <s> $79.95 </s> |
| | + | |- |
| | + | | <s> '''NovaeLED 64x64 RGB LED Matrix (2-Pack)''' </s> |
| | + | | <s> [https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B07LFJ73GQ/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o00_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1 Amazon] </s> |
| | + | | <s> 1 </s> |
| | + | | <s> $80.99 </s> |
| | + | |- |
| | + | | '''64x64 RGB LED Matrix'''* |
| | + | | [https://www.adafruit.com/product/3649 Adafruit] |
| | + | | 1 |
| | + | | $104.07 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | | '''5V 4A PSU''' |
| | + | | - |
| | + | | 1 |
| | + | | FREE |
| | + | |- |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| Line 486: |
Line 275: |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | | | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> RC CAR </span> | + | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> Breakout Board PCB** </span> |
| | |- | | |- |
| | + | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| | + | Item # |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| | PART NAME | | PART NAME |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | PART MODEL & SOURCE | + | PART SOURCE |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| | QUANTITY | | QUANTITY |
| Line 497: |
Line 288: |
| | COST PER UNIT (USD) | | COST PER UNIT (USD) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 1 |
| − | * '''RC Car'''
| + | | IC REG LINEAR LD1117S33CTR |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stmicroelectronics/LD1117S33CTR/497-1241-1-ND/586241 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/Traxxas-Slash-2-4GHz-Radio-Battery/dp/B01DU474B0 Traxxas 1/10 Slash 2WD RTR with 2.4GHz Radio]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | $0.351 |
| − | * 1
| + | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 2 |
| − | * $205.99
| + | | MHS16N-ND 16POS CONN 2.54MM |
| − | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/3m/N3408-6302RB/MHS16N-ND/1239801 DIGIKEY] |
| | + | | 2 |
| | + | | $2.60 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | ! scope="row"| 3 |
| | + | | CAP CER 0.1UF 25V X7R 1206 |
| | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/avx-corporation/12063C104JAT2A/478-11943-1-ND/8573579 DIGIKEY] |
| | + | | 5 |
| | + | | $0.221 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | ! scope="row"| 4 |
| | + | | CAP CER 10UF 16V X5R 1206 |
| | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/taiyo-yuden/EMK316BJ106MD-T/587-4881-1-ND/6563724 DIGIKEY] |
| | + | | 5 |
| | + | | $0.202 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | ! scope="row"| 5 |
| | + | | RES SMD 470 OHM 1% 1/4W 1206 |
| | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/te-connectivity-passive-product/CRG1206F470R/A106077CT-ND/3477734 DIGIKEY] |
| | + | | 10 |
| | + | | $0.0267 |
| | + | |- |
| | + | ! scope="row"| 6 |
| | + | | PTC RESET FUSE 24V 500MA 1206 |
| | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/bel-fuse-inc/0ZCJ0050AF2E/507-1803-1-ND/4156312 DIGIKEY] |
| | + | | 10 |
| | + | | $0.1588 |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 7 |
| − | * '''Lithium-Ion Battery'''
| + | | CONN SOCKET 40POS 0.1 TIN PCB |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/samtec-inc/ESQ-120-14-T-D/SAM11108-ND/6693975 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/Traxxas-7600mAh-7-4V-2-Cell-Battery/dp/B00S1R0VEY/ref=pd_bxgy_img_2/144-5345940-5723349?_encoding=UTF8&pd_rd_i=B00S1R0VEY&pd_rd_r=e09ce3bf-3d35-11e9-b225-a780b44e51f2&pd_rd_w=VRlhQ&pd_rd_wg=VQ7ho&pf_rd_p=6725dbd6-9917-451d-beba-16af7874e407&pf_rd_r=0MECMTYSG4H3SDRR4GR8&psc=1&refRID=0MECMTYSG4H3SDRR4GR8 Traxxas 7600mAh 7.4V 2-Cell 25C LiPo Battery]
| + | | 2 |
| − | | | + | | $5.03 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $74.95
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 8 |
| − | * '''Battery Charger''' | + | | Manufacturing x 5 boards * |
| − | | | + | | [https://jlcpcb.com/ JLCPCB] |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/Traxxas-2970-EZ-Peak-Charger-Identification/dp/B00OAFYLJC/ref=pd_bxgy_img_3/144-5345940-5723349?_encoding=UTF8&pd_rd_i=B00OAFYLJC&pd_rd_r=e09ce3bf-3d35-11e9-b225-a780b44e51f2&pd_rd_w=VRlhQ&pd_rd_wg=VQ7ho&pf_rd_p=6725dbd6-9917-451d-beba-16af7874e407&pf_rd_r=0MECMTYSG4H3SDRR4GR8&psc=1&refRID=0MECMTYSG4H3SDRR4GR8 Traxxas 2970 EZ-Peak Plus 4-Amp NiMH/LiPo Fast Charger with iD Auto Battery Identification]
| + | | 1 |
| − | | | + | | $29.81 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $47.95
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | <BR/>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == <font color="696969"> HARDWARE INTEGRATION PCB </font> ==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="696969"> Hardware Design </font> ===
| |
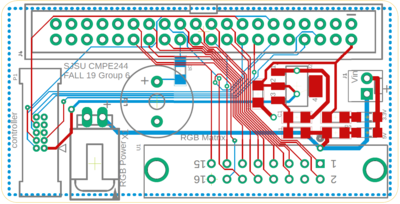
| − | [[File:RUN DBC PCB layout.jpeg |thumb| center | 800px|RunDBC PCB]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The hardware integration PCB was designed with two goals: <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''1. Minimize the footprint of the onboard electronics''' <br>
| |
| − | '''2. Minimize the chances of wires disconnecting, during drives''' <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | To accomplish these goals, all controllers were directly connected to the board's 34 pin header arrays, while all sensors were connected to the board, using ribbon cables and locking connectors. The master controller's header pins were inverted and then connected to a header array on top of the PCB, while the other controllers were mounted to the bottom. This guaranteed secure power and signal transmission paths, throughout the system.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The board consisted of 4 layers:
| |
| − |
| |
| − | '''Signal''' <br>
| |
| − | '''3.3V''' <br>
| |
| − | '''5.0V''' <br>
| |
| − | '''GND''' <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="696969"> Technical Challenges </font> ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== <font color="696969"> Design </font> ====
| |
| − | * Balancing priorities between HW design and getting a working prototype
| |
| − | * Finalizing a PCB design, when some components and module designs are not nailed down
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== <font color="696969"> Assembly </font> ====
| |
| − | * DB-9 connector for CAN dongle was wired backwards in the PCB design. Because there are several unused pins, we were able to just solder jumper wires to connect CAN HI and CAN LOW to the correct pins.
| |
| − | * Spacing for headers with clips were not accounted for properly in the design. two of them are very close. It's a tight fit, but it should work.
| |
| − | * Wireless antenna connector on master board not accounted for in footprint, it may have to be removed to avoid interference with one connector.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="696969"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#696969;" | | + | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> HARDWARE INTEGRATION PCB </span> | + | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> Gamepad PCB** </span> |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| + | Item # |
| | + | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| | + | PART NAME |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| + | PART SOURCE |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| + | QUANTITY |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| + | COST PER UNIT (USD) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 1 |
| − | * '''CAN Transceiver'''
| + | | Analog 2-axis Thumb Joystick w/ select button |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B00NAY2Q6O/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o00_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1 Amazon] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/texas-instruments/SN65HVD230DR/296-11654-2-ND/404367 SN65HVD230-SOIC8]
| + | | 1 |
| − | | | + | | $7.67 |
| − | * 5
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $2.38
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 2 |
| − | * '''Buzzer'''
| + | | SAM8205-ND 10POS 1.27MM |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/samtec-inc/EHF-105-01-L-D/SAM8205-ND/1106564 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/products/en?keywords=CEM-1203 BUZZER-CEM-1203]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | $3.38 |
| − | * 2
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $0.83
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 3 |
| − | * '''Buzzer Switch'''
| + | | LED GREEN 1206 SMD |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/lite-on-inc/LTST-C150GKT/160-1169-1-ND/269241 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/micro-commercial-co/MMBT2222A-TP/MMBT2222ATPMSTR-ND/717279 MMBT2222A-TP]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | $0.24 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $0.15
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 4 |
| − | * '''3.3V Regulator'''
| + | | LED RED 1206 SMD |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/lite-on-inc/LTST-C150CKT/160-1167-1-ND/269239 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stmicroelectronics/LDL1117S33R/497-17239-1-ND/7102079 LDL1117S33R]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | $0.257 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $0.46
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 5 |
| − | * '''5V Regulator'''
| + | | RES 1K OHM 1% 1/2W 1206 SMD |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stackpole-electronics-inc/RNCP1206FTD1K00/RNCP1206FTD1K00CT-ND/2240675 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/products/en?keywords=LM1085IS-12 LM1085IS-12/NOPB-ND]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | 0.0358 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $2.36
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 6 |
| − | * '''Red LED'''
| + | | CAP CER 0.1UF 50V X7R 1206 |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/kemet/C1206C104K5RAC7800/399-C1206C104K5RAC7800CT-ND/411524 DIGIKEY] |
| − | * [http://www.kingbrightusa.com/category.asp?catalog_name=LED&category_name=KCSOT-23%20SMD%20LED&page=1 LED-0603]
| + | | 5 |
| − | | | + | | $0.088 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $-.--
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 7 |
| − | * '''Diode'''
| + | | 12x12x7.3mm Tactile Push Button w/ cap (pack of 25) |
| − | | | + | | [https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B01NCQVGLC/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o00_s01?ie=UTF8&psc=1 Amazon] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/diodes-incorporated/S1AB-13-F/S1AB-FDITR-ND/751512 Diode]
| + | | 1 |
| − | | | + | | $7.89 |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $0.32
| |
| − | | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | ! scope="row"| 8 |
| − | * '''100uF Capacitor'''
| + | | Manufacturing x 5 boards * |
| − | |
| + | | [https://jlcpcb.com/ JLCPCB] |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/kemet/C1206C104KARACTU/399-4674-1-ND/992199 SMD 603 100uF Capacitor]
| + | | 1 |
| − | |
| + | | $14.21 |
| − | * 1
| + | |} |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * '''10uF Capacitor''' | |
| − | | | |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/kemet/C1206C104KARACTU/399-4674-1-ND/992199 SMD 603 10uF Capacitor]
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''4.7uF Capacitor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/kemet/C1206C104KARACTU/399-4674-1-ND/992199 SMD 603 4.7uF Capacitor]
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''1uF Capacitor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/kemet/C1206C104KARACTU/399-4674-1-ND/992199 SMD 603 1uF Capacitor]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''10K Resistor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stackpole-electronics-inc/CSR0603FKR250/CSR0603FKR250TR-ND/1742486 SMD 603 10K Resistor]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| + | <nowiki>*</nowiki> Shipping and tax included in value shown in the cost per unit column <br> |
| − | |
| + | <nowiki>**</nowiki> Only parts that were purchased are displayed. <br> |
| − | * '''5.1K Resistor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stackpole-electronics-inc/CSR0603FKR250/CSR0603FKR250TR-ND/1742486 SMD 603 5.1K Resistor] | |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1 | |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44 | |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''1K Resistor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/stackpole-electronics-inc/CSR0603FKR250/CSR0603FKR250TR-ND/1742486 SMD 603 1K Resistor]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $0.44
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <HR>
| |
| | <BR/> | | <BR/> |
| | | | |
| − | == CAN NETWORK == | + | == Game Design == |
| − | | + | === <font color="000000"> Game Rules </font> === |
| − | In order to eliminate the risk of accidentally writing (and potentially sending) CAN messages with duplicate message id's, we created a rule that the first digit in messages for each submodule would be unique to that submodule. For example, CAN messages sent from the motor controller, always began with 5 (514, 515, 516, etc.), while messages for the geographic controller began with 7 (769, 770, etc.). This scheme proved to be effective and we never worried about duplicate message id's.
| + | Gameplay is split into 2 phases: <br> |
| − | | + | <b>Intermission</b> - Player sets up tower locations <br> |
| − | In order to detect MIA (missing in action) modules, we implemented a heartbeat system. We sent an integer value of 0, in the 1Hz periodic callback task (once a second), from the bridge controller, motor controller, sensor controller and geographic controller to the master controller. The master controller responded by illuminating one of the 4 onboard LED's on itself (specific to each sub module), if it detected an MIA node. In order to detect an MIA master node, we had the master controller send a heartbeat message to the motor controller, which responded the same way as the master did to MIA events. If a node waited more than 3 seconds to send a heartbeat message, that node was assumed to be MIA, until a heartbeat was received by the master controller. This approach was simple to implement and made it easy to spot MIA modules.
| + | <b>Combat</b> - Player watches round unfold <br> |
| | | | |
| − | We took care never to send CAN messages faster than we were receiving them, in order to avoid distorting data. We almost always sent CAN data in the 10Hz periodic callback function.
| + | During the <b>Intermission Phase</b>: <br> |
| − | | + | #The player places towers strategically around the enemy path. <br> |
| − | | + | #The number of towers is fixed per round <br> |
| − | === Hardware Design ===
| + | #Towers can only be placed in marked areas that do not lie on a path <br> |
| − | During the early stages of development, we purchased 5 Waveshare SN65HVD230 CAN modules, in order to implement our CANbus. We mounted them to a perfboard and wire-wrapped the CAN-H and CAN-L nodes. We found that the design was unecessarily bulky and unclean.
| + | #The built-in software will find a valid tower location and move the cursor there automatically according to joystick input. <br> |
| − | | + | #There are 5 types of towers (increasing damages, ranges, and of different colors). Each tower type depends on the current wave.<br> |
| − | Because the CAN modules were designed around the SN65HVD230 CAN transceiver chip, we simply purchased 5 individual IC's and soldered them directly to our system integration PCB. The resulting circuit implemented the same functionality, while significantly reducing the CAN transceiver footprint.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC can chip sch.png | thumb |left| 200px| Electrical Pinout]]
| |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC can chip pinout.png | thumb |center| 200px| CAN Transceiver]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | <br> | + | During the <b>Combat Phase</b>: <br> |
| − | <br> | + | #Enemies will enter the gameplay area at one end of the path and attempt to reach the other end <br> |
| | + | #Towers will automatically engage enemies when they come within range <br> |
| | + | #Towers shoot until the enemy is either dead or out of range <br> |
| | + | #Tower proximity is 8 directions (top, bot, left, right, top-right, top-left, bot-left, bot-right) and 1 unit (not necessarily 1 pixel) away <br> |
| | + | #Enemies that reach the end of path while being alive will result in losing the game. <br> |
| | + | #If any spaceship reaches the end of the path, the player loses and the game ends <br> |
| | + | #The round is over when the player loses or a set number of enemies have been defeated. <br> |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | | | |
| − | We used SMD 603 120 ohm termination resistors; one connected between CAN-H and CAN-L near the DB-9 connector and one near the master controller. This design mitigated the influence of signal reflections on the CANbus. Due to our low CAN baud rate (100kbps), this wasn't a big problem, but if we increased our baud rate to around 1Mbps, it could have affected the integrity of the CANbus.
| + | [[File:combatPhase_0.JPG|300px|thumb|right|Dashboard (Combat Phase)]] |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:system_block_diagram.png | thumb | center | 900px| Design of Run DBC Autonomous Car]]
| + | There will be a <b>dashboard</b> on the LED matrix that displays basic UI information: <br> |
| | + | <b>Intermission Phase:</b> |
| | + | #Time until combat phase <br> |
| | + | #Current wave number <br> |
| | + | #Number of towers left that you can still place <br> |
| | + | <b>Combat Phase:</b> |
| | + | #Current wave number <br> |
| | + | #Number of enemies still remaining in the current wave<br> |
| | | | |
| − | === DBC File === | + | === <font color="000000"> Game Objectives </font> === |
| | + | #There are 5 waves (rounds) total. <br> |
| | + | #In each round, enemies in various amounts, groupings, and health levels (armor) pass through the path. <br> |
| | + | #If any enemies reach the end of the path, then the user loses. <br> |
| | + | #After each round, the user will be able to place more towers which are stronger and can shoot farther. <br> |
| | + | #Each round will have waves of enemies that are more difficult to stop. <br> |
| | + | #The user needs to carefully place their towers such that it will have a maximum number of opportunities to shoot at the enemies. <br> |
| | + | #The trick is that the user will need to preserve early level towers, otherwise they will not have enough room to place the high level towers in the optimal location. <br> |
| | | | |
| − | <pre> | + | === <font color="000000"> How To Play </font> === |
| − | VERSION ""
| |
| | | | |
| − | NS_ :
| + | The gamepad controller consists of a joystick and two buttons. |
| − | BA_
| + | *Joystick - move the cursor and decide where to place the towers. |
| − | BA_DEF_
| + | *Black button - select and confirm the location of the towers. |
| − | BA_DEF_DEF_
| + | *Red button - restart the game (If the player knows that he/she has made a mistake in the middle of the game and will eventually lose the game, the player can press the red button and restart the game.) |
| − | BA_DEF_DEF_REL_
| |
| − | BA_DEF_REL_
| |
| − | BA_DEF_SGTYPE_
| |
| − | BA_REL_
| |
| − | BA_SGTYPE_
| |
| − | BO_TX_BU_
| |
| − | BU_BO_REL_
| |
| − | BU_EV_REL_
| |
| − | BU_SG_REL_
| |
| − | CAT_
| |
| − | CAT_DEF_
| |
| − | CM_
| |
| − | ENVVAR_DATA_
| |
| − | EV_DATA_
| |
| − | FILTER
| |
| − | NS_DESC_
| |
| − | SGTYPE_
| |
| − | SGTYPE_VAL_
| |
| − | SG_MUL_VAL_
| |
| − | SIGTYPE_VALTYPE_
| |
| − | SIG_GROUP_
| |
| − | SIG_TYPE_REF_
| |
| − | SIG_VALTYPE_
| |
| − | VAL_
| |
| − | VAL_TABLE_
| |
| | | | |
| − | BS_:
| + | During the <b>Intermission Phase</b>: <br> |
| | + | # The player places towers strategically around the enemy path by using the joystick to move the cursor and pressing the black button to select the location of the towers. |
| | + | # The player needs to place all remaining towers under 45 seconds. |
| | + | During the <b>Combat Phase</b>: <br> |
| | + | # Cheer on your towers and watch them defend Earth from the alien invasion! |
| | | | |
| − | BU_: BRIDGE MASTER GEO MOTOR SENSOR
| + | == <font color="000000"> Hardware Design - Electrical </font> == |
| | | | |
| | + | === <font color="000000"> Overview </font> === |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 768 GEO_HEARTBEAT: 1 GEO
| + | At a high level hardware integration requirements fell into two categories: <br> |
| − | SG_ GEO_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 256 SENSOR_HEARTBEAT: 1 SENSOR
| + | '''1.''' Reduce risk of unreliable cable connections and eliminate possibility of damage to components through unexpected disconnections, power surges, etc. <br> |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| + | '''2.''' Provide a more fluid physical interface for the user to interact with the game via hardware <br> |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 1024 BRIDGE_HEARTBEAT: 1 BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ BRIDGE_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 512 MOTOR_HEARTBEAT: 1 MOTOR
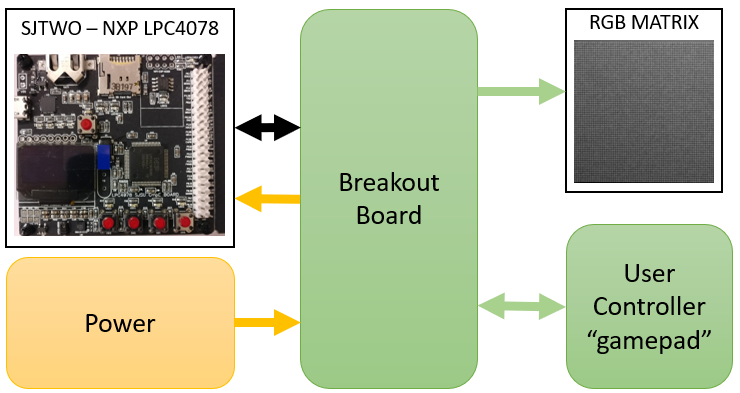
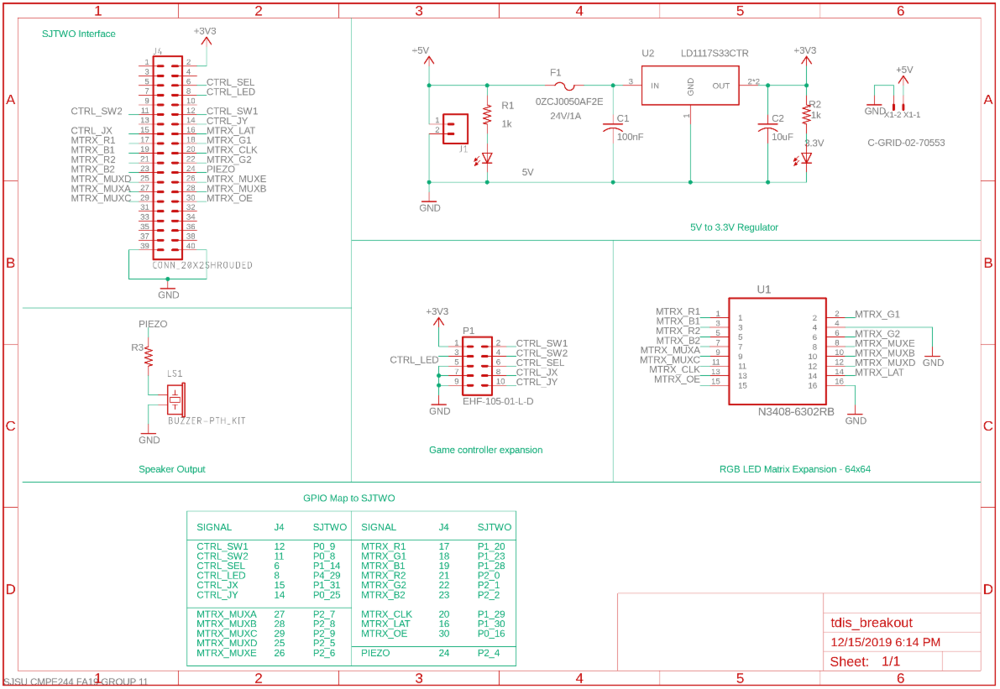
| + | To accomplish these goals, two boards were designed: a breakout board and a gamepad controller. The breakout board serves as a connection hub between all system hardware components; power, the RGB matrix, the SJTWO board, etc. while the joystick provides a cleaner package to present the user with the games inputs. The diagram below shows the relationship between the main subsystems: <br> |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 0 MASTER_HEARTBEAT: 1 MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ MASTER_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR
| |
| − |
| |
| − | BO_ 770 GEO_COORDINATE_DATA: 8 GEO
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_DATA_Latitude : 0|32@1+ (0.00000001,0) [0|0] "" MASTER, BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_DATA_Longitude : 32|32@1+ (0.0000001,-150) [0|0] "" MASTER, BRIDGE
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 769 GEO_DATA: 8 GEO
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_DATA_Distance : 0|32@1+ (0.01,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_DATA_Angle : 32|32@1+ (0.1,-180) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| − |
| |
| − | BO_ 771 GEO_DEBUG_DATA: 8 GEO
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_COMPASS_Calibration : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ GEO_COMPASS_Heading : 8|32@1+ (0.1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 257 SENSOR_DATA: 8 SENSOR
| + | [[File:tower_defense_in_space_hw_block_diagram.PNG]] |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_LeftBumper : 0|1@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_RightBumper : 1|1@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_LeftUltrasonic : 8|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_RightUltrasonic : 16|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_MiddleUltrasonic : 24|16@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ SENSOR_DATA_RearIr : 40|16@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
| |
| − |
| |
| − | BO_ 1025 BRIDGE_DATA_CMD: 1 BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ BRIDGE_DATA_CMD_start_stop : 0|1@1+ (1,0) [0|1] "" MASTER
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 1026 BRIDGE_CHECKPOINT: 8 BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ BRIDGE_DATA_Latitude : 0|32@1+ (0.00000001,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,GEO
| |
| − | SG_ BRIDGE_DATA_Longitude : 32|32@1+ (0.0000001,-150) [0|0] "" MASTER,GEO
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 513 MOTOR_DATA: 4 MOTOR
| + | All board designs were done using [https://www.autodesk.com/products/eagle/overview EAGLE] and manufactured by [https://jlcpcb.com/ JLCPCB]. Both boards were only two layers and used passive components for the most part. <br> |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DATA_steer : 0|8@1- (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DATA_speed : 8|16@1+ (0.1,0) [0|0] "MPS" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DATA_direction : 24|2@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 514 MOTOR_DEBUG_RPM_PARTIAL: 4 MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_rpm_part : 0|32@1- (1,0) [0|0] "RPM" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 515 MOTOR_DEBUG_RPM_ACTUAL: 4 MOTOR
| + | === <font color="000000"> Breakout Board Design </font> === |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_rpm_act : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "RPM" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 516 MOTOR_DEBUG_PI_ERROR: 4 MOTOR
| + | The breakout board design requirement was to interface all external hardware components with the embedded system (SJTWO). The hardware connections are: <br> |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_pi_err : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "MPS" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 517 MOTOR_DEBUG_LARGE_ERROR_CNT: 4 MOTOR
| + | '''1.''' The 64x64 RGB Matrix <br> |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_lg_err_cnt : 0|32@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| + | '''2.''' Output power to the RGB Matrix <br> |
| | + | '''3.''' User game controller (see next section) <br> |
| | + | '''4.''' Input power supply (5V) <br> |
| | + | '''5.''' The SJTWO embedded system <br> |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 518 MOTOR_DEBUG_PROPORTIONAL_CMD: 4 MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_prop_cmd : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 519 MOTOR_DEBUG_INTEGRAL_CMD: 4 MOTOR
| + | {| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_int_cmd : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
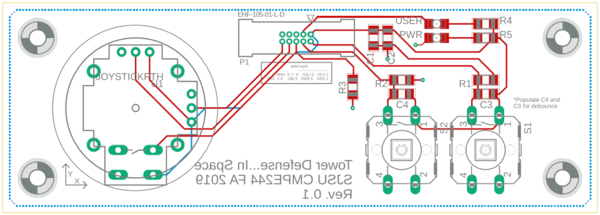
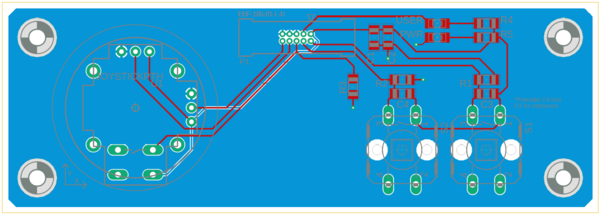
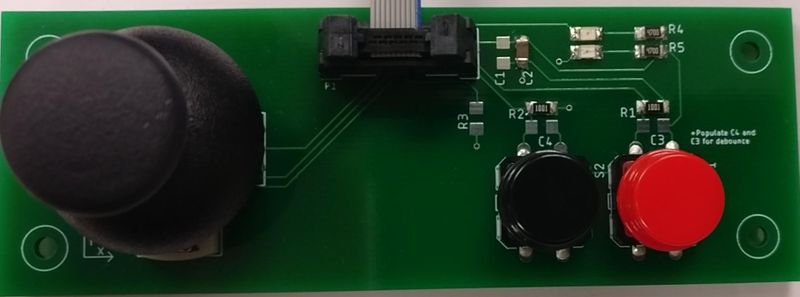
| + | |[[File:Breakout_Rev0.2.PNG|1000px|thumb|left|Breakout Board Schematic]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 520 MOTOR_DEBUG_INTEGRAL_CMD_OLD: 4 MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_int_cmd_old : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 521 MOTOR_DEBUG_OUTPUT: 4 MOTOR
| + | {| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_out : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "Percent" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| + | |[[File:breakout_board_layout_top.PNG|400px|thumb|left|Breakout Board PCB Top Layout]] |
| | + | |[[File:breakout_board_layout_bottom.PNG|400px|thumb|left|Breakout Board PCB Bottom Layout]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 522 MOTOR_DEBUG_PWM_ACTUAL: 4 MOTOR
| + | {| |
| − | SG_ MOTOR_DEBUG_pwm_act : 0|32@1- (0.01,0) [0|0] "PWM_Pulse_Width" MASTER,BRIDGE,DEBUG
| + | |[[File:breakout_pcb_top.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Breakout Board PCB Top Layout]] |
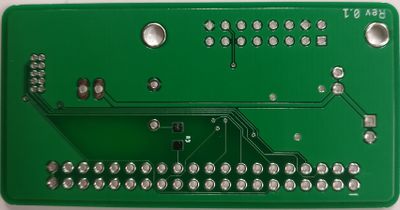
| | + | |[[File:breakout_pcb_bottom.jpg|400px|thumb|left|Breakout Board PCB Bottom Layout]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| | + | {| |
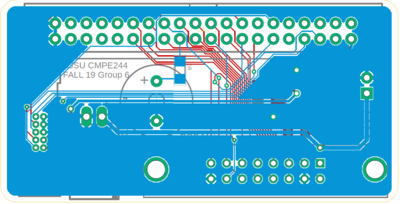
| | + | |[[File:breakout_pcb_mounted_assembled.jpg|800px|thumb|left|Populated and mounted to the SJTWO board]] |
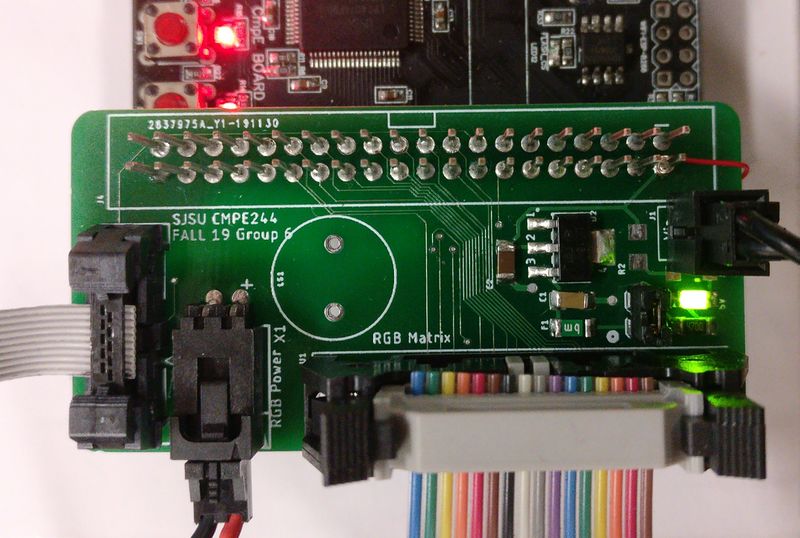
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | BO_ 1 MASTER_DRIVE_CMD: 4 MASTER
| + | ==== <font color="000000"> Known Breakout PCB Issues </font> ==== |
| − | SG_ MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_steer : 0|8@1- (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_speed : 8|16@1+ (0.1,0) [0|0] "MPS" MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_direction : 24|2@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR
| |
| − |
| |
| − | BO_ 2 MASTER_DEBUG: 4 MASTER
| |
| − | SG_ MASTER_DEBUG_navigation_state_enum : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR
| |
| − | SG_ MASTER_DEBUG_navigation_go : 8|1@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR
| |
| − | | |
| − | BA_ "FieldType" SG_ 2 MASTER_DEBUG_navigation_state_enum "MASTER_DEBUG_navigation_state_enum";
| |
| − | | |
| − | BA_ "FieldType" SG_ 1 MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_direction "MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_direction_E";
| |
| − | BA_ "FieldType" SG_ 513 MOTOR_DATA_direction "MOTOR_DATA_direction_E";
| |
| − | | |
| − | VAL_ 1 MASTER_DRIVE_CMD_direction 0 "stop_cmd" 1 "forward_cmd" 2 "backward_cmd" ;
| |
| − | VAL_ 2 MASTER_DEBUG_navigation_state_enum 0 "NAV_INIT" 1 "NAV_WAIT" 2 "NAV_NAVIGATE" 3 "NAV_OBSTACLE_RIGHT" 4 "NAV_OBSTACLE_LEFT" 5 "NAV_OBSTACLE_MIDDLE_FAR" 6 "NAV_OBSTACLE_MIDDLE_CLOSE" ;
| |
| − | VAL_ 513 MOTOR_DATA_direction 0 "stop_act" 1 "forward_act" 2 "backward_act" ;
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | BA_DEF_ "BusType" STRING ;
| |
| − | BA_DEF_ BO_ "GenMsgCycleTime" INT 0 0;
| |
| − | BA_DEF_ SG_ "FieldType" STRING ;
| |
| − | | |
| − | BA_DEF_DEF_ "BusType" "CAN";
| |
| − | BA_DEF_DEF_ "FieldType" "";
| |
| − | BA_DEF_DEF_ "GenMsgCycleTime" 0;
| |
| − | </pre>
| |
| − | | |
| − | <HR>
| |
| − | <BR/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | == <font color="green"> ANDROID MOBILE APPLICATION </font> == | |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Software Design </font> === | |
| − | Development of the Android Mobile Application happened in two phases. The first involved setting up bluetooth communication between the HC-05 and the Android mobile phone, while the second involved integrating Google Maps into the application. Both phases presented unique technical challenges that we had to address.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:start_screen1.png|thumb|400x500|left|Start Screen]]
| |
| − | [[File:source_destination.png|thumb|400x500|Map Showing Source(Blue) and Destination(Red) Markers along with Geo and Sensor data]]
| |
| − | [[File:start_screen2.png|thumb|400x500|center|Bluetooth Turn On Screen]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC android app.jpg|thumb|500px|center|Flow Chart of Android Application]]
| |
| | | | |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> '''''Bluetooth Integration''''' </font> ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | NOTE: Future CMPE 243 students looking to develop an Android Mobile Application, should start here: [https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth Android Developer Guide]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Maintaining a bluetooth connection between the Android phone and the HC-05 module, proved to be more arduous that we expected. Luckily, Google provided extensive resources to help with the process, on the Android developer website (this might be the best starting point for future CMPE 243 app developers, or anyone else interested in developing an app like this.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The first step was to grant the application bluetooth permissions as well as location permissions. This enabled the application to enable bluetooth (assuming the phone could support it), as well as access the phone's location. These permissions were included in the Application's manifest file.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Next, we created a bluetooth adapter, which represented the phone's bluetooth radio.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | After enabling bluetooth, we started discovering available devices. We named our HC-05 module "HC-05", so that we could pair with the device name (as well as the MAC address).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | In order for the RF communication socket to connect to the HC-05, we used the following UUID: 00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB. This enabled the socket to correctly identify the HC-05 and maintain the connection.
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> '''''Google Maps Integration''''' </font> ====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | After the device was discovered, paired and connected, the next step was launching a Google Maps fragment. Below the fragment, we displayed feedback from various sensors on the car: distance sensors, heading, deflection angle and (the car's) starting latitude and longitude. The Sensor Controller and Geographic Controller sent updated feedback to the Bridge Controller during drives, allowing current data to be displayed on the application. This was useful for debugging and allowed us to avoid scanning the onboard LCD (mounted to the car) during drives.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Upon launching the map fragment, the user was able to place a destination marker on the map. This allowed the destination's latitude and longitude to be parsed and sent to the Bridge Controller, for pathfinding purposes. Once the destination coordinates were sent to the Bridge, it was able to use Djikstra's algorithm, to generate a path-to-goal (with checkpoints along the way).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Once a destination was set, the user was able to click the START button, which sent a START command to the master controller (letting it know that the car was ready to drive). While driving, the user was allowed to stop the car at any time, by clicking the STOP button. Regardless, upon reaching the destination, the car stopped itself anyway.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="green"> Technical Challenges </font> ===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''App Crash on Receiving NULL String''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The software on bridge was designed in such a way as to concatenate Geo and Sensor Data into one string separated by delimiters and send it over bluetooth (UART) to android application. Because the UART baud rate is 9600, it could send 960 characters in a second which was slow and the android application could handle much faster data rate than that, this caused the application to crash since it received a NULL string. This was a major technical challenge which was hard to resolve. Finally, we created a dedicated parse function and called in an "if" statement on the condition that the string was not NULL and its length was greater than 40 characters. This fixed the issue and we were able to display real time GPS, Compass and sensor data on the app.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''INTERNET Permission not enabled''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | One issue that set us back a day, during Google Maps integration, was not realizing that we never enabled the INTERNET permission the Application's manifest file. As a result, Google Maps was not able to launch properly; only a grey screen with the Google logo would display. While this may seem like a silly problem, as the code grows during development, it becomes easy to overlook basic requirements. Also, there are many factors involved in launching a Google Map Fragment (or intent) that can cause this type of issue. Once we enabled the INTERNET permission, the map fragment launched correctly.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''Broken Android Phone''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | During Google Maps integration, our progress was delayed for 2 days, due to a broken phone. The phone was unable to launch the updated application correctly, even though it had done so without issue, prior. Upon rolling back our Application software and launching it on the phone, we realized that it wouldn't run properly either. Luckily, we were able to get another Android phone to run the App on. Both iterations of the code ran without problems, when launched on the new phone.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="green"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| | {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#008000;" | | + | ! colspan="5" style="background:#000000;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> ANDROID MOBILE APPLICATION </span> | + | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> Known Issues </span> |
| | |- | | |- |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| + | Summary |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| + | Description |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| + | Version |
| | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | | | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" | |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| + | Status |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | | 5V should not be routed to game controller. |
| − | * '''Android Mobile Phone'''
| + | | 3.3V should be routed to the game controller instead of 5V since the ADC pins are not 5V tolerant. |
| − | |
| + | | 0.1 |
| − | * Samsung Galaxy S4
| + | | <span style="color:green">Resolved Rev 0.2</span><br/> |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * N/A (Supplied by Nuoya Xie)
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | <HR>
| |
| − | <BR/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | == <font color="green"> BRIDGE CONTROLLER </font> ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Hardware Design </font> ===
| |
| − | The Bridge controller acted as an interface between the Android mobile phone and the car. Its main purposes were to start and stop the car wirelessly and to send destination (latitude and longitude) coordinates to the geographic controller, for use with its pathfinding algorithm.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Our approach, involved pairing an HC-05 bluetooth transceiver with the Android mobile phone and then transmitting coordinates to and from the bridge controller using UART. Checkpoints along the path-to-goal, were transmitted over CAN, to the bridge, from the geographic controller.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Upon startup, 3.3V was supplied to the HC-05.
| |
| − | | |
| − | When the user clicked the "Discover" button the app, the Android mobile phone, initiated a pair and connect sequence, with the HC-05 (using its MAC address). Upon a successful pairing, the HC-05's LED blinks slowly as opposed to a few times a second (when unpaired).
| |
| − | | |
| − | The HC-05 used UART transmit and receive queues on the SJOne board, to store data, before transmitting it to the mobile app over bluetooth.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> Bluetooth Module SJone connection </font>====
| |
| − | [[File:SJone_bluetooth_android.png |thumb|center|600px|Bluetooth Module (HC-05) to SJone connection]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''Bridge Controller Schematic''''' </font> =====
| |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC Bridge Sch.jpeg|thumb|center|800px|Bridge Controller Schematic]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Software Design </font> ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> '''''Periodic Callback: Init''''' </font> ====
| |
| − | Upon startup, the bridge controller initiated both its UART and CAN peripherals. In order to communicate with the Android mobile phone over bluetooth, we had to use a baud rate of 9600bps. We set our transmit and receive queue sizes to 64 bytes, respectively. We also reset the CANbus, in order to ensure proper functionality.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> '''''Periodic Callback: 1Hz''''' </font> ====
| |
| − | In order to verify that the Bridge Controller's CAN transceiver was operational, we sent a heartbeat message every 1Hz, to the master controller. We used an integer value '0', for simplicity. If the bridge's CAN transceiver malfunctioned, the master controller illuminated the first (onboard) LED on itself (SJOne board). This allowed us to detect MIA modules quickly, without needing to connect to the Busmaster immediately.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We also checked the status of the CANbus every 1Hz and reset the bus if it was not operational. This was to ensure that a CAN glitch would not permanently compromise the bridge controller.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> '''''Periodic Callback: 10Hz''''' </font> ====
| |
| − | As stated before, the Bridge Controller acted as an interface between the Android Mobile phone and the car. Therefore we needed to transmit and receive coordinates and command from the phone, as well as to/from other modules on the car.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We checked the UART receive queue for START and STOP commands from the Android mobile phone. If one was received, then a CAN message was transmitted to the Master Controller, suggesting that it either apply or terminate power to the motor. For simplicity, we sent a character, '1' for START and '0' for STOP.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We also checked for essential navigation data from the Geographic Controller and Sensor Controller. We expected the car's starting coordinates (latitude and longitude), heading, deflection angle and distance to destination from the Geographic Controller. From the Sensor Controller, we expected feedback from the front, middle and rear distance sensors, as well as the infrared sensor mounted on the back of the car. This data was stored in a UART transmit queue and then transmitted to the Android mobile phone over bluetooth, every 2Hz. The Android application displayed feedback from the Geographic and Sensor controllers below its Google Map fragment.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC Bridge Software Flowchart.jpg|thumb|center|600px|Bridge Module Flowchart]]
| |
| − | <br> | |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Path-finding </font> === | |
| − | Because there might exist obstacles between the starting location and destination, In order to successfully navigate to the end, a map of intermediate checkpoints needs to be plotted. Although simpler algorithms are available, we chose Dijkstra's path-finding algorithm because of its readily available code online and the promise of no dead zone.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In order to use the actual algorithm, a NxN matrix that represents the allowed path between checkpoints needs to be populated manually, with N being the total number of checkpoints.The image below shows the actual map of checkpoints with their distances:
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:dijkstra_rundbc.jpg | thumb | center | 600px | Checkpoint Diagram]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | Here we have a total of 6 points. Because not all points are interconnected with each other, user of the algorithm has to fill out a matrix[i][j] with distance value. For example, if point 1 and 2 form a path, then in matrix[1][2] and matrix[2][1] the value should be 1000. Since a point has 0 distance with itself, the diagonal of the matrix is zero. When a path is not available, the distance is written as infinite. The filled matrix from the path image is shown below:
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:dijkstra2_rundbc.jpg | thumb | center | 600px | Populated Distance Matrix]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | The populated matrix above then can be fed into Dijkstra algorithm, with other parameter such as the size of the matrix, the starting checkpoint, and the ending checkpoint. Actual parameters depend on the implementation of the algorithm. However, one more step is needed before obtaining the above matrix. Since our checkpoints are in the form of longitude-latitude pairs, a distance conversion function has to be called to change coordinate data to distance. Therefore, we have a hard-coded array of coordinate structs as available checkpoints, and when the time comes to populate the matrix, a get_distance() function is called on every pair to obtain distance data.
| |
| − | | |
| − | One problem surfaced as we were working on this task: Since we do not know where our starting location or destination would be, how do we use the algorithm to calculate path? We solved this problem by adding two more checkpoints to our matrix: one representing source and one representing destination. When the bridge SJone board starts, it receives source coordinates from geographic module and populate the source checkpoint. When the Android phone sends the destination coordinates to the bridge module, it then populates the destination checkpoint. When these two points are populated, a segment of code is run that makes path between each of these two points to their nearest neighbor. Once the make_path() function finishes, then the Dijkstra algorithm kicks in at the end.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== <font color="green"> Path-finding sample code </font> ====
| |
| − | After the current location from the GEO module and the destination location from the bridge module are received, we put these two coordinates into an array which stores all the checkpoints.In order to connect the source location and the destination location to the rest of the checkpoints, we need to make a path between the source location and its closest checkpoint and another path between the destination location and its closest checkpoint with the code below. In this code segment, coordinate_array[] is an array filled with checkpoint coordinates in the form of structs. coordinate_distance[] is the NxN matrix mentioned above. gps_get_distance() function takes coordinate struct of two checkpoints and return the distance between them.
| |
| − | | |
| − | // place current location gotten from GPS into coordinate array
| |
| − | coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 2].latitude = current_location.latitude;
| |
| − | coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 2].longitude = current_location.longitude;
| |
| − | // place destination location into coordinate array
| |
| − | coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 1].latitude = destination.latitude;
| |
| − | coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 1].longitude = destination.longitude;
| |
| − |
| |
| − | //Now the 2 points has to link to the rest of the checkpoint array
| |
| − | float min_distance_start = INF;
| |
| − | int min_index_start = -1;
| |
| − | float min_distance_dest = INF;
| |
| − | int min_index_dest = -1;
| |
| − | //looping through all checkpoints to find the closest one to current location and to destination
| |
| − | for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE - 2; i++) {
| |
| − | if (gps_get_distance(coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 2], coordinate_array[i]) < min_distance_start) {
| |
| − | min_distance_start = gps_get_distance(coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 2], coordinate_array[i]);
| |
| − | min_index_start = i;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | if (gps_get_distance(coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 1], coordinate_array[i]) < min_distance_dest) {
| |
| − | min_distance_dest = gps_get_distance(coordinate_array[MAX_SIZE - 1], coordinate_array[i]);
| |
| − | min_index_dest = i;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | //after finding the index to the closest points, run make_path function
| |
| − | make_path(MAX_SIZE - 2, min_index_start);
| |
| − | make_path(MAX_SIZE - 1, min_index_dest);
| |
| − | | |
| − | The following code snippet is used to calculate the distance between two checkpoints and the result will be stored in the Dijkstra’s matrix. (if there is a path exists between these two checkpoints.)
| |
| − | | |
| − | void make_path(int i, int j) {
| |
| − | coordinate_distance[i][j] = gps_get_distance(coordinate_array[i], coordinate_array[j]);
| |
| − | coordinate_distance[j][i] = coordinate_distance[i][j];
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | | |
| − | The following code snippet is used to determine whether the RC car has arrived to its checkpoint or destination. If the distance between the current coordinates and the checkpoint coordinates is less than 10 meters, we would consider the car has arrived to its checkpoint location and the bridge module would send the next checkpoint to the master module.
| |
| − | | |
| − | bool is_checkpoint_arrived(void) {
| |
| − | return (gps_get_distance(current_location, coordinate_array[path[path_current_index]]) < 10); }
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Technical Challenges </font> ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''UART Receive While Loop''''' </font> =====
| |
| − | The primary technical challenge that we encountered, while developing the Bridge Controller, occurred during a demo. In an effort to display readings from sensor and geo on the Android application in real time, "CAN Receive" function was used, which in turn used a while loop to receive all CAN messages and then extract geo and sensor data, parse them and send them over UART to android application. Initially, we compiled all the data received and sent them within the CAN receive function which caused the app to crash/display junk values. To overcome this we replaced the while loop with if, however, this slowed down the rate at which messages were received and we displayed old data on App.
| |
| − | It took a while to figure out, but we created a new function called compile and send where we concatenated data and called it at 2Hz which fixed the issue.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="green"> '''''Interfacing Bridge and Geographic Modules''''' </font> =====
| |
| − | Another challenge we faced is the task of interfacing between geographic and bridge modules. Not long after starting the task, we realized that timing is very important. Since Dijkstra path-finding algorithm is only needed to run once, we need to make sure we obtain destination from Android phone first before running the algorithm. We also had to make sure geographic module receives the checkpoint from bridge module first before doing the bearing and distance calculations. We solved the first issue by setting a flag for Dijkstra algorithm. Every second the SJone board will check to see if the destination structure is populated. If it is, it sets a flag that enables the population of matrix needed by the algorithm and the algorithm itself is run shortly after. Latter issue by inputting a dummy distance of 1000m as the output of our distance calculation, before any checkpoint data arrives from bridge module. If a value of 1000 is showing on the LCD screen attached to the car, we know that geographic module has not yet gotten a checkpoint coordinate from bridge.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="green"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#008000;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> BRIDGE CONTROLLER </span>
| |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| + | | Wrong silkscreen/not enough room near power input. |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| + | | Power input silkscreen too small, part too big for 3.3V LED to fit |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| + | | 0.1 |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| + | | <span style="color:green">Resolved Rev 0.2</span><br/> |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span> | |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | | + | | Linear regulator not needed. |
| − | * '''Bluetooth Serial Communication Module'''
| + | | The schematic for the SJTWO board labels the input voltage pin as VIN RAW, which is different than the label on the |
| − | | | + | optional input port. They are both the same, so this input feeds directly into the on-board 3.3V regulator. Essentially |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/LeaningTech-HC-05-Module-Pass-Through-Communication/dp/B00INWZRNC LeaningTech HC-05 Module Bluetooth Serial Pass-Through Module Wireless Serial Communication with Button for Arduino] '''(Supplied by Nuoya Xie)'''
| + | we're driving the regulator with the same voltage it outputs which just won't work well. |
| − | | | + | | 0.1, 0.2 |
| − | * 1
| + | | <span style="color:red">UNRESOLVED</span><br/> |
| − | | | |
| − | * N/A
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | <HR> | + | === <font color="000000"> Gamepad Hardware Design </font> === |
| − | <BR/> | |
| | | | |
| − | == <font color="0000FF"> GEOGRAPHIC CONTROLLER </font> ==
| + | The gamepad board design requirement was to provide a more packaged interface for the user to interact with the game. <br> |
| | | | |
| | + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:gamepad_schematic.PNG|1000px|thumb|left|Gamepad Schematic]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> Hardware Design </font> ====
| |
| − | The geographical controller is responsible for providing the required directions for the car to reach its destination. This is achieved using the Adafruit MTK3339 Ultimate GPS module and the CMPS14 9DOF compass module to obtain the heading, bearing, and distance to checkpoint. Geographical controller receives checkpoint from bridge module, with which the distance and deflection angle are calculated. In our design, the pathfinding and the continuous sending of different checkpoints as car reaches each of them is checked by the Bridge module. The geographic controller is only responsible for obtaining the car’s current coordinates, computing distance and angle to the next checkpoint that is provided by the Bridge module over CAN and send these results over the CAN bus.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The car's starting latitude and longitude coordinates, were calculated by the GPS and then transmitted over CAN to the bridge controller, which transmitted them to the Android phone, using bluetooth. Upon executing the RUN-D.B.C Android mobile application, the user was able to select a destination location, by placing a marker on the Google Map fragment. The app parsed the destination's latitude and longitude coordinates and then sent them to the bridge controller. The pathfinding algorithm (Dikstra's algorithm) is used to calculate a path to the destination based on the starting location and a series of pre-defined checkpoints comprised of longitude and latitude data.
| + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:gamepad_layout_top.PNG|600px|thumb|left|Gamepad PCB Top]] |
| | + | |[[File:gamepad_layout_bottom.PNG|600px|thumb|left|Gamepad PCB Bottom]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> Geographic Controller Schematic </font>====
| + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:gamepad_pcb_assembled.jpg|800px|thumb|left|Gamepad PCB Fully Populated (no enclosure)]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC geo sch.jpeg | thumb | center | 800px | Geographic Controller Schematic]]
| + | == <font color="000000"> Hardware Design (Mechanical) </font> == |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> GPS Module SJone connection </font>====
| + | Only a few mechanical components were needed for this project. Namely simple brackets for mounting electrical hardware to the RGB matrix and displaying the matrix itself. All CAD designs were done using [https://www.onshape.com/ Onshape], a free CAD tool that can be used entirely through your web browser. |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:geo_pin_connection.jpg | thumb | center | 500px | Geographic module pin connection]]
| + | For displaying the RGB matrix, two brackets were 3D printed to prop it up. Their STL files can be found under our source repository. |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> GPS Module </font>====
| + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:matrix_bracket_1.PNG|100x|thumb|left|Mounting bracket design used to prop up the RGB matrix]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| | + | == <font color="000000"> Hardware Integration </font> == |
| | + | === RGB LED MATRIX === |
| | + | The LED matrix that we use is 64 pixels by 64 pixels and is controlled through a 12-pin header consisting of the following pins: |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:S19_RUNDBC.jpg| thumb | left | 300px | Adafruit Ultimate GPS module]]
| + | *Five Mux pins (A,B,C,D,E) for Row Selection |
| − | [[File:S19_RUNDBC_antenna.jpg| thumb|center|300px | Cirocomm GPS antenna]]
| + | **In order to select a specific row of the LED matrix, we need to control the output level of each mux pin. Since the LED matrix light up two rows of LEDs at one time, we can only select 1 out of 32 rows. |
| | + | *Two sets of RGB pins (R1,G1,B1,R2,G2,B2) for Color Selection |
| | + | **Since we are driving two rows of LED matrix at once, we need 2 sets of RGB pins. One set is used to control the color pixels of the upper half of the display and the other set for the bottom half of the display. |
| | + | *Output Enable Pin (OE) |
| | + | **Output Enable (OE) pin is used to turn on or off the LEDs of the current row. |
| | + | *Latch Pin (LAT) |
| | + | **Latch pin is used to prevent the data being shifted into the shift registers and tells the shift register when it is time to switch to newly entered data. |
| | + | *Clock Pin (CLK) |
| | + | **triggers a shift on the shift registers |
| | | | |
| − | <br>
| + | All these pins are required to display a specific color on a specific pixel of the LED matrix display. |
| − | <br>
| + | {| |
| − | <br>
| + | |[[File:Pin assignment LED Matrix.jpg|500px|thumb|middle|Pin Connections between SJtwo Board and REG LED Matrix]] |
| − | <br>
| + | |[[File:scan116.gif|200px|thumb|right|LED Matrix - Row Scanning]] |
| − | <br>
| + | |} |
| − | As stated before, we used an Adafruit MTK3339 Ultimate GPS module. The GPS, along with the compass, was responsible for calculating bearing angle and distance from destination checkpoints. An external antenna was integrated, in order to help parse the GPS data more efficiently. The GPS module used UART, to communicate with the SJOne board. The baud rate for the UART interface had to be initialized twice: 9600 bps at first and then again at 57600 bps. This was because the Ultimate GPS module could only receive data at 9600 bps upon startup, but its operational baud rate was specified as 57600 bps.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The GPS module came with a GPS lock, which allowed it to use satellite feedback to parse its location. This lock was indicated by an LED, which illuminated once every 15 seconds. If no lock was found then the LED illuminated once every 1-2 seconds. The parsing of data from the GPS was in terms of NMEA sentences, each of which had a specific functionality. Out of the several NMEA sentences, $GPRMC was used. It provided essential information, such as latitude and longitude coordinates. The $GPRMC sentence is separated by commas, which the user had to parse in order to get useful data out of the module. The strtok() function was used to parse data from the GPS module, with comma(,) as the delimiter.
| + | Apparently, it is impossible to driver all 4096 LEDs all at one time and thus, we can only drive two rows of LEDs at a time (one row on the upper half of the display and another row on the lower half of the display). By refreshing the LED matrix two rows at a time in a fast frequency, we can display all the game objects with animation on the LED matrix. |
| | | | |
| | + | === Joysticker controller === |
| | + | The joystick that we use is the product from Adafruit, the Analog 2-axis Thumb Joystick. This 2-axis Thumb Joystick provides the following pins: |
| | | | |
| − | The $GPRMC sentence looks like this: $GPRMC,225446,A,4916.45,N,12311.12,W,000.5,054.7,191194,020.3,E*68
| + | # Two ADC pins |
| | + | ## In order to control the tower location, we need to control the Joysticker, since the direction has four: Up, Down, Left, Right, we use the Y and X-axis to implement this function. |
| | + | # Three GPIO pins |
| | + | ## In order for selecting for the tool we need two GPIO pin for button and 1 GPIO pin for controlling the LED on the JOY STICKER controller |
| | | | |
| − | The below table explains what each of the datum in the GPRMC sentence stands for:
| + | * Pin configuration |
| | + | [[File:Selection 999(032).png]] |
| | | | |
| | + | === MP3 Decoder === |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC geo table pic.png |thumb | center | 600px | GPRMC Sentence Structure]]
| + | The MP3 decoder that we use is Sparkfun’s vs1053 shield MP3 decoder which is the board based on the vs1053b chip. |
| | | | |
| | + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:MP3DECODER PON.png|600px|thumb|left|MP3 Decoder Module Pinout]] |
| | + | |} |
| | + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:Selection 999(034).png|600px|thumb|left|MP3 Decoder Pin Table]] |
| | + | |} |
| | + | * Three SPI pin |
| | + | In order to communicate with the mp3 decoder with SJtwo Board, we choose the SPI as the protocol to control the decoder. Hence, we need the one pin SCK0 |
| | + | (clock), one pin MOSI(Master In Slave Out) and one pin (Master Out Slave In). |
| | + | * Four GPIO pin for the decoder |
| | + | There are four major GPIO pin for DREQ(Data Request Pin), Reset, CS(Chip Select), XDCS(Data Chip Select), this 4 GPIO pin is how we transfer data and send |
| | + | the command to activate the mp3 decoder work with SJ2 Board. |
| | | | |
| − | The first 6 fields in the NMEA sentence are the most important ones. If field 4 said ‘N’, we checked the data in field 3 which had the latitude. Likewise, if field 6 said ‘W’, we check the data in field 5 which contained the longitude. It is important to note that the longitude and latitude data are in the form degree-minute-seconds instead of true decimal. If not properly converted, they could have offset the location readings by miles.
| + | == <font color="000000"> Software Design </font> == |
| | + | === <font color="000000"> RGB LED Matrix </font> === |
| | + | [[File:RGB_data.jpg|400px|thumb|right|RGB Data Element]] |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> '''Compass Module''' </font>====
| + | All the LED Matrix data are stored in a buffer with its size equal to 32 by 64. Each element in this buffer store the color of two pixels, one pixel from the upper half of the display and one pixel from the lower half of the display. |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:compass_rundbc.jpg| thumb | center | 500px | CMPS14 Compass Module]]
| + | In order to display the gaming objects in animation, we need to refresh the display by displaying the color pixels on each row one by one very fast. Below is a simple flowchart that describes the process of refreshing the display. |
| | | | |
| − | The compass module is responsible for redirecting/navigating the car towards the required destination as chosen on the mobile app. The heading angle is obtained from the compass module, which tells us where the car is pointing to the magnetic north. Since it is true north that we want, we need to add an offset, called magnetic declination, to the heading angle.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The compass module chosen is CMPS14 – Tilt compensated compass module which has a 3-axis gyro, 3-axis accelerometer and a 3-axis magnetometer. It is powered on by 3.6-5V but works on 3.3V too. It uses I2C to communicate with the SJOne board for which the mode pin can be left open or pulled up to the supply voltage. Due to the presence of the magnetometer, the compass must be placed away from all other components of the car to minimize magnetic interferences from other controllers. In our car, the compass was placed at an elevated position, high enough to be away from other controllers’ magnetic interferences. The compass need not be calibrated manually, as CMPS14 has automatic calibration.
| + | * Loop through each row of the LED display |
| | + | # Select Row (By controlling the output level of 5 mux pins, we can select one row at a time) |
| | + | # Disable the LED Display output (Turn off the LEDs of the current row of the display) |
| | + | # Unlatch the Data |
| | + | # Clock in Data for each column(Store the color of each pixel inside display_matrix buffer) |
| | + | # Latch the Data |
| | + | # Enable the LED Display output (Display the color of each pixel of the current row) |
| | + | # Delay for a 100us (Increase the light intensity of the LEDs by delay a short amount of time) |
| | + | # Disable the LED Display output (Turn off the LEDs of the current row of the display) |
| | | | |
| − | ===== <font color="0000FF"> '''Read Compass Heading''' </font>=====
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> |
| − | Compass heading is read by initiating the I2C read operation, and by passing the compass address (0xC0) and the register address (0x2). These values, along with the temporary array must be passed in a single I2C read operation. An example of the code snippet is as below:
| + | void refreshDisplay(void) { |
| | + | for (uint8_t row = 0; row < LEDMATRIX_HALF_HEIGHT; row++) { |
| | | | |
| − | if (read_byte_from_i2c_device(COMPASS_ADDRESS, first_reg_address, 2, temp)) {
| + | select_row(row); |
| − | temp_result = temp[0] << 8 | temp[1];
| + | led_matrix__disable_output(); // gpio__set(OE); |
| − | float temp_float = temp_result / 10.0; // from 3599 to 359.9 | + | led_matrix__unlatch_data(); // gpio__set(LAT); |
| − | temp_float += 13.244; // correct for magnetic declination | + | led_matrix__clock_in_data(row); |
| − | if (temp_float >= 360) { | + | led_matrix__latch_data(); // gpio__reset(LAT); |
| − | temp_float -= 360;
| + | led_matrix__enable_output(); // gpio__reset(OE); |
| − | } | + | delay__us(100); // Change Brightness |
| − | *result = temp_float; | + | led_matrix__disable_output(); |
| − | return true; | |
| | } | | } |
| − | return false; | + | } |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | + | |
| | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="c"> |
| | + | void led_matrix__clock_in_data(uint8_t row) { |
| | + | /* Clock in data for each column */ |
| | + | for (uint8_t col = 0; col < LEDMATRIX_WIDTH; col++) { |
| | + | |
| | + | /* Set all the RGB pins as low*/ |
| | + | LPC_GPIO1->PIN &= ~(0x1 << R1.pin_number | 0x1 << G1.pin_number | 0x1 << B1.pin_number); |
| | + | LPC_GPIO2->PIN &= ~(0x1 << R2.pin_number | 0x1 << G2.pin_number | 0x1 << B2.pin_number); |
| | | | |
| − | ===== <font color="0000FF"> '''Check Compass Calibration''' </font>===== | + | /* Set the RGB pins as High or Low depends on the data stored inside the buffer */ |
| − | The calibration level is checked to see how well the compass is calibrated. The 8-bit value resides in register 0x1E according to the diagram below:
| + | LPC_GPIO1->PIN |= ((((display_matrix[row][col] >> 0) & 0x1) << R1.pin_number) | |
| − | [[File:compass_calibration_rundbc.jpg| thumb | center | 800px | CMPS14 calibration register]] | + | (((display_matrix[row][col] >> 1) & 0x1) << G1.pin_number) | |
| | + | (((display_matrix[row][col] >> 2) & 0x1) << B1.pin_number)); |
| | | | |
| − | When each of the 2-bit calibration value is 0, this means the specific field is not calibrated, a value of 3 means the field is fully calibrated. This is done by performing an I2C read operation, whilst reading the 0xC0 and the 0x1E registers, to determine if it’s calibrated or not. The code snippet looks as below:
| + | LPC_GPIO2->PIN |= ((((display_matrix[row][col] >> 4) & 0x1) << R2.pin_number) | |
| | + | (((display_matrix[row][col] >> 5) & 0x1) << G2.pin_number) | |
| | + | (((display_matrix[row][col] >> 6) & 0x1) << B2.pin_number)); |
| | | | |
| − | bool check_calibration_level(uint8_t* result) {
| + | gpio__set(CLK); |
| − | char calibration_state_address = 0x1E; // register 30
| + | gpio__reset(CLK); |
| − | bool is_calibration_successful = false;
| |
| − | if (read_byte_from_i2c_device(COMPASS_ADDRESS, calibration_state_address, 1, result)) {
| |
| − | is_calibration_successful = true;
| |
| − | }
| |
| − | return is_calibration_successful;
| |
| | } | | } |
| | + | } |
| | + | </syntaxhighlight> |
| | | | |
| − | ==== <font color="0000FF"> '''Essential GPS Data''' </font>====
| + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:RefreshDisplaySequence.jpg|300px|Process of refreshing display]] |
| | + | |} |
| | + | === <font color="000000"> MP3 Decoder </font> === |
| | + | The MP3 deocder is executed with the mainly two task: read task and play task. |
| | + | The reader task would read data from the sd card and sned queue data for the player task to play music. |
| | | | |
| | + | {| |
| | + | |[[File:MP3DECODERMODULE.png|600px|thumb|left|MP3 Decoder Module API]] |
| | + | |} |
| | + | * Read Task |
| | + | * Loop through each row of the LED display |
| | + | # Queue sned the target filename |
| | + | # Queue receive the target name |
| | + | # Find the mp3 file name is exit or not |
| | + | # Open the file(fopen) |
| | + | # Read data store to the buffer(Binary) |
| | + | # Sent the data from bufder with queuesend API |
| | | | |
| − | ===== <font color="0000FF"> '''''Bearing, Distance, and Deflection Angle Calculation'''''</font>=====
| + | {| |
| | + | |[[File: READ TASK.png]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | Bearing, calculated as an angle from true north, is the direction of the checkpoint from where the car is. The code snippet to calculate bearing is below. Lon_difference is the longitude difference between checkpoint and current location. GPS is the current location, and DEST is checkpoint location. For all trig functions used below, the longitude and latitude values have to be converted to radian. After the operations, the final bearing angle is converted to degrees and a positive value between 0 and 360.
| + | * Play Task |
| | + | Receive the data of the song from the queue, and use the receiving data and sent the command to make decoder to play music. |
| | | | |
| − | bearing = atan2((sin(lon_difference) * cos(DEST.latitude)), ((cos(GPS.latitude) * sin(DEST.latitude)) - (sin(GPS.latitude) *
| + | * Read Task |
| − | cos(DEST.latitude) * cos(lon_difference))));
| + | * Loop through each row of the LED display |
| − | bearing = (bearing * 180) / PI;
| + | # Queue receive the data(music) |
| − | if (bearing <= 0) bearing += 360;
| + | # disable the chip select |
| − | return bearing;
| + | # Check the DREQ pin to know is ready or not |
| | + | # exchange the data to the decoder to play the music |
| | + | # Check the DREQ pin to know is ready or not |
| | + | # disable the chip select |
| | + | {| |
| | + | |[[File: Play Task.png]] |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | Distance between the car and the checkpoint can be calculated using GPS along. The code snippet to calculate distance is shown below. It utilizes the haversine formula to calculate the great-circle distance between two points on a sphere given their longitudes and latitudes. Like the bearing calculation, all coordinates must be in radian. The value 6371 below is earth’s radius in km.
| + | === <font color="000000"> JOY STICKER </font> === |
| | + | The JOY_STICKER is using the task to pool the ADC channel data to get the direction from the Joysticker. |
| | | | |
| − | float a = pow(sin((DEST.latitude - GPS.latitude) / 2), 2) + cos(GPS.latitude) * cos(DEST.latitude) *
| |
| − | pow(sin((DEST.longitude - GPS.longitude) / 2), 2);
| |
| − | float c = 2 * atan2(sqrt(a), sqrt(1 - a));
| |
| − | float distance = 6371 * 1000 * c;
| |
| − | return distance;
| |
| | | | |
| − | After obtaining heading and bearing values, deflection angle, the difference in angle between your car and the checkpoint, is calculated. This is the angle value that is given to the master for steering purposes. We made that if the deflection angle is negative, the car should steer to the left. If the angle is positive, then the car should steer to the right.
| + | * Loop through each time to poll the enum type data to get direction |
| | + | # Receiving the data from two ADC channel(5=x, 4=y) |
| | + | # Comparing which one has higher absolute data |
| | + | # If (X > Y == YES) ,then we go to the loop to compare It's closer to Right or Left |
| | + | # If (X > Y == YES && Right > LEFT == YES), then the status is Right |
| | + | # If (X > Y == YES && Right > LEFT == NO), then the status is Left |
| | + | # If (X > Y == NO) ,then we go to the loop to compare It's closer to Up or Down |
| | + | # If (X > Y == NO && Up > Down == YES), then the status is Up |
| | + | # If (X > Y == NO && Up > Down == NO), then the status is Down |
| | | | |
| − | deflection = gps_bearing - compass_heading;
| + | {| |
| − | if (deflection > 180)
| + | |[[File:Joystickermodule.png|1000x|thumb|left|Game controller]] |
| − | deflection -= 360;
| |
| − | else if (deflection < -180)
| |
| − | deflection += 360;
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="0000FF"> Software Design </font> ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | The complete flowchart for the geo module is shown below. We broke all the tasks in two iterations of the 10Hz function because if we do them in one iteration, we get the task overrun error. Therefore, the gps update rate is 5Hz.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:geo_diagram_rundbc.jpg | thumb | center | 500px | Geographic Module Flow Diagram]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="0000FF"> Technical Challenges </font> ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Getting correct BAUD rate for GPS'''
| |
| − | * When we first started interfacing with GPS module, we can never get the gps to output the BAUD rate we want (57600). Hercules was showing random symbols when we switch BAUD rate to 57600 even though we made sure the message we send to the GPS was correct. Browsing through Adafruit's help forum showed that the GPS, upon startup, only accepts messages in 9600 bps. If the user wants to switch BAUD rate to a higher value, he/she has to first send the command to switch BAUD rate in 9600, then rest of the command can be in the higher BAUD rate. As soon as we added the missing component, our GPS was giving us correct information shown in Hercules.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Compass reading was not accurate and would deviate from initial calibration'''
| |
| − | * The initial compass we got (CMPS12) exhibited unstable heading reading. Even after we calibrated manually to make sure it points to magnetic north, after some testing we would check again and it would not point to magnetic north anymore. We tried to both factory preset and manually saving calibration profiles but nothing changed. We ended up buying another compass (CMPS14) that offered the ability to turn off auto-calibration. At the start of the SJone board we send a command to the compass to disable auto-calibration and auto-profile saving, we lengthened the wooden rod that takes the compass away from the EM-generating components of the car, and we replaced our GPS antenna for one without build-in magnet. All of these things together solved our issue and our compass was accurate within 2-3 degrees from magnetic north, which is sufficient for our application.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Parsing NMEA sentences'''
| |
| − | * When we are receiving NMEA sentences from the gps module, sometimes we would receive garbled up messages. Since our GPS module continuously send out NMEA sentences and lacks a trigger pin that send NMEA sentence when prompted, we have no idea, when we are using uart driver to read the message, when the start of the message will first appear. To solve this issue, we implemented several checks to our GPS parsing. First, the processing of the messages only happens if the first character of the message is the character '$', which begins our GPRMC sentence. Next, we will only take in latitude and longitude values if the third and fifth entries read are 'N' and 'W', respectively. These checks ensure that the message is not fragmented and allow us to obtain correct longitude and latitude data.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="0000FF"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#36C;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> GEOGRAPHIC CONTROLLER </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''GPS'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/Adafruit-Ultimate-GPS-Breakout-External/dp/B00I6LZW4O/ref=sr_1_fkmrnull_5?keywords=Adafruit+Ultimate+GPS+Breakout+Kit&qid=1554334740&s=gateway&sr=8-5-fkmrnull Adafruit Ultimate GPS Breakout Kit]
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * $69.13
| |
| − | | |
| − | |- | |
| − | | | |
| − | * '''GPS antenna'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.amazon.com/CIROCOMM-Antenna-Ceramic-25x25x2mm-Geekstory/dp/B078Y2WNY6 Cirocomm 5cm Active GPS Antenna]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $8.79
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''Compass'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.robotshop.com/en/tilt-compensated-magnetic-compass-cmps14.html CMPS14 Tilt Compensated Magnetic Compass]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $33.99
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | <HR>
| + | {| |
| − | <BR/>
| + | |[[File:JOY STICKER ADC FLOW.png|1000x|thumb|left|Game controller flow chart]] |
| − | | |
| − | == <font color="FF8C00"> MASTER CONTROLLER </font> ==
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF8C00"> Hardware Design </font> ===
| |
| − | The master controller is primarily interfaced with the other controllers over CAN bus. The other main interface is control of the LCD display for debug data, which communicates over UART.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC master sch.png |thumb| center | 800px|Master Module Schematic]] | |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RunDBC_LCD.jpg |thumb| center | 800px |LCD Showing speed, steer and state information]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF8C00"> Software Design </font> ===
| |
| − | [[File:Master stateMachine.PNG |thumb| right | 400px| Master State Machine]]
| |
| − | * LCD display
| |
| − | ** The LCD is controlled over UART, printing single lines at a time
| |
| − | ** There are three available screens that can be cycled through by pushing button 0 on the master board
| |
| − | *** Operation Data: This screen shows a range of info including the commanded and actual speed, the distance and deflection to the next checkpoint, and the current state of the state machine.
| |
| − | *** Sensor Data: This screen shows the distances being read from each of the four distance sensors (in cm)
| |
| − | *** Geo Debug: This screen shows the latitude, longitude, heading, and deflection angle of the car as well as compass calibration levels and distance to the checkpoint.
| |
| − | * CAN read and send
| |
| − | ** All CAN messages are read and MIAs are handled in a single 50Hz receive function.
| |
| − | ** There are separate send functions for the motor commands and the debug info.
| |
| − | * Navigation: The primary function of the master module is to process the geo and sensor data, and send steering and motor commands to the motor module.
| |
| − | ** obstacle avoidance
| |
| − | ** steer to checkpoint
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The state machine above handles the data processing to decide what steering and motor commands to send to the motor module.
| |
| − | # INIT: The state machine always starts here. It sets the motor speed and direction to zero and the steering to straight before transitioning to the WAIT state.
| |
| − | # WAIT: The car will stay in this state with the motor set to zero speed and steering set to straight until there is a ''go'' command is received, '''and''' the distance to the next checkpoint is > 10 meters, at which point it transitions to the NAVIGATE state.
| |
| − | # NAVIGATE: While in this state, the master will set the motor command to the predetermined NAVIGATE_SPEED (2.0m/s standard) and the steering angle based on the deflection between the bearing to the next checkpoint and the heading of the car.
| |
| − | # OBSTACLE LEFT/RIGHT: These states are triggered when the left or right ultrasonic sensor detect an object closer than the STEER_THRESHOLD, and will command the motor speed to OBSTACLE_SPEED and steer in the opposite direction of the obstacle.
| |
| − | # OBSTACLE MID FAR: This will be triggered when there is an obstacle straight ahead closer than the MIDDLE_THRESHOLD_FAR (and has a higher priority than the left and right obstacle states). The module will command the speed to OBSTACLE_SPEED and attempt to steer around the obstacle to the right.
| |
| − | # OBSTACLE MID CLOSE: This will be triggered when there is an obstacle straight ahead closer than the MIDDLE_THRESHOLD_CLOSE (and has the highest priority). The car will be commanded to drive backwards if there is nothing behind the car, or stop in place if there is something behind the car, until the front obstacle is cleared or far enough away to attempt to navigate around it.
| |
| − | # REVERSE_PAUSE: This is a short pause after the OBSTACLE MID CLOSE state. This allows the car to coast to a stop before commanding forward again, to avoid integral wind-up of the PI controller on the Motor module.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF8C00"> Technical Challenges </font> ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Quickly switching from reverse to forward "winds up" integral term of PI controller on motor module
| |
| − | ** Solved by adding short (1 second) delay after reversing
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | * One of the MIA LEDs would blink, even when the appropriate node was on the CAN bus and messages were being received.
| |
| − | ** Probable related to not properly cleaning the build after making some changes. The problem resolved itself
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF8C00"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#FF8C00;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> MASTER CONTROLLER </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''LCD'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * N/A
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * Supplied by Preet Kang
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | <HR> | + | === <font color="000000"> System Flow Charts </font> === |
| − | <BR/> | + | <br> |
| | + | <b> Basic Software Environment: </b> <br> |
| | + | [[File:Flow1 TDIS.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | == <font color="EE82EE"> MOTOR CONTROLLER </font> ==
| + | <br> |
| − | | + | <b> Game Master (how the user sees the game flowing): </b> <br> |
| − | | + | [[File:Flow2_TDIS.png]] |
| − | === <font color="EE82EE"> Hardware Design </font> ===
| |
| − | The motor board was responsible for both steering and spinning the wheels in order to move the car towards the target destination. <br>
| |
| − | The front 2 wheels of the car handled the steering portion and it accomplished this with the utilization of the servo. <br>
| |
| − | The back 2 wheels of the car handled spinning the wheels and it accomplished this through the utilization of the Electronic Speed Control (ESC) that was interfaced to the DC motor directly.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The servo was included with the RC we purchased and it was interfaced with 3 pins:
| |
| − | <b> <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the power supply, which was powered by the battery that came with the RC car (as opposed to the same supply that other components shared on our PCB) <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the ground signal <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the servo dedicated PWM control signal <br>
| |
| − | </b> <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The ESC was included with the RC we purchased and it was interfaced with 3 pins:
| |
| − | <b> <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the power supply (powered similar to the servo) <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the ground signal <br>
| |
| − | 1 pin for the ESC dedicated PWM control signal <br>
| |
| − | </b> <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Managing the steering was relatively simple. The servo mainly requires a PWM signal in order to operate. <br>
| |
| − | As seen through the timing diagrams below (and through experimentation), we found the frequencies and duty cycles that corresponded to actual steer left, steer right, and steer straight. <br>
| |
| − | With our SJ1 board, we were able to match our frequencies and duty cycles and steer the car using the APIs that we designed. <br>
| |
| − | Our code allows for the steering to be set to any turn angle that is mechanically allowed by the car. <br>
| |
| − | In order to reach the maximum turn angle setting, the programmer needs to set the PWM to either 10% (left) or 20% (right) duty cycle. <br>
| |
| − | If the programmer wants a smaller turn angle, they need to program the PWM to a duty cycle that is closer to 15% (15% duty cycle means steer straight). <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | Managing wheel spin was a more complicated process. The ESC also requires a PWM signal in order to operate, but is not as simple as the servo's operation. <br>
| |
| − | In order to reach the maximum speed in the forward direction, the programmer needs to set the PWM duty cycle to 20%. <br>
| |
| − | In order to stop spinning the wheels, the programmer needs to set the PWM duty cycle to 15%. <br>
| |
| − | In order to safely reverse the car, the RC car manufacturer implemented a special feature to make sure that the DC motor doesn't burn up when switching from high speed forward to going in the reverse direction. <br>
| |
| − | When controlling the car with the handheld RC remote (manual control), this feature is present and the user needs to first stop and toggle some reverse commands before the car can actually move in reverse. <br>
| |
| − | This means that a state machine was also needed in our code in order to enable reverse functionality. <br>
| |
| − | Our software implementation of this reverse state machine is:
| |
| − | <b><br>
| |
| − | Stop for 100ms <br>
| |
| − | Reverse for 100ms <br>
| |
| − | Stop for 100ms <br>
| |
| − | Reverse for 100ms <br>
| |
| − | User can then reverse at any given PWM duty cycle from <15% (low speed) to 10% (full speed)
| |
| − | </b><br>
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | + | <b> Intermission Phase (what happens while the user is placing towers): </b> <br> |
| | + | [[File:Flow3_TDIS.png]] |
| | | | |
| − | In order to maintain constant speed while moving up/down an inclined road, a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) loop is commonly used. <br>
| |
| − | We didn't find the need to include the derivative component, so our speed control loop just contained the proportional and integral components. <br>
| |
| − | Actual moving car speed is another component of this loop, we were able to read and calculate actual car speed through the use of an encoder. <br>
| |
| − | Portions of the PID loop use constant values for the gains of each component. <br>
| |
| − | Our gains were determined through a trial and error testing process. <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="EE82EE"> '''''Speed Control Timing Diagrams''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:Run DBC Speed timing diagrams.PNG |thumb| 600px|center| Speed Timing Diagrams]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="EE82EE"> '''''Steering Control Timing Diagrams''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:Run DBC Steering timing diagrams.PNG |thumb| 600px |center| Steering Timing Diagram]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===== <font color="EE82EE"> '''''Motor Controller Schematic''''' </font> =====
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC motor sch.png |thumb| center | 800px | Motor Module Schematic]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | === <font color="EE82EE"> Software Design </font> ===
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <b>Periodic Callback: Init (beginning of program)</b><br>
| |
| − | - The CAN bus is initialized <br>
| |
| − | - The encoder interrupts are enabled <br>
| |
| − | - The 2 PWM signals are initialized and set to default values <br>
| |
| − | - Memory is initialized to speed values of 0 which imply the stopped state<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <b>Periodic Callback: 1Hz (every 1sec)</b><br>
| |
| − | - Check if the motor board's CAN node is either on or off the CAN bus. <br>
| |
| − | - If the motor board is not on the CAN bus, reset the CAN bus for this node. <br>
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| − | <b>Periodic Callback: 10Hz (every 100ms)</b><br> | + | <b> Combat Phase (what happens when the aliens invade): </b> <br> |
| − | - Send a Heartbeat message to the Master board (to ensure these 2 boards have reliable communication). <br>
| + | [[File:Flow4_TDIS.png]] |
| − | - Read all CAN messages and filter out the ones we care about. <br>
| |
| − | - Check and handle the BIST for basic motor functions (self test is started only when the user presses Button #1 on the SJ1 board). <br>
| |
| − | - If the BIST is not currently running, control the steering and car movements based on CAN communication with the Master controller. <br>
| |
| − | - Send the actual car speed, steering angles, and motor direction to the Master (for determining future drive commands) and to the Bridge (for displaying real-time data on the phone app). <br>
| |
| − | - Send motor debug messages to the Master (for LCD display), Bridge (for phone app display), and Debug (for BusMaster display) nodes to help troubleshoot motor functionality. <br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | === <font color="EE82EE"> Technical Challenges </font>===
| + | == <font color="000000"> System Testing and Validation </font> == |
| − | | + | {| |
| − | ===== <font color="EE82EE"> '''''SJOne PWM''''' </font>=====
| + | |[[File:StartScreenTowerDefense.gif|400px|thumb|left|Start Screen]] |
| − | When we were matching PWM signals of the SJ1 board to the same PWM frequencies and duty cycles based on the RC car's remote, we were not getting consistent results. <br>
| + | |[[File:CombatPhase.gif|400px|thumb|left|Combat Phase]] |
| − | In the \SJSU_Dev\projects\lpc1758_freertos\L2_Drivers\src\lpc_pwm.cpp file on line #37, we found out that the function sys_get_cpu_clock() was giving different frequencies for several program executions. <br>
| + | |} |
| − | Our short-term workaround was to replace that function call with the known system clock frequency. <br>
| |
| − | Our long-term solution was to to keep that driver file as was originally developed and we could declare our PWM objects globally and each as a pointer. <br>
| |
| − | This method gave us the correct result when matching our PWM frequencies and duty cycles. <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="EE82EE"> '''''Encoder''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | The original encoder we sourced was designed for slower speed purposes, such as for a knob. <br>
| |
| − | The additional rotational resistance with this encoder caused vibrations and resulted in it becoming disconnected from the motor shaft several times. <br>
| |
| − | Our solution was to use an encoder with higher quality although more expensive. <br>
| |
| − | Our new encoder was designed for higher speed and continuous operation on a fast paced motor. <br>
| |
| − | This higher grade encoder provided us with more reliable and more accurate encoder sensor values. <br>
| |
| − | In addition to a hardware solution, we also implemented a software solution. <br>
| |
| − | The original purpose of our software solution was to control the damage that a loose encoder could cause on the rest of the car. But we found it to be a safe feature to include in case any abnormality occurs on the encoder.<br>
| |
| − | Our PID loop works such that if the commanded speed is higher than the actual speed calculated by the encoder sensor, then the PWM drive will increase accordingly (the motor will work harder). <br>
| |
| − | If the encoder comes loose, the values from the encoder sensor will always result in being a 0 value. This consequences in the actual speed being calculated to 0 m/s even though the car may actually be moving. <br>
| |
| − | Without software protection, this effect will eventually result in the PWM being driven to full strength. At full strength, our RC car could move very fast and definitely was at risk of being damaged if it collided with an object at such speeds. <br>
| |
| − | For autonomous car operation, many subsystems and electronics need to be perfectly connected and stable in order to work safely. <br>
| |
| − | To keep all of these systems safe from high speed collisions, we enforced hard limits on the PWM drive strength (in terms of duty cycle output). <br>
| |
| − | We also checked for cases where our PWM was driven to these limits we enforced. If it did reach these limits, we would shut off the motor if the encoder was continuously reading values of 0. <br>
| |
| − | Another stability check we included was limiting the amount of integral windup that could occur during an iteration of our PI loop. This helped to make sure the car gradually increased and decreased its speed accordingly. <br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | === <font color="EE82EE"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| + | {| |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | |[[File:EndGame.gif|400px|thumb|left|Player Loses the game]] |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#EE82EE;" |
| + | |[[File:VictoryScreen TowerDefense.gif|400px|thumb|left|Player Wins the game]] |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> MOTOR CONTROLLER </span>
| |
| − | |- | |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| |
| − | |- | |
| − | | | |
| − | * '''Motor Encoder'''
| |
| − | | | |
| − | * [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/nidec-copal-electronics/RE12D-100-201-1/563-2051-ND/6469487, Nidec Copal Optical Rotary Encoder]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $63.16
| |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| − | <HR> | + | == <font color="000000"> Technical Challenges </font> == |
| − | <BR/> | |
| | | | |
| − | == <font color="FF0000"> SENSOR CONTROLLER </font> == | + | === Game Map (2D array) to LED matrix (2D pixels) Conversion === |
| | + | Issue: |
| | + | # The game map (consisting of the path as well as all of the active enemies and towers) is managed through the use of a 2D char array. |
| | + | # In order to display each object on the LED matrix, there needs to be a mechanism that converts the object along with its 2D array location to a row/column on the LED matrix. |
| | + | # An algorithm to do this conversion is not as straightforward as it may appear. This is because objects stored in the array take up more/less display space than what is available on the LED matrix. |
| | + | Solution: |
| | + | # In order to align the array locations with the LED matrix pixel locations, some areas on the 2D array needed to be marked as "ignore". <br> |
| | + | # If each array location is not carefully correlated to a specific pixel location, then there would be issues where objects are displayed overlapping each other on the LED matrix (or simply displayed in the wrong spot). |
| | + | # There were some simple algorithms that used math to help implement this conversion. <br> |
| | + | # However, a LUT is what was primarily used. It was not efficient in terms of code size, it took over 500 lines of code. <br> |
| | + | # But it was an effective solution and allowed us to easily decide exactly where each pixel of each object would be displayed. |
| | | | |
| − | === <font color="FF0000"> Hardware Design </font>=== | + | === LED Matrix Flickering Issue === |
| | + | Issue: While we are developing the game, we notice that some color pixels are turned on when they are supposed to be off. |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:Image002.jpg |thumb| center | 800px | Pin connection of Different sensors to SJOne Board]] | + | Investigation/Solution: |
| | + | # See [[Known Breakout PCB Issues]] as a possible cause. It's possible the SJTWO board is getting inconsistent power. |
| | + | # Refreshing the matrix should not be handled by an interrupt and not a task. The task should only push new display data and not have direct control of the matrix. Keeping the refresh interrupt driven would keep the refresh rate more consistent by removing the process being context switched out mid update. |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:sensors_rundbc.jpg |thumb| center | 600px | Placement of Sensors on RC Car]]
| + | === MP3 Decoder - SJtwo Board SPI Selection === |
| − | | |
| − | Sensor module consists of 4 sensors: 3 Maxbotix ultrasonic sensors in the front, and one ir sensor in the back. The three sensors in the front are detecting obstacles in three directions: directly in front, to the left, and to the right. We chose ultrasonic sensors instead of Lidar because of its cheaper price, easier implementation, and independence of lighting conditions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | On the SJone board there are only three ADC pins that has pin headers for users to attach sensors. Since we have a total of 4 sensors that need ADC to obtain data, we had to desolder the light sensor on the SJone board to free up ADC0.2 for our use.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Sensor Controller Schematic''''' </font>===== | |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:RUN DBC sensor sch.png|thumb| center | 800px | Sensor Module Schematic]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''CAD Design''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | We gave a lot of thought regarding how and where sensors should be mounted to the car. In order to facilitate adjusting the directions of individual sensors, we incorporated circular grooves in the sensor bases. The hinge of the sensor mount also allowed sensors to be vertically adjusted Together with the sensor mount, this approach gave the sensor's two degrees of freedom.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The picture on the left shows that the hinge of the sensor guard can be adjusted to minimize the amount of interference between sensors. <br>
| |
| − | The picture on the right shows the hinge of the sensor mount, allowing vertical adjustment.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:SW001.gif | thumb | left | 200px | Sensor Guard to Minimize Interference]]
| |
| − | [[File:SW002.gif | thumb | center | 200px | Sensor Guard Mount showing Vertical Adjustment]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Placement for the Ultrasonic Sensors''''' </font color="FF0000">=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | We realized that when the sensors were active, the left and right sensor ultrasonic wave output, sometimes interfered with the middle sensor, resulting in incorrect feedback. This occurred despite polling the sensors in separate periodic tasks. We discovered that, mounting the middle sensor on a higher surface than the left and right sensors decreased the interference substantially. Furthermore, by attaching two guard pieces on the left/right sensors (acting as shields), we further decreased the interference between sensors. We rigorously tested the integrity of sensor feedback with the guards in different positions, to ensure that they didn't introduce interference of their own (in certain positions).
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Sensor Value Conversion''''' </font color="FF0000">=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | In order to convert ADC readings from sensors to distance, we needed to plot conversion curves for both the ultrasonic sensors and the IR sensor. We used a tape measure and laid a piece of wide metal board directly in front of the sensor and gradually move it back 5cm at a time to record the corresponding ADC value. According to datasheets, the Maxbotix sensors should have a linear relationship between distance and reading, whereas the Sharp IR sensor curve is nonlinear. After obtaining the values, we fitted a line over the Maxbotix sensors and a power curve to the IR. The curves can be seen below:
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:sensor_curve_rundbc.jpg |thumb| center | 800px | Sensor Graphical Representation]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF0000"> Software Design </font>===
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Flowchart''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | The flow diagram for sensor is shown below. We split the sensor readings to two different 10Hz tasks to minimize amount of interference between left/right and middle sensors. In one of the iterations, we read the left/right ultrasonic sensors using adcx_get_reading() function, and immediately after reading them we trigger the middle ultrasonic sensor to output ultrasonic wave. Since it takes time for sound waves to bounce back from solid surface, by the time the next task begins the middle ultrasonic sensor can then read the wave outputted from the previous task. In the other iteration, the middle and rear sensors are read, and left/right ultrasonic sensors are triggered to output sound wave. At the end, when all information are received by the SJone board, it is send out on the CAN bus in frequency of 5Hz. It is optional to use the trigger pin (RX) to trigger the sensors to send out ultrasonic waves, but we use it because instead of letting the sensors continuously outputting ultrasonic waves and allowing them to interfere with each other, it is better to let them output waves in bursts for a much cleaner signal.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:software003.png | thumb| center | 500px |Flowchart of Sensor Module]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Timing Diagram''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | [[File:software002.jpg |thumb| center | 800px | Timing Diagram]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF0000"> Technical Challenges </font>===
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Sensor Interference''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | We saw a lot of interference between the front 3 sensors. We were able to overcome the issue with both hardware and software tweaks:
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Higher placement of middle ultrasonic sensor and interference guard for the left and right sensors
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Instead of leaving the RX pin of the sensors unconnected, which causes the sensors to output ultrasonic waves continuously, we toggled the RX pin, to turn off sensor ranging and only allow wave output when we needed it. The periodic callback function was also written in a way that staggered sensor triggering and reading, to allow sufficient time to process the ADC feedback.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Power Deficiency''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | At first, when the sensors were tested individually (as well as together on early iterations of the car), they performed to specifications. However, when other subsystems were integrated into the car, the sensor feedback fluctuated wildly. After many hours of troubleshooting, we realized that our 1A power supply was not enough to supply sufficient power to all systems on the car. We addressed the problem by using a power supply with a 3.5A output.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Unstable HR-04 Readings''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | At first, we used two HC-SR04 modules, as our left and right sensors. However when we tested them during obstacle avoidance we realized that their range was too narrow to reliably detect obstacles. As a result we switched to more expensive, but reliable Maxbotix EZ line of sensors.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''ADC Supply Voltage''''' </font>=====
| |
| − | | |
| − | The middle sensor's also fluctuated wildly at times. After hours of testing we realized that our 5V power supply was distorting its feedback signal, due to the SJOne's ADC peripheral being powered by 3.3V. Applying a 3V power signal to the middle sensor corrected the issue.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== <font color="FF0000"> '''''Slow car response to obstacle due to large queue size (running average)''''' </font>===== | |
| − | During our first try at obstacle avoidance we found that the car reacts very slowly to obstacles, even though the sensor update rate is 10Hz. Later we found out that the reason is because of our queue implementation. We used to have a very large queue to calculate running average. This filters out spikes but also means when an obstacle is detected it takes very long time for the running average to be updated.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Decreasing the queue size and using the median value instead of the average value solved the issue.
| |
| − | | |
| − | === <font color="FF0000"> Bill Of Materials </font> ===
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! colspan="5" style="background:#D33;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#FFFFFF"> SENSOR CONTROLLER </span>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART NAME </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> PART MODEL </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> QUANTITY </span>
| |
| − | ! scope="col" style="text-align: center;" style="background:#C0C0C0;" |
| |
| − | <span style="color:#000000"> COST PER UNIT (USD) </span>
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''Infrared Sensor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.sparkfun.com/products/242, Infrared Proximity Sensor]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $13.95
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''Front-left-right Distance Sensor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.maxbotix.com/Ultrasonic_Sensors/MB1010.htm MB1010, LV-MaxSonar-EZ1]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 2
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $29.95
| |
| − | | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * '''Front-middle Distance Sensor'''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * [https://www.maxbotix.com/Ultrasonic_Sensors/MB1000.htm MB1000, LV-MaxSonar-EZ0]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * 1
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | * $29.95
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | <HR>
| |
| − | <BR/>
| |
| | | | |
| − | == CONCLUSION ==
| + | Issue: |
| − | This project was an introduction to the realities of putting together a team, with a common goal and then executing a strategy to bring the team's vision to life. In our case, it was developing an autonomously navigating RC car. Each team member brought unique skills, passions and personalities to the project. Some team people were skilled with designing components in SolidWorks, while others were skilled in PCB design, firmware development, project management, catching bugs, etc. Some people had the ability to lighten the mood on disappointing demo days, while others had the management skill to keep the team focused and firing on cylinders, while avoiding burning the team out. When these skillsets came together, it resulted in a product that we are all exceptionally proud of, as well as one that performed well on the final demo day. It sparked a fun and lively debate at the end of the semester as to who would keep the car.
| + | # The mp3 decoder1053b's document is a kind of confusing for the mode when 1032b have several modes |
| | + | # It's hard to know the configuration is successful or not. |
| | + | Solution: |
| | + | # Doing the survey on the GitHub is really important. For example, using the sin wave and hello binary example to test how the Initialization and HZ parameter would save a lot of time.Moreover, in the document from the vs1053b, we could use the binary file line "hello", "sine wave" function for testing. |
| | + | # Besides, we also have to be careful to check the SJBoard's SPI because of the SD card reader is using for reading SDcard. Hence, I would recommend using other |
| | + | SPI0, SPI1 instead of using SPI2. |
| | | | |
| − | It wasn't always fun and lively though. We experienced soaring highs, such as during our first progress demo, where we hit almost all of our specs. We also experienced devastating lows, such as when our encoder signal connector snapped on our second progress demo, resulting in the car not having any speed control. While we look back fondly on our project, the reality is that it was the result of 7 graduate students spending almost every day of the semester developing and fine tuning the final product. We failed as a team and then we succeeded as a team. No members were ever singled out. The goal was too important. Blame fell on the team as a whole. As one single unit. Yet, so did success and praise. When we succeeded, it was a team success. We succeeded because we were greater than the sum of our parts. We succeeded because we failed together. We succeeded because we didn't let failure break us. As Winston Churchill once said, "if you are going through hell, keep going". At times this project pushed us to our limits. It exhausted us. But we kept pushing. We grit out teeth and kept working, even on our worst days. We never stopped learning and that was what allowed our project to succeed.
| + | == <font color="000000"> Conclusion </font> == |
| | + | We successfully designed and implemented the video game "Tower Defense In Space". All of our team members now have a better understanding of how to use FreeRTOS to handle the synchronization of multiple tasks and to communicate with multiple hardware components in an embedded application system. After completing this project, we learned how to manage a project on a tight schedule. Starting from purchasing hardware components, developing hardware drivers and game logic and then integrating all of the drivers and APIs into the game logic. Furthermore, all of us are now better at coding and debugging code. |
| | + | For a game design project like this, we learned that it's not always best to assign tasks independently between the team members. We learned that this type of project would benefit moreso from pair programming and other cooperative tasks that enable collaboration between teammates. Otherwise, project tasks may be done in such a way that they only work for 1 specific configuration, and wouldn't help progress towards the end goal of the integrated system. We also learned that not every day was going to be perfect, but as long as we never gave up and worked hard, then the final result would not be disappointing! |
| | | | |
| − | There was so much to learn. Always something new, it felt like. We developed a 4-layer PCB, to integrate all of our subsystems together, even though none of us had experience developing a board that complex before. We also approached new challenges such as developing an Android Mobile Application, even though none of us knew JAVA or knew what Android Studio was beforehand. We never stopped learning. We learned the value of investing in quality components, such as robust distance sensors and a reliable GPS. We honed our unit testing skills, trying to write firmware that was as high quality as our hardware. We learned about CANbus on an intimate level and applied all of the knowledge. We simply never stopped learning. Our passion and drive even encouraged one of our friends (who wasn't even in the class) to drop what he was doing and help us debug a motor issue (thanks again Zach Smith!!!).
| |
| | | | |
| − | Working on this project was a difficult yet ultimately rewarding experience. We can't stress enough how important is to start the project as early as possible in the semester and to keep pushing until the final demo. Each of contributed roughly 20 hours a week to work on the project. As a result, we were exhausted by the end of it, but we also never had to pull an all nighter. We had excellent leadership from our team lead, Tristan, as well as our mentors, Preet and Pratap. We also had excellent peers in CMPE 243 and are proud of what they achieved as well. Overall, we were happy to be part of this class and we hope that our project will inspire future students (and non-students) to develop electric vehicles.
| + | We would like to say thank you to Prof. Preet and all the ISAs for their precious suggestions and assistance during the development of this project! |
| | | | |
| | + | == Advice for Future Students == |
| | | | |
| − | === Project Video === | + | ==== Source Control ==== |
| | + | Unless everyone in your group is comfortable using source control, don't use it. It will likely end up costing you time in the long run. |
| | | | |
| − | [https://youtu.be/zhRfc7wB4kA RUN-D.B.C project video]
| + | ==== Start working on your LED Matrix driver ASAP ==== |
| | + | The first 64x64 LED Matrix that we got from Sparkfun suffers from a serious flickering issue. After spending for a week trying to debug what causes the flickering issue, we still have no idea whether it is a hardware issue or software issue. Later, we borrow another LED matrix from a student of our class and test our code. With the other student's LED matrix (we use our own power supply and ribbon cables), there is no flickering issue at all. According to some online resources, some matrix vendors scatter the selected rows and columns differently. It is possible that your designed driver may only work on some LED matrix vendors' displays. |
| | | | |
| − | === Project Source Code === | + | == <font color="000000"> Video Demonstration </font> == |
| | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b2isxUJta6Q Demo Video (Player Wins)] |
| | | | |
| − | [https://gitlab.com/run-dbc/autonomous-car RUN-D.B.C project source code] | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fylwPk5g_3Q Demo Video (Player Loses)] |
| | | | |
| − | === Advice for Future Students === | + | == <font color="000000"> Source Code </font> == |
| − | * '''FORM YOUR TEAM AS EARLY AS POSSIBLE AND START WORKING ON THE PROJECT AS EARLY AS POSSIBLE (WEEK 1 IF POSSIBLE)'''
| + | * [https://gitlab.com/rollin_nolan/tower-defense-in-space Tower_Defense_In_Space_Gitlab] |
| − | * If you are having trouble with your GPS or compass, try testing on top of one of the SJSU parking garages on a weekend. There is much less signal interference.
| + | * [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1kggWmH2kcPciE4tFG8gYCbF9gfV2dXkk/view zip file (must have SJSU email address)] |
| − | * Order spare parts whenever possible. You will encounter defective parts and shipping wastes time and increases stress (especially nearing demo day)
| |
| − | * Make sure to get a power supply that can supply upwards of 1A. When all the car's subsystems are running, the current draw may be higher than expected | |
| − | * Don't go for cheap modules from Ebay, those will probably waste more of your time than the difference in price. Get quality modules and they will pay for themselves down the road.
| |
| − | * AGAINT DON'T ORDER THE CHEAPEST MODULE...it won't work well and you will spend so many fruitless hours trying to get it to work reliably (especially when integrated into the car) | |
| − | * Spring break is the best time to catch up to all the tasks. If that time is not utilized for this project, then most likely your group will be behind when the demo day comes.
| |
| − | * Getting access to a 3D printer can be very useful for this project, with which you can customize sensor, compass, and encoder mounts to your specification.
| |
| − | * Take advantage of the code reviews that Preet offers! They will fix a lot of bugs in your code and will make it a lot easier to manage each module.
| |
This project involves creating and developing a video game where output is displayed on a LED matrix. Development of the relevant hardware/software components and modules was divided among 4 team members. Each team member lead or significantly contributed to the development of multiple components. The project was focused on not only technical skills, but team building as well, and working with others towards a common goal.
This project provides us hands-on experience using freeRTOS in a real application. Our objective is to apply what we have learned in class and develop a video game using our SJtwo Board. In this project, we create different tasks for different modules, such as a display task for displaying the game objects on LED matrix, a tower task for detecting nearby enemies and shoot them, a stage task to manage each game stage etc. We need to use both cooperative scheduling and preemptive scheduling technique to make this video game run efficiently. In order to make this game run in a particular sequence, we also need to synchronize and sequentialize each task by setting the task priorities carefully and using binary semaphore correctly.
Like most traditional tower defense games, the player needs to defend our planet from the invasion of aliens. The gameplay can be split into 2 phases, Combat Phase and Intermission Phase. During the intermission phase, the player can place different kinds of towers strategically that will attack the invading aliens from entering into our homeland by shooting the enemies. During the combat phase, spaceships follow the path and try to land on our planet. If any enemy spaceship reaches the end of the path, then the player loses. If there are no more spaceships remaining in a wave, the player can build a stronger tower that has a longer attack range and can shoot a more powerful laser to the spaceships in the next wave. The player wins the game after surviving 5 waves of attack.
The gamepad controller consists of a joystick and two buttons.
The breakout board design requirement was to interface all external hardware components with the embedded system (SJTWO). The hardware connections are:
The gamepad board design requirement was to provide a more packaged interface for the user to interact with the game.
Only a few mechanical components were needed for this project. Namely simple brackets for mounting electrical hardware to the RGB matrix and displaying the matrix itself. All CAD designs were done using Onshape, a free CAD tool that can be used entirely through your web browser.
For displaying the RGB matrix, two brackets were 3D printed to prop it up. Their STL files can be found under our source repository.
The LED matrix that we use is 64 pixels by 64 pixels and is controlled through a 12-pin header consisting of the following pins:
All these pins are required to display a specific color on a specific pixel of the LED matrix display.
Apparently, it is impossible to driver all 4096 LEDs all at one time and thus, we can only drive two rows of LEDs at a time (one row on the upper half of the display and another row on the lower half of the display). By refreshing the LED matrix two rows at a time in a fast frequency, we can display all the game objects with animation on the LED matrix.
The joystick that we use is the product from Adafruit, the Analog 2-axis Thumb Joystick. This 2-axis Thumb Joystick provides the following pins:
The MP3 decoder that we use is Sparkfun’s vs1053 shield MP3 decoder which is the board based on the vs1053b chip.
In order to communicate with the mp3 decoder with SJtwo Board, we choose the SPI as the protocol to control the decoder. Hence, we need the one pin SCK0
(clock), one pin MOSI(Master In Slave Out) and one pin (Master Out Slave In).
There are four major GPIO pin for DREQ(Data Request Pin), Reset, CS(Chip Select), XDCS(Data Chip Select), this 4 GPIO pin is how we transfer data and send
the command to activate the mp3 decoder work with SJ2 Board.
All the LED Matrix data are stored in a buffer with its size equal to 32 by 64. Each element in this buffer store the color of two pixels, one pixel from the upper half of the display and one pixel from the lower half of the display.
In order to display the gaming objects in animation, we need to refresh the display by displaying the color pixels on each row one by one very fast. Below is a simple flowchart that describes the process of refreshing the display.
The MP3 deocder is executed with the mainly two task: read task and play task.
The reader task would read data from the sd card and sned queue data for the player task to play music.
Receive the data of the song from the queue, and use the receiving data and sent the command to make decoder to play music.
The JOY_STICKER is using the task to pool the ADC channel data to get the direction from the Joysticker.
Issue: While we are developing the game, we notice that some color pixels are turned on when they are supposed to be off.
SPI0, SPI1 instead of using SPI2.
We successfully designed and implemented the video game "Tower Defense In Space". All of our team members now have a better understanding of how to use FreeRTOS to handle the synchronization of multiple tasks and to communicate with multiple hardware components in an embedded application system. After completing this project, we learned how to manage a project on a tight schedule. Starting from purchasing hardware components, developing hardware drivers and game logic and then integrating all of the drivers and APIs into the game logic. Furthermore, all of us are now better at coding and debugging code.
For a game design project like this, we learned that it's not always best to assign tasks independently between the team members. We learned that this type of project would benefit moreso from pair programming and other cooperative tasks that enable collaboration between teammates. Otherwise, project tasks may be done in such a way that they only work for 1 specific configuration, and wouldn't help progress towards the end goal of the integrated system. We also learned that not every day was going to be perfect, but as long as we never gave up and worked hard, then the final result would not be disappointing!
Unless everyone in your group is comfortable using source control, don't use it. It will likely end up costing you time in the long run.
The first 64x64 LED Matrix that we got from Sparkfun suffers from a serious flickering issue. After spending for a week trying to debug what causes the flickering issue, we still have no idea whether it is a hardware issue or software issue. Later, we borrow another LED matrix from a student of our class and test our code. With the other student's LED matrix (we use our own power supply and ribbon cables), there is no flickering issue at all. According to some online resources, some matrix vendors scatter the selected rows and columns differently. It is possible that your designed driver may only work on some LED matrix vendors' displays.