S16: Expendables
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Project Title
Abstract
This section should be a couple lines to describe what your project does.
Objectives & Introduction
Show list of your objectives. This section includes the high level details of your project. You can write about the various sensors or peripherals you used to get your project completed.
Team Members & Responsibilities
Schedule
| Sl. No | Start Date | End Date | Task | Status | Actual Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3/07/2016 | 3/13/2016 | Components buying | Completed | 3/18/2016 |
| 2 | 3/14/2016 | 3/20/2016 | LED panels study | Completed | 3/20/2016 |
| 3 | 3/28/2016 | 4/03/2016 | Raspberry Pi 3 study | Completed | 4/03/2016 |
| 4 | 4/04/2016 | 4/10/2016 | Pixel Driver Design | Completed | 4/20/2016 |
| 5 | 4/11/2016 | 4/17/2016 | PCB Design | Completed | 3/30/2016 |
| 6 | 4/18/2016 | 4/24/2016 | Testing Text Display | Completed | 4/20/2016 |
| 7 | 4/25/2016 | 5/01/2016 | UI Webserver | Ongoing | |
| 8 | 5/02/2016 | 5/08/2016 | Final Testing and Debugging | Ongoing |
Parts List & Cost
| Sl. No | Part Name | Source of purchase | Quantity | Cost($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raspberry Pi 3 | https://www.adafruit.com/products/3055 | 1 | 44.49 |
| 2 | LED panels | Preet | 4 | 0 |
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 8 |
Design & Implementation
Hardware Design
LED Panels
The display panels use multiplexing to draw picture information, which means that the rows and columns are updated fast than the human eye can process. If the updating speed is fast enough, eyes will see a complete picture without flickering. The updating process is as follows
- Select the row to be updated.
- Output the desired column data on selected row.
Row Selection
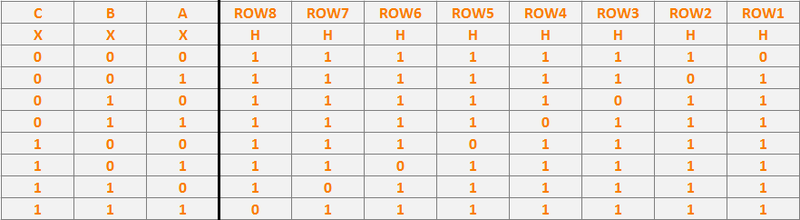
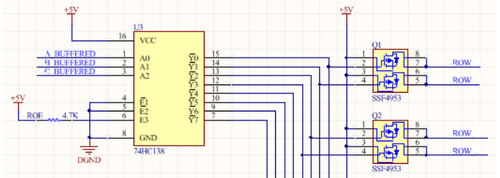
Row selection is done by using a 3-to-8 address decoder (74HC138D). There are three address inputs to the display marked A, B and C. Based on the truth table, only one input is active (low) at a time.
Since the panels has 16 rows, the 3-to-8 address decoder select rows in parallel. For example, when the 1st row (Row1) is selected, it also selects the 9th row (Row9). Using this technique implies that we must supply data for the columns for two unique rows at a time.
The outputs of the decoder is connected to a P-Channel MOSFET, because the decoder itself can only handle low currents and cannot drive a row of LEDs directly. The P-Channel MOSFET provides the high current needed to drive a row of LEDs.
The decoder outputs are shared between every 8 outputs (1 and 9, 2 and 10, repeating that pattern until row 8 and 16).
Column Selection
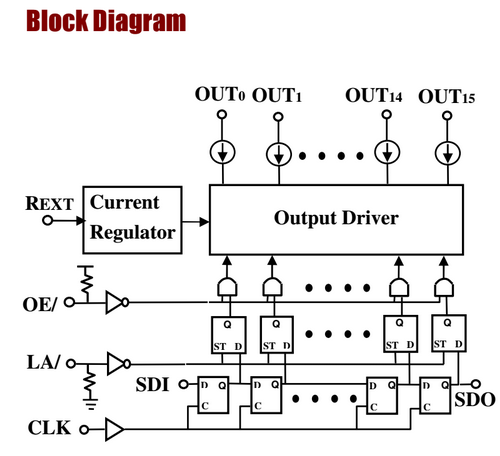
The column data is stored in a 16-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register. Since the display is 32 pixels wide, two shift registers must be chained together. The shift register is designed to work with LEDs and implements a constant-current system that ensures the LED brightness remains uniform. The panels that we are using utilize SCT2026 shift registers. These are 16-bit Serial-In/Parallel-Out registers.
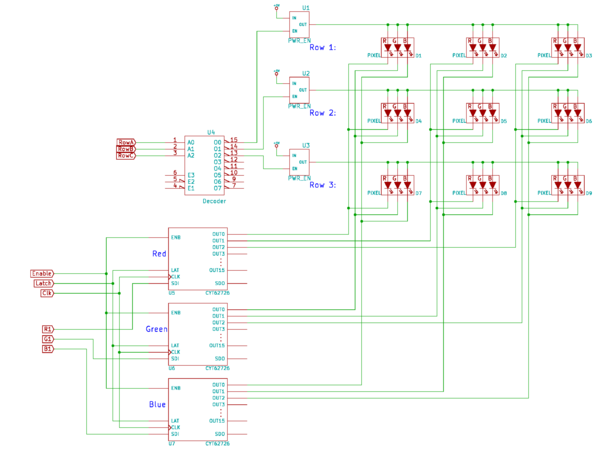
There are 12 of these shift registers on the display. 3 each are used to hold the Red, Green, and Blue data for 1 of 4 quadrants of the display. (3 colors * 4 quadrants = 12 chips)
For drawing 16 rows using the 8 outputs of the decoder, we must have unique data for each row pair. When Row 1 and Row 9 are selected, we must provide each row with unique data. This forces us to use two different shift registers for each row pair, an upper register and a lower register. Because of this, the display is divided into an upper half and a lower half. The data is shifted into the top half via the R1, G1 and B1 signals on the connector. The bottom half’s data is supplied by the R2, G2 and B2 signals on the connector. Then, since our display is 32 pixels wide, we must use 2 shift registers to hold all 32 bits of pixel data for a single row. This creates the left and right halves of the display.
Each quadrant of the display is controlled by 3 shift registers, one for each color. First, Row 1 and Row 9 are selected. 32 bits of data are shifted into each color’s shift register (R1, G1, B1), and then latched. At the same time, 32 bits of data are also shifted into each color’s shift register for the bottom half (R2, G2, B2), and then latched. The process repeats 7 more times, each time incrementing which rows are selected, until every line has been updated.
Hardware Interface
The connector on the RGB panels is called a Hub75 interface. Each panel typically has two ports, one is the input and the other is the output to chain additional panels.
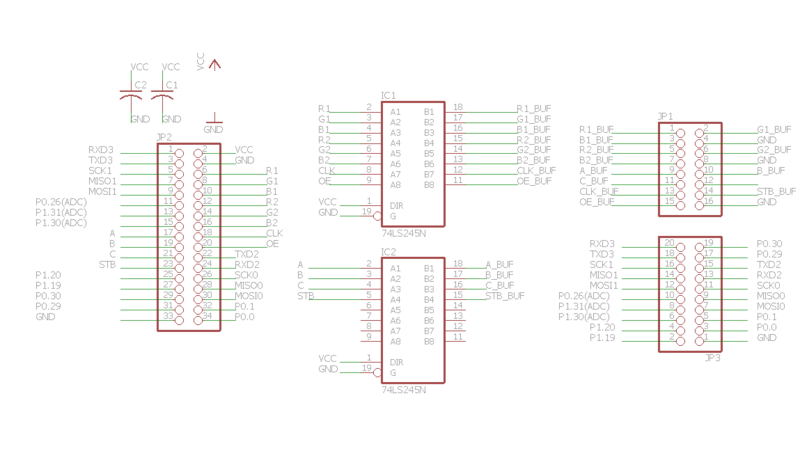
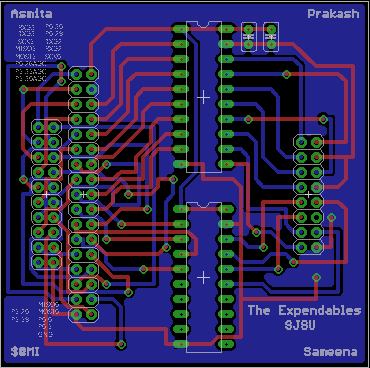
PCB Design
The LED panels use 74HC245 line drivers, these transceivers require 5v logic levels whereas the SJONE board only supports 3.3v logic. In order to drive the LED panels from 3.3v GPIO pins of the SJONE board, level-shifting IC is used to level shift signals from 3.3V to 5V and shield the SJONE board GPIOs from overloading. For this purpose, and to make it easier to connect the panels to the SJONE board a PCB was designed in EAGLE. The PCB attaches to GPIO pins of SJONE board and provides easily accessible, level-shifted output for the LED panels. The PCB also breaks-out free pins so that they can be used for other purposes.
Software Design
Classes
The software for driving the LED panels is divided into two classes, GFX and RGB. The GFX class implements all the methods for drawing various characters on the LED panels, setting their heights, and colors. It does not concerns with how the LED panel works, and just assumes the LED panels to be a canvas to draw on. The GFX class has virtual functions, which deals with how to actually display something on he panels. These virtual functions are implemented in the RGB class, which inherits from GFX class.
Tasks
Further there are three tasks to get the LED panel running, and displaying the required task. The first task is setuppanel, which has a low priority. This task only runs once, and sets all the parameters like text size, wrap, etc. The second task called panel runs continuously, and has high priority because it is responsible for displaying the text and refreshing the LED panels. The third task is simply called gpioTask, it is a medium priority task, and is reponsible for receiving the text to display over UART from raspberry PI.
Webpage
A webpage was designed hosted on Amazon AWS. The raspberry pi connects to the service provided by the webpage, any text entered on the website is transmitted to raspberry pi, which sends the received text over UART to the SJONE board to be displayed on the LED panels.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
The code tries to use a technique called Binary Code Modulation to control the colors of the display. Driving with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) would turn the LED on for an amount of time proportional to the desired brightness, then turn it off for the rest of the period. BCM divides the period into binary-length segments (1x, 2x, 4x, etc), and turns the LED on or off for each of these segments according to the bits of the LED’s desired brightness. The pixel data must be divided up into bitplanes. These bitplanes are nothing but an array in which each element is a single bit from a color value in the displayed image. Each pixel would require three separate bitplanes, one for each color element. However to drive the display, all three colors are written out for two different pixels at the same time. The code stores six bits, one from each bitplane, together in a byte. This way the bytes are immediately ready to be written to the GPIO port during the interrupt. The code refers to the arrays of ready-to-write bytes as “planes,”. In each interrupt (RGB::updateDisplay) a byte from the appropriate plane is written out to the GPIO port and the delay until the next interrupt is set.
void refreshISR(void)
{
activePanel->updateDisplay();
}
Messaging Protocol
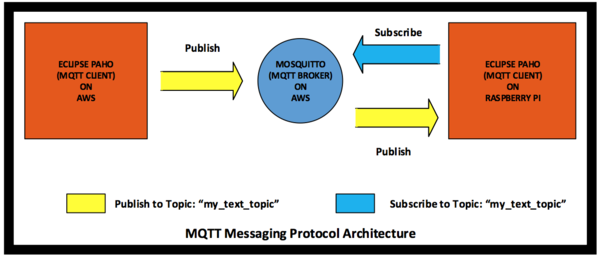
MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is the messaging protocol used for sending text from our webapp to the LED panels. MQTT is a light weight messaging protocol that uses publisher and subscriber architecture. Publishers are the devices that send data and subscribers are the ones that receive data. Devices that need to receive data must have MQTT client program such as Eclipse Paho running on them. Furthermore, the client program running on these devices need to subscribe to topics from which they want to receive data. The devices that need to send data also must have Paho MQTT client running on them. To send data, devices need to publish data to certain topics. There is another program that sits in between the sending and the receiving devices which is called an MQTT broker. The job of an MQTT broker is to receive data from senders and then send the data to receivers with appropriate topics.
The figure below shows our MQTT messaging protocol architecture. The architecture shows an eclipse Paho client program, running on AWS (Amazon Web Service), is publishing text on a topic called "my_text_topic". It also shows the Paho client program running on raspberry pi subscribing to the topic "my_text_topic". The MQTT broker known as Mosquitto running on AWS receives text from the publisher publishing on topic "my_text_topic" and sends the data to the receiver that has already subscribed to topic "my_text_topic".
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
My Issue #1
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.