F18: Hit the Balloon
Contents
Hit the Balloon
Abstract
The objective of our project is to implement a game called "Hit the Balloon." Hit the Balloon is a game that has balloons that randomly spawns from the bottom of the screen to the top. There is a bow and arrow that moves vertically on the left side of the display. The player is able to control the vertical movement of the bow and shoot arrows at the balloons that are moving upward. When the arrow hits the balloons, the balloon object will be a hit. The objective of the game is to hit the maximum number of balloons with a limited number of arrows and time. At the end of the game, it will display the score, number of balloons the player hits. A screenshot of the "Hit the ballon" game that will be emulated is shown in Figure X.
Objectives & Introduction
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Aaron Lee
- Arrow object(display, shoot, movement), testing, packaging, and report
- Rahul Kadam
- PCB, start/end screen, scoreboard, acceleration sensor, and testing
- Vijay Vanapalli
- Balloons, hit detection, and testing
Schedule
| Week# | Date | Task | Actual |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10/29 |
|
|
| 2 | 11/5 |
|
|
| 3 | 11/12 |
|
|
| 4 | 11/19 |
|
|
| 5 | 11/26 |
|
|
| 6 | 12/3 |
|
|
| 7 | 12/10 |
|
Parts List & Cost
| Item# | Part Description | Manufacturer | Qty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SJOne LPC1758 Microcontroller | Preet | 3 | $240.00 |
| 2 | Adafruit 16x32 RGB LED Matrix | Adafruit [1] | 3 | $75.00 |
| 3 | 5V/2A Power Supply Adapter | Amazon [2] | 2 | $11.99 |
| 4 | DC Power Connectors Socket 5.5mm x 2.1mm - Female | Amazon [3] | 10 | $6.99 |
PCB Build of Materials
| Item# | Part Description | Manufacturer | Qty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | $ | |||
| Amazon [4] | $11.99 | |||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | PCB Fabrication | [] | 10 | $ |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
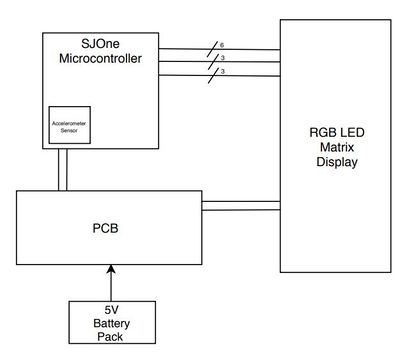
This project consists of using the SJOne microcontroller, 16x32 RGB LED display, and our custom PCB, used to power the microcontroller and the LED display. The system design of this project is shown below in Figure X.
The first step after receiving all of the hardware was understanding how the RGB LED Matrix worked by reviewing AdaFruit's documentation [5], SparkFun's documentation [6], and watched a few youtube tutorials [7] to get the RGB LED Matrix and the SJOne microcontroller properly connected.
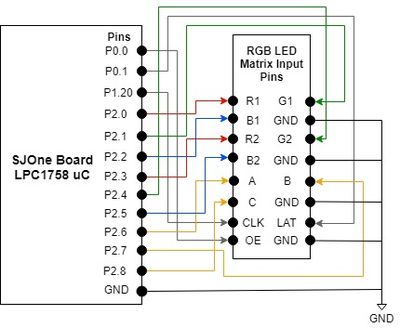
The connections for the RGB LED Matrix consist of six data pins (R1, G1, B1, R2, G2, B2), three control pins (CLK, Output Enable, Latch), three row-select pins (A, B, C), and four GND pins. The 5V/2A power supply connects to the backside of the LED matrix board. The ribbon cable that came with the Adafruit LED matrix was attached to the 'INPUT' connection on the backside of the LED matrix and the following connections were made to the SJOne microcontroller's GPIO pins using male-to-female wires. Please note that the ground connections from the SJOne board was connected to the ground of the LED Matrix and the power supply as shown in Figure X. The SJOne microcontroller is also supplied power through USB or an external source.
If these connections are properly connected, the LED matrix should be on with the LEDs of random rows flashing. To test the LED Display, the AdaFruit Arduino library was used as a reference to port over the displaying of a design.
Hardware Interface
To begin this project, understanding the various pins on the input of the 16x32 RGB LED Matrix display is important in knowing how the display gets updated. The 16 and 32 indicate that the display has a total of 16 and 32 rows and columns, respectively. As mentioned above, there are 3 pins for row selection (A, B, C), 6 data pins (R1, G1, B1, R2, G2, B2), and 3 control pins (LAT, OE, and CLK).
The 16x32 display is divided into two sections as shown in Figure X, which is why the microcontroller needs to drive the top and bottom section of the display at the same time.
To update the display, the output enable pin must be cleared. Then, on the rising edge of the clock, you can update a 32-bit shift register that is used to store data. Each corresponding bit [0:31] corresponds to the column on the display. Depending on if the bit is set in this register, will determine if you want that column of the LED to light up. When this register is updated, then you can toggle the clock bit.
After connecting the display with the SJOne board, you should see bright LEDs lighting up different rows as shown in Figure X. After seeing this display, when you press on the wire to the input of the LED matrix, you will notice the LEDs on different rows will begin to flicker.
Now that the board is powered up, we utilized Adafruit's display library ported the Arduino code to the SJOne LPC17XX microcontroller.
The first objective was to display a static screen, such as the start screen, on the display to learn how to manipulate the LEDs on the 16x32 matrix. A 16x32 two-dimensional array was created to indicate the color of a particular LED located on the matrix display.
Following are the list of colors that are attainable by the LED
Software Design
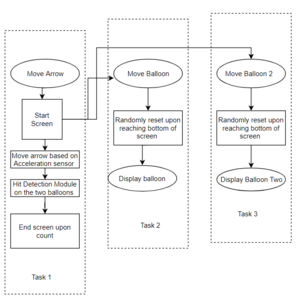
The following diagram elaborates on the flow chart that each task follows. The project is designed primarily on tasks handling different modules of the project viz, Balloon movements, level selector, hit detection and so on. The main two types of objects are arrows and balloons although by default they are of the same object type and simply have different parameter declarations. The input for the system includes the movements picked up by the onboard acceleration sensor and the button press from the player.Scores are kept throughout the session of the game and are updated accordingly.
RGB LED Matrix
The API detailed in the following flowchart, is a function that is committed towards generating the center of the object and holding its respective dimensions. Another function called display Object is tasked with drawing the object on the LED matrix.
Below is a snippet of printing out the shape of the balloon, keeping its dimensions in mind. Essentially the display is updated with the object after iterating through each pixel in the matrix, with the exception of the specified boundaries of the object in question
The challenging part of the moving object design was to ensure how the object was to be shown drifting downward or upward in a smooth way. By design the LED Matrix sets color in sets of 8 rows as can be deciphered from the attached code snippet. More of the problem and how it was tackled is elaborated in the Testing.
At an overview, we make use of semaphores and FreeRTOS to manage and switch between tasks.Implementation
All the functions used are enlisted in the following class. Moreover, these are to be considered with the tasks in main that are dedicated towards the different background screens of the game itself from Start to the Final Score screen.
The game consists of a single player navigating through different levels (currently implemented two levels with varying number of balloons).
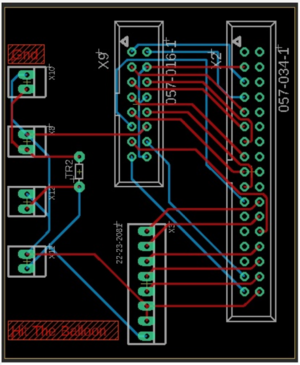
PCB Design
The Printed Circuit Board design was done using Eagle PCB editor which was a free open-source software for students. The software design tool enables designers to seamlessly connect schematic diagrams, component placement, PCB routing, comprehensive library content. Following components are added while designing the PCB -
- 34 pin female header to connect the SJONE board.
- 16 pin male header for the 16x32 RGB matrix.
- 8 pin male header to connect the external switch to the SJONE board & extra ground and vcc pin
- 2 pin power connector
- 100 ohm resistor
PCB design Issue
It is difficult to design a PCB without having components in hand because we are not able to set the exact drill size and component spacing. It was difficult to tune in our components because we were using EAGLE PCB autorouter to create traces and if the component orientation,placement and organisation is not proper the autorouter will not create 100% trace for you and then we have to manually create traces, in best case scenarios the autorouter can create vias between two connections.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
1. Implementing two arrow objects caused flickering between the two objects
- Solution: Rather than having two objects in one task, the objects were separated into their own task. As a result, we have one task displaying the arrow object that is fixed on the left side and another task that displays the arrow that is shot across the screen.
2. Balloon object that is created and moving down the display is displaying a very faint color.
- Solution:
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.