S19: Zeus
Contents
- 1 Project Title
- 2 Abstract
- 3 Objectives & Introduction
- 4 Team Members & Responsibilities
- 5 Schedule
- 6 Parts List & Cost
- 7 Design & Implementation
- 8 CAN BUS Design
- 9 DBC File
- 10 Motor & I/O Controller
- 11 Geographical Controller
- 12 Sensors Controller
- 13 Android Application and Bridge
- 14 Master Controller
- 15 Testing & Technical Challenges
- 16 Conclusion
- 17 References
Project Title
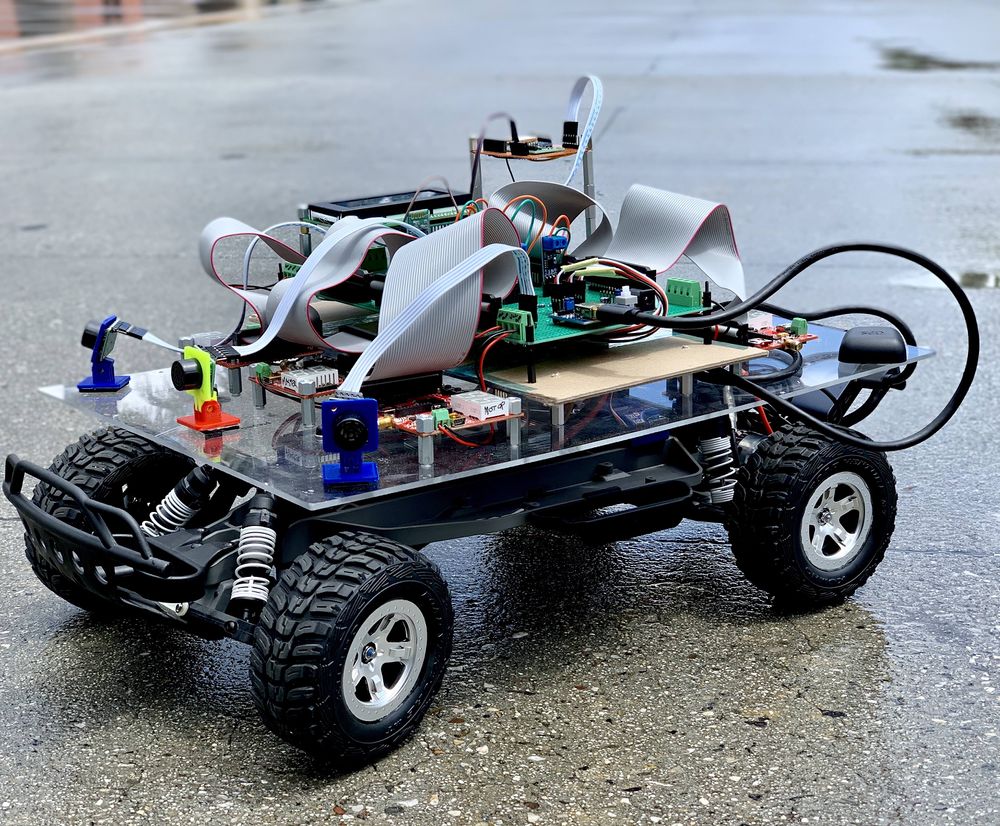
Zeus : The Autonomous Car
Abstract
When over a century ago Karl Benz invented the first car, it came as a miracle to people. Now, Almost every household owns a car. The industry has come from a 20 Horse power producing 2.9 liter Ford Model T (1908) to a massive 1500 Horsepower 5 liter Koenigsegg Regera (2018). And as such, further developments into the driving industry are bound to come. One such major field is the realm of Driverless smart cars. This project focuses on developing a driverless smart car(model) that is capable of going from one place to the destination without any manual input, avoiding obstacles along the way.
Objectives & Introduction
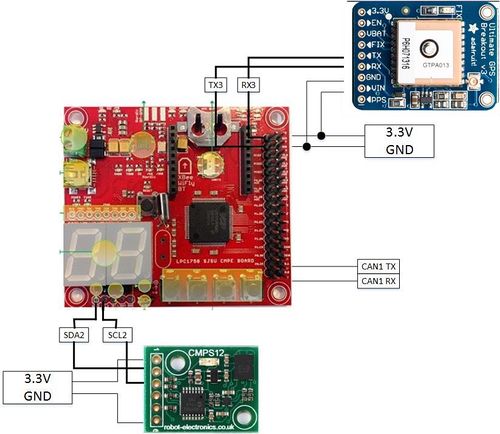
Zeus revolves around 5 SJone boards that have LPC 1758 at the center and has many peripherals ranging from motor, GPS and Bluetooth modules connected to them. Each SjOne board has the responsibility to control a specific peripheral. These 5 SJOne boards form the 5 modules of this project viz. Master module, Motor module, BLE module, GPS module, and the sensor module. These individual modules combine together to achieve the objective of this project. Following are the objectives of this project.:
- Zeus should successfully navigate from a fixed starting point to a fixed destination based on GPS.
- Obstacles on the way should be avoided.
- Code should be 100% Unit-Tested
- Communication should be established between Zeus and a mobile phone through an APP.
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Neel Patel
- Team Lead
- Master Module
- Android App
- BLE Module
- Aman Chandan
- Material/ Components Manager
- GEO module
- Artik Shetty
- Wiki Report Manager
- Motor Module
- PCB Design
- Himanshu Gunjal
- Master Module
- Karan Daryani
- Car Layout Designer
- Motor Module
- PCB Design
- Namdev Prabhugaonkar
- GEO module
- PCB Design
- Oliver Zhu
- GIT repository Manager
- Sensor Module
- Wen Yuen Chao
- Sensor Module
- Unit Testing
Schedule
| Week# | Date | Task | Activities | Status | Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 02/12/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 | 02/19/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 | 02/26/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 | 03/05/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 | 03/12/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 | 03/19/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 | 03/26/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 | 04/02/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 9 | 04/09/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 | 04/16/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 11 | 04/23/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 12 | 04/30/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 13 | 05/07/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 | 05/14/19 |
|
|
|
|
| 15 | 05/22/19 |
|
|
|
|
Parts List & Cost
| Item# | Part Description | Vendor | Qty | Cost $ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RC Car | Sheldon's Hobby Store | 1 | 180.00 |
| 2 | SJOne board | Preet | 5 | 400.00 |
| 3 | GPS Module | Amazon | 1 | 62.99 |
| 4 | Lipo Battery (7200 mAh) | Amazon | 1 | 37.99 |
| 5 | DB9 Connector | Amazon | 1 | 6.50 |
| 6 | LIPO Battery Charger | Sheldon's Hobby Store | 1 | 39.99 |
| 7 | Ultrasonic sensor | Robotshop | 4 | 99.80 |
| 8 | PCB | Fry's Electronics | 1 | 12 |
| 9 | CAN Transceiver | Amazon | 5 | 49.95 |
| 10 | LCD Display | Obtained From Preet | 1 | Free |
| 11 | Xbee | Obtained From Preet | 1 | Free |
| 12 | Adapter for Lipo Charger | Amazon | 1 | 15.84 |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
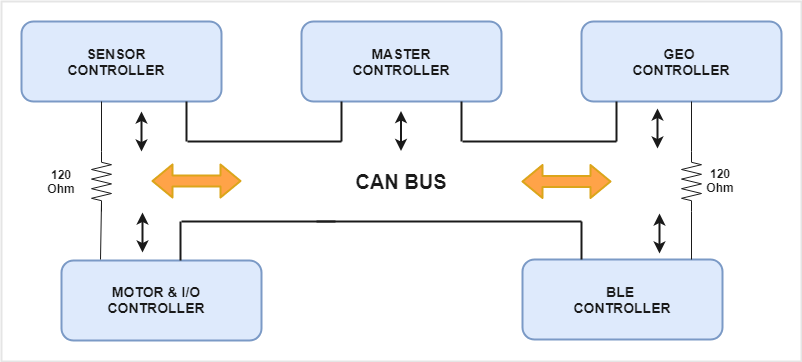
CAN BUS Design
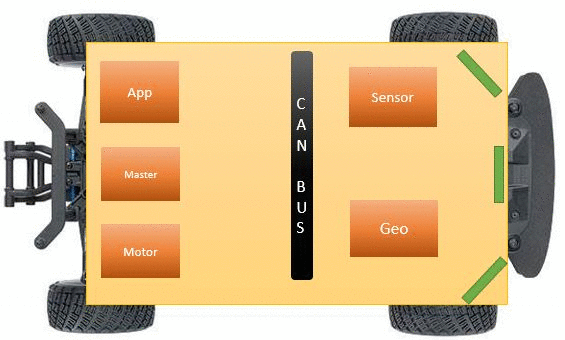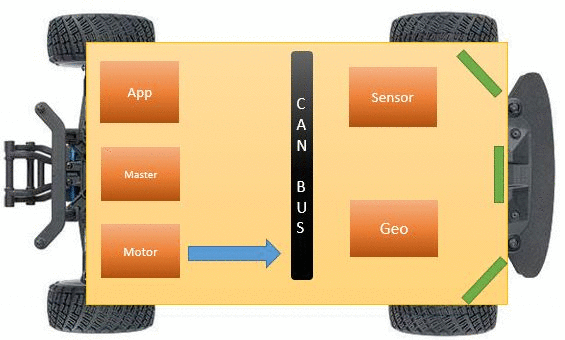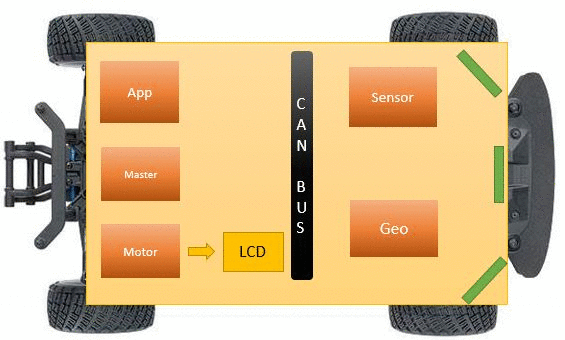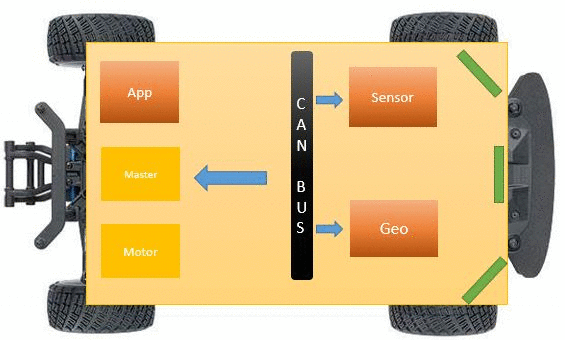
CAN Communication is used to communicate between all the boards and it requires the bus to be terminated using two 120 Ohm resistors. CAN is a very deterministic broadcast bus. Based on the .dbc file, each module will transmit only selected messages. Receiving of the messages is enabled by filtering. The module can be configured to receive all messages or receive selected messages. GIven below are features of CAN bus:
- Stadard baud rate of 100K, 125K, 250K, 500k or 1M
- Differential Pair - Half duplex
Working of CAN bus
A CAN frame has the following data:
- 4 bits for Data Length Code
- Remote Transmission Request
- ID extend bit
- Message ID (11 bit or 29 bit)
For CAN we require a transciever(unlike) other BUSes. This transciever converts the Rx and Tx lines to a single differential pair. where Logic 1( recessive) is represented by a ZERO volt difference and Logic 0(dominant) is represented by 2V difference.
Arbitration happens in can bus to make sure no two nodes are transmitting at the same time. A lower Message ID has Higher priority on the CAN bus, since 0 is the dominant bit.
To make sure that a node does not put a lot of consecutive 1s or 0s together Bit Stuffing is done, where the CAN HW stuffs extra bits to improve CAN BUS integrity. Our project's overall design is described below.
CAN Communication Table
The table indicates the messages based on the transmitter.
| Sr. No | Message ID | Message function | Receivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Master Controller Commands | |||
| 1 | 101 | Master System Command for motor direction (forward/reverse), speed (m/sec) and steer for the motor. | Motor |
| 2 | 900 | Debug message for sensor values | DBG |
| 3 | 905 | Debug for obstacle flags | DBG |
| Sensor Controller Commands | |||
| 4 | 121 | Obstacle Data for the front, left and right sensor | Master |
| BLE Controller Commands | |||
| 5 | 181 | Start & stop command for master | Master |
| 6 | 182 | Destination latitude and longitude from App | GPS |
| Geo Controller Commands | |||
| 7 | 141 | Direction values from the GPS for master. | Master |
| 8 | 191 | Heading value | Motor |
| 9 | 901 | Debug current latitude and longitude | DBG |
| 10 | 902 | Start Debug compass | DBG |
| 11 | 904 | Debug for the difference in distance and heading | DBG |
| 12 | 899 | Bearing Debug | DBG |
| 13 | 898 | Debug checkpoint | DBG |
| 14 | 897 | Next Co-ordinate | DBG |
| 15 | 896 | Number of checkpoints | Motor |
| Motor Controller Commands | |||
| 16 | 903 | Debug motor to show current and required speed | DBG |
DBC File
DBC file is designed based on the designed CAN messages and signals. Preet's python script is used to auto-generate CAN communication-related structures and functions. Each module will generate its specific generated_can.h by changing the module name in 'pre_build.sh' file. The following is the example of auto-generated code for the master module.
python ../_can_dbc/dbc_parse.py -i ../../snf.dbc -s MASTER > ../_can_dbc/generated_can.h
The DBC file for the project is as shown below:
VERSION ""
NS_ :
BA_
BA_DEF_
BA_DEF_DEF_
BA_DEF_DEF_REL_
BA_DEF_REL_
BA_DEF_SGTYPE_
BA_REL_
BA_SGTYPE_
BO_TX_BU_
BU_BO_REL_
BU_EV_REL_
BU_SG_REL_
CAT_
CAT_DEF_
CM_
ENVVAR_DATA_
EV_DATA_
FILTER
NS_DESC_
SGTYPE_
SGTYPE_VAL_
SG_MUL_VAL_
SIGTYPE_VALTYPE_
SIG_GROUP_
SIG_TYPE_REF_
SIG_VALTYPE_
VAL_
VAL_TABLE_
BS_:
BU_: DBG BLE GPS MOTOR SENSOR MASTER
BO_ 90 MASTER_HEARTBEAT: 1 MASTER
SG_ MASTER_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR, SENSOR, GPS
BO_ 91 MOTOR_HEARTBEAT: 1 MOTOR
SG_ MOTOR_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
BO_ 92 SENSOR_HEARTBEAT: 1 SENSOR
SG_ SENSOR_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
BO_ 93 GPS_HEARTBEAT: 1 GPS
SG_ GPS_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER, BLE
BO_ 94 BLE_HEARTBEAT: 1 BLE
SG_ BLE_HEARTBEAT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER, GPS
BO_ 101 MOTOR_COMMAND: 2 MASTER
SG_ STEER_cmd : 0|8@1- (1,0) [-2|2] "" MOTOR
SG_ SPEED_cmd : 8|8@1- (0.1,0) [-1|3] "" MOTOR
BO_ 121 SENSOR_SONARS: 8 SENSOR
SG_ SENSOR_SONARS_LEFT : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
SG_ SENSOR_SONARS_MIDDLE : 8|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
SG_ SENSOR_SONARS_RIGHT : 16|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
SG_ SENSOR_SONARS_BACK : 24|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
BO_ 141 DIRECTION_GPS: 2 GPS
SG_ DIRECTION_VAL : 0|8@1- (1,0) [-2|2] "" MASTER
SG_ DESTINATION_REACHED : 8|1@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER
BO_ 161 SPEED_MOTOR: 2 MOTOR
SG_ MOTOR_SPEED : 0|12@1+ (0.001,0) [0|0] "mph" MASTER
BO_ 181 APP_DATA: 8 BLE
SG_ START_CAR : 0|2@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" MASTER, DBG
BO_ 182 APP_DATA_LAT_LONG: 8 BLE
SG_ DEST_LAT : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [36.000000|38.000000] "" MASTER,GPS
SG_ DEST_LONG : 32|32@1+ (0.000001,-123) [-123.000000|-120.000000] "" MASTER,GPS
BO_ 191 HEADING: 4 GPS
SG_ HEADING_VAL : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [0|0] "" MOTOR, DBG
BO_ 900 DEBUG_MASTER: 8 MASTER
SG_ MASTER_LEFT_cmd : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
SG_ MASTER_MIDDLE_cmd : 8|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
SG_ MASTER_RIGHT_cmd : 16|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
SG_ MASTER_BACK_cmd : 24|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
BO_ 901 DEBUG_GPS: 8 GPS
SG_ CURR_LAT : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [36.000000|38.000000] "" DBG
SG_ CURR_LONG : 32|32@1+ (0.000001,-123) [-123.000000|-120.000000] "" DBG
BO_ 902 DEBUG_COMPASS: 2 GPS
SG_ HEADING : 0|16@1+ (1,0) [0|360] "degrees" DBG
BO_ 903 DEBUG_MOTOR: 3 MOTOR
SG_ CURR_SPEED : 0|8@1+ (0.01,0) [0|0] "m/s" DBG
SG_ REQD_SPEED : 8|8@1+ (0.01,0) [0|0] "m/s" DBG
SG_ RPM_VALUE : 16|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
BO_ 904 DEBUG_NAVIGATION: 8 GPS
SG_ DIST_DIFF : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [0|0] "m" DBG
SG_ HEAD_DIFF : 32|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [0|0] "Degrees" DBG
BO_ 899 DEBUG_BEARING: 4 GPS
SG_ BEARING : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [0|0] "degrees" DBG,MOTOR
BO_ 898 DEBUG_CHECKPOINT: 1 GPS
SG_ INDEX : 0|8@1+ (1,0) [0|0] "" DBG
BO_ 897 NXT_COORD: 8 GPS
SG_ LAT : 0|32@1+ (0.000001,0) [36.000000|38.000000] "" DBG
SG_ LONG : 32|32@1+ (0.000001,-123) [-123.000000|-120.000000] "" DBG
CM_ BU_ DRIVER "The driver controller driving the car";
CM_ BU_ MOTOR "The motor controller of the car";
CM_ BU_ SENSOR "The sensor controller of the car";
CM_ BU_ BLE "The bluetooth controller of car";
CM_ BU_ GPS "The GPS controller of the car";
CM_ BO_ 100 "Sync message used to synchronize the controllers";
BA_DEF_ "BusType" STRING ;
BA_DEF_ BO_ "GenMsgCycleTime" INT 0 0;
BA_DEF_ SG_ "FieldType" STRING ;
BA_DEF_DEF_ "BusType" "CAN";
BA_DEF_DEF_ "FieldType" "";
BA_DEF_DEF_ "GenMsgCycleTime" 0;
BA_ "GenMsgCycleTime" BO_ 500 100;
BA_ "GenMsgCycleTime" BO_ 100 1000;
BA_ "GenMsgCycleTime" BO_ 101 100;
BA_ "GenMsgCycleTime" BO_ 400 100;
BA_ "GenMsgCycleTime" BO_ 200 100;
BA_ "FieldType" SG_ 500 DBC_TEST1_enum "DBC_TEST1_enum";
BA_ "FieldType" SG_ 100 DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd "DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd";
VAL_ 500 DBC_TEST1_enum 2 "DBC_TEST1_enum_val_two" 1 "DBC_TEST1_enum_val_one" ;
VAL_ 100 DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd 2 "DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd_REBOOT" 1 "DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd_SYNC" 0 "DRIVER_HEARTBEAT_cmd_NOOP" ;
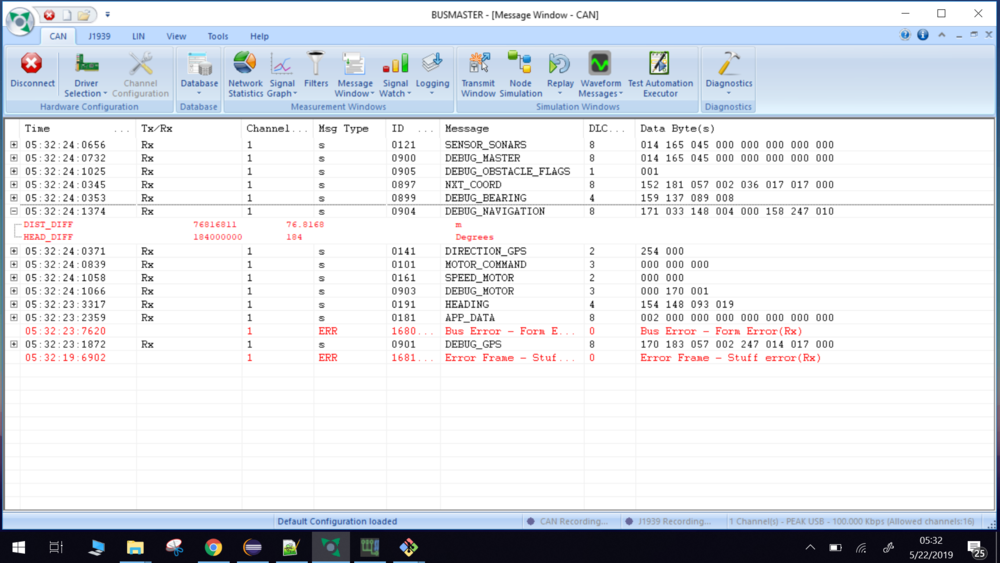
Can Bus analyzer
The PCAN-USB adapter enables simple connection to CAN networks. Bus Master software has been used to read and debug CAN messages. Bus Master requires DBC file to be converted to a .dbf file. The messages can be viewed in a very detailed format in the Bus Master. The bus master along with PCAN dongle is very useful in debugging the CAN communication. It is also possible to record the logs of communication.
Motor & I/O Controller
Group Members
Motor and I/O controller is one of the five controller in the autonomous car. It is responsible for car's steering, movement, input commands and to display critical information regarding the car. The controller is connected to different hardware modules that take care of the mentioned features. These modules comprise of servo motor which is used for steering, electronic speed controller for controlling the DC motor which in turn controls the movements of the car and a touch-screen LCD display for data input and to display critical information. These modules are explained in further detail in hardware interface section of the Motor & I/O Controller below.
Design & Implementation
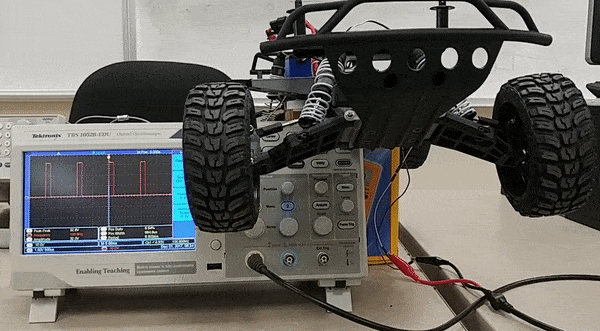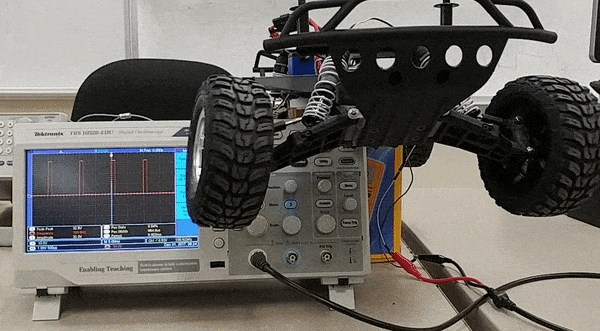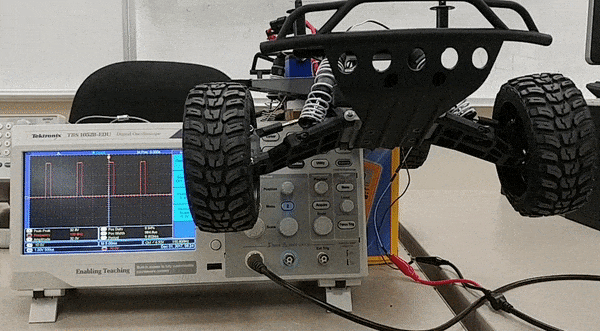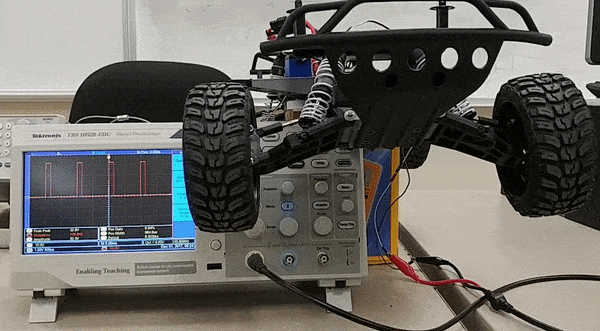
To design the motor controller to control servo and dc motor, research on required duty cycle was done. The dc motor can rotate with different speed based on the duty of the PWM signal. For our design we have three different speeds at which the car can move forward. In addition to the forward movement of the car we also have a reverse movement. All of these speeds in forward and backward direction require different PWM duty cycle. Based on this analysis, research of specific duty cycle required for each speed level was done using an oscilloscope. Similarly, for steering control different duty cycle is required to position the wheel in certain direction. Since we have five different wheel positions , we required five different duty cycle to perform these position control.
Furthermore, research on speed sensor was done using oscilloscope to find the behavior of signal that the sensor generates. By probing the signal wire on the speed sensor we found out that with every revolution the sensor sends out a pulse in the signal wire. Based on this analysis we designed an interrupt based pulse reader that tells exactly how many rotation the wheel took within a minute. Using this data we calculate our actual car speed.
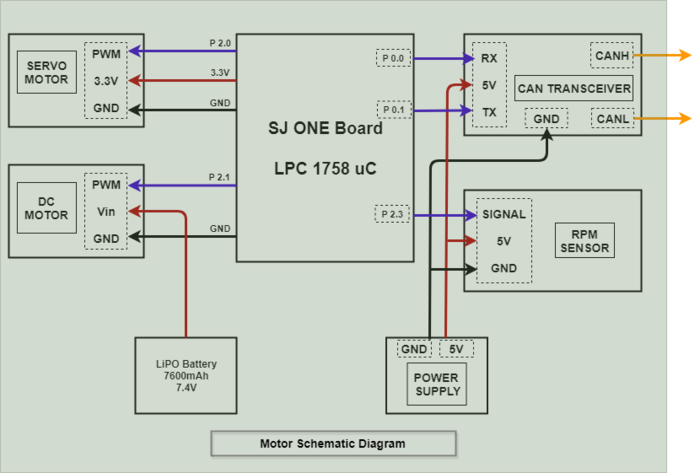
Hardware Design
The motor and I/O controller hardware design consists of SJOne microcontroller board connected to servo motor, electronics speed control, LCD module and LED lights. Servo motor and electronics speed control are connected to the microcontroller using PWM signal. The touch screen LCD is connected to the microcontroller board using UART interface. The LED lights are connected to the board using GPIO interface. The electronic speed controller is powered using the 6v power supply from the car battery pack. The servo motor for steering control is power on using 5V from the power bank. The touch screen LCD module is also powered on using the 5V using the power bank.
Hardware Interface
Electronic Speed Controller (ESC)
The Electronic Speed Controller is a component used for feeding PWM signal to a DC motor to control the speed at which it rotates. In addition to the speed it also controls the direction in which the motor rotates. These features help the car move forward and reverse and do these in different speeds. From the diagram below you can see the ESC has three color coded wires that are used for PWM signal(WHITE Color), VCC(RED Color) and GND(BLACK Color). These three color coded wires connect to the SJOne micro-controller board and power bank used in the car. There are also two wires coded red and black that have wire adapter at the end connect to the battery pack. The other two red and black wire connect directly to the DC Motor. The ESC also has a EZ Set button to switch between different speed modes, calibrate the speed and steering, and most important of all switch on the ESC itself. Please refer to the documentation provided by TRAXXAS for using the ESC.
| S.No | Wires on (ESC) | Description | Wire Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | (+)ve | Connects to DC Motor (+)ve | RED |
| 2. | (-)ve | Connects to DC Motor (-)ve | BLACK |
| 3. | (+)ve | Connects to (+)ve of Battery | RED |
| 4. | (-)ve | Connects to (-)ve of Battery | BLACK |
| 5. | P2.1 (PWM2) | PWM Signal From SJOne | WHITE |
| 6. | NC | NC | RED |
| 7. | (-)ve | Negetive terminal | BLACK |
DC Motor
The DC motor is the primary component that controls the rotation of the car wheel. Based on the direction of the current flow to the motor it rotates the wheel in forward or backward direction. Also, based on the amount of current flow to the motor, it controls the speed at which the wheels rotate. In the figure below you can see the DC motor has two wire, red and black for (+)ve and (-)ve connection respectively. For forward movement of the wheels the current flows from (+)ve to (-)ve. For reverse movement the current flows from (-)ve and (+)ve. For controlling the speed of the wheel the motor is fed with different amount of current from the ESC, which is controlled based on the duty cycle fed to ESC.
| S.No | Wires on (ESC) | Description | Wire Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | (+)ve | Positive Terminal | RED |
| 2. | (-)ve | Negetive terminal | BLACK |
Servo Motor
The servo motor is the component responsible for the steering of the car. The servo motor is controlled directly from the SJOne micro-controller board. It has three color coded wire white, red and black which are used for PWM signal, 5 Volts and GND respectively. Based on the duty cycle of the signal sent to the servo, it rotates in left/right direction. The PWM signal fed to the servo motor is of frequency 100Hz. Detailed duty cycle values and corresponding steering position are provided in the software design section.
| S.No | Pin No. (SJOne Board) | Function | Wire Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | P2.3 (PWM4) | PWM Signal | WHITE |
| 2. | VCC | 5 Volts | RED |
| 3. | GND | 0 volts | BLACK |
Speed Sensor
The speed sensor is one of the hardware component used in the autonomous car for sensing the speed of the car and feeding the information to SJOne microcontroller. The sensor is installed in the gear compartment of the Traxxas car along with the magnet trigger. When the magnet attached to the spur gear rotates along with the gear it passes the hall-effect RPM sensor after every revolution. As soon as the magnet comes in front of the sensor the sensor sends a pulse on the signal line which is color coded as white. The other color coded wires red and black are used for VCC and GND to power the sensor. The sensor is powered using the 5 volts power supply from the power bank.
| S.No | Pin No. (SJOne Board) | Function | Wire Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | P2.6 | GPIO (INPUT) | WHITE |
| 2. | VCC | 5 Volts | RED |
| 3. | GND | 0 volts | BLACK |
IO module
IO module consists of touch LCD for displaying critical information, head lights, brake lights and running lights. The LCD is interfaced to UART3 of the micro controller. The lights are interfaced via the GPIO pins.
The below figure shows how the LCD and the Headlights are connected to the motor module. All nodes broadcast data on CAN bus. Motor node receives, converts it into LCD format and displays on LCD.
Software Design
Motor Controller
Software design for the motor controller consist of different software modules that control speed, steering, inputs and outputs interface using touch screen LCD, and sensing the speed of the car. Controlling speed, steering and sensing speed is done using 10Hz periodic loop. On the other hand the code for LCD input and output run as a task that get scheduled in between the 10Hz periodic scheduler.
The second phase of the motor controlling is maintaining a constant speed i,e., to find out the speed at which it is running and control the car based on the speed at which it is traveling. This comes in handy when the car has a destination that goes uphill. This operation can be called as speed controlling. This operation is done with the help of a speed sensor that can be fixed either on to the wheel or on to the transmission box of the car.
DC Motor and Servo Motor
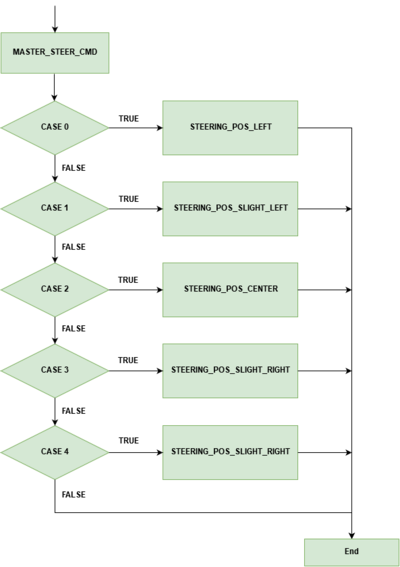
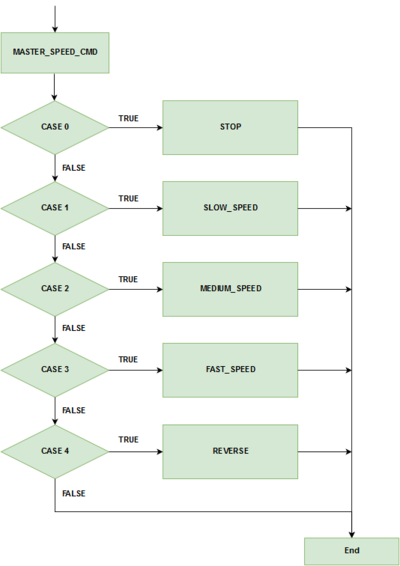
Software design for the speed control and steering control is done using 5Hz and 10Hz periodic loop respectively. The periodic loop consists of two switch cases, one switch case for speed control and another one for steering control. For speed control, switch cases are for stop, 'slow' speed, 'medium' speed, 'fast' speed, and reverse. For steering control, the switch cases are for the positions of the wheel that are 'hard' left, 'slight' left, center, 'slight' right and 'hard' right. After the CAN message for speed and steering are decoded, the values are fed into switch cases for speed and steering control. Based on the values of the steering and speed sent by the master, motor controller takes action. Below flowchart are for steering control and speed control, which shows a command being received from master which is then used in a switch case to choose between different steering positions and speeds. The provided gif here shows change in five steering positions and their respective PWM duty cycle applied to the servo motor. The macro defined for the duty cycle below are percentage of the duty cyle for PWM signal applied to the servo. For our design these are X percentage of 100Hz, which is the frequency of the PWM signal used to control the servo motor.
| No. | PWM | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | Full Left |
| 2 | 6 | Slight Left |
| 4 | 7 | Straight |
| 6 | 8 | Slight Right |
| 7 | 9 | Full Right |
RPM Sensor
The RPM sensor code calculates the revolution of the spur gear every 200 ms. It calculates the revolution based on the interrupt signal generated on the GPIO pin connected to the SJOne board. The function for calculating the number of revolution is called from inside the switch case for slow speed shown in the speed control flowchart. The formula used to calculate mph is shown below.
Formula used for calculating mph:
mph = 5 * (((2 * PI * WHEEL_RADIUS) * no_of_revolution * SECS_PER_HOUR) / (CENTIMETERS_PER_MILES * FINAL_DRIVE));
NOTE: Multiplier value 5 is used to convert calculation of no_of_revolution every 200 ms to 1 second which depends on the periodic loop the
above code is running in.
Macros used for above parameter are given below:
#define FINAL_DRIVE 12.58 //Gear to Wheel Ratio: Wheel rotates 1x for every 12.58 revolution of the DC motor
#define PI 3.14159
#define WHEEL_RADIUS 2.794 //Unit is centimeters
#define SECS_PER_HOUR 3600
#define CENTIMETERS_PER_MILES 160934.4
Other than providing the speed at which the car is moving, the RPM sensor has another critical functionality which is the speed control. For constant speed control we have implemented a Proportional and Integral (PI) controller that takes care of speed control up and down any slope which would otherwise be variable due to gravity. Based on the output from the PI controller, the PWM duty cycle is added to the duty cycle already provided for slow speed. If the actual speed calculated using the RPM sensor is less than the set speed (slow speed),case during uphill, the error is positive. So in this case the PI controller increments the the duty cycle to reach the set speed. On the other hand when the actual speed is more than that of the set speed,which is the case during downhill, the error is negative so the PI controller tries to decrease the duty cycle in order to reduce the speed down to the set speed. Although, our actual PI controller code contains lot of filters to confine speed within safe limits , snippet for basic PI controller is provided below to show the flow of calculation for proportional and integral values for speed control.
error = set_speed - pi_mph; //Error between set speed and the actual speed of the car
p_controller = Kp * error; //Calculation of the proportional value based on the errors
i_controller = Ki * speed_error_sum; //Calculation of the integral value based on the sum of previous error
speed_error_sum = speed_error_sum + error; //Calculation of sum of previous errors
duty_cycle = p_controller + i_controller; //Controller output based on integral and proportional value
IO module
Since motor's functional information is critical, the LCD uses UART as a communication medium to transmit messages. The LCD and lights working in the software is
designed as low priority tasks running at 500 ms. Even though UART takes a long time to process, it will not clog the periodic tasks.
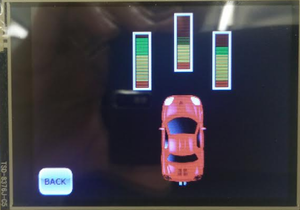
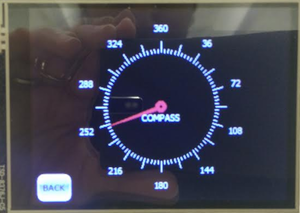
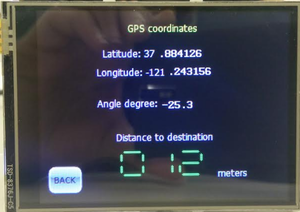
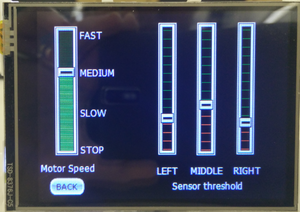
The LCD is interfaced early in the project since it aids in debugging while the car is on the move. Critical information such as sensor readings, motor speed, compass direction, GPS coordinates, the degree to turn and distance to the destination are displayed on the LCD. The below screens show the information displayed on the LCD.
There is also a Settings menu through which the motor speed and sensor thresholds can be configured without having to re-build and re-flash the software.
Implementation
IO module algorithm
The critical data is received from different nodes via CAN and packed into packets and sent to the LCD via UART. The LCD used requires a specific format of data from the micro controller for it to display the data.Refer the below datasheet for information on the packet format for 4D systems uLCD-32PTU.
Datasheet: http://www.4dsystems.com.au/productpages/uLCD-32PTU/downloads/uLCD-32PTU_datasheet_R_2_0.pdf
User manual: http://www.4dsystems.com.au/productpages/PICASO/downloads/PICASO_serialcmdmanual_R_1_20.pdf
The below flowchart explains how the tasks work in order to transmit and receive data from the LCD.
LCD screens
Technical Challenges
Car Moving Too Fast While Downhill
Problem Summary: In spite of controlling speed using RPM sensor, the car was not in control while on a downhill.
Solution: After trying all possible solutions we could think of, we applied a brake momentarily at the start to reduce the sudden increase in PWM and then controlled the car based on the inclination. Also, made sure that if PWM value went below a certain range, then no brake was applied to the car.
Car Not Going in Reverse
Problem Summary: Although the PWM given to the car was ideal for making the Car go reverse. There was some issue with the car and it did not go reverse at all.
Solution: When checked with the transmitter/remote, I was seen that for the car to go reverse we had to first give a reverse signal then a stop signal and again a reverse signal. We implemented this easily with a simple block of code and manage to get the ESC working.
Servo Movements were slow
Problem Summary: Proper PWM Signals was given to the servo for going left or right but the movements were too slow.
Solution: Previously the Servo was running at 3.3v. After checking its manual realised that the servo works better and swift with 5v. Thus powered the servo motor with 5v and it started working promptly.
PWM being initialised at 1.9kHz instead of 50Hz
Problem Summary: Initialised the PWM Peripherals to 50Hz. But when checked on the same on a Digital Oscilloscope the value was 1.9kHZ.
Solution: When reviewing the code we realised that we have initialised the PWM peripheral but that code was not actually executed. We solved this by using a pointer instance of the PWM and initialising the PWM Signal in the motor init function.
PWM *SERVO_MOTOR, *DC_MOTOR;
void motor_init(void)
{
SERVO_MOTOR = new PWM(PWM::pwm1); /* P2.0 and 50Hz */
DC_MOTOR = new PWM(PWM::pwm2); /* P2.1 and 50Hz */
}
After doing initialisation using a pointer we were able to get proper 50Hz Signal for PWM Peripherals.
Geographical Controller
Team Members:
The main purpose of the geographical controller is to guide the car towards its destination. This is done by processing data from the GPS and Compass module in order to get the Heading, Bearing, and Distance. The compass will allow the user to calculate the Heading, which tells us which direction the car is pointing relative to magnetic north or simply, "Which way the car is pointing"? The GPS will allow the user to get the current coordinates of the car, which will be useful when calculating the Bearing and Distance. The Bearing tells us the direction from the current location to a checkpoint coordinate, and is given as the angle between the location and the current location of the car. The Distance tells us how many meters away the current checkpoint is. Essentially, How far away are we from our destination?
The geographical controller is also responsible for:
1. Parse the data from GPS and Compass module.
2. Navigate a path towards the destination using the nearest checkpoint
2. Navigate to nearest checkpoints and to set course towards the nest checkpoint along the path towards the destination .
3. Setting up the heading of the car towards the direction of the next checkpoint .
Hardware Design
Pin Configuration:
| Sl. No | Pin on SJOne Board | Pin on CMPS12 | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SDA | SDA | Serial Data pin from SJONE to CMPS12 |
| 2 | SCL | SCL | Clock signal from SJONE to CMPS12 |
| 3 | 5V | VCC | 5V voltage supply |
| 4 | GND | GND | Ground |
| Sl. No | Pin on SJOne Board | Pin on Adafruit Ultimate GPS Breakout | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TXD3 | RXD | Transmit using UART3(TXD3) to Adafruit Ultimate GPS Breakout |
| 2 | RXD3 | TXD | Receive using UART3(RXD3) from Adafruit Ultimate GPS Breakout |
| 3 | 5V | VCC | 5V voltage supply |
| 4 | GND | GND | Ground |
Hardware Interface
CAN Bus
The CAN bus interface allows the geographical controller to send and receive data from other microcontrollers on the bus. For example, the geographical controller will send requests to the master controller to tell it to turn right, left, or keep straight in order to reach the set checkpoints. The geographical controller will plan a path towards the destination using the closest checkpoint towards the destination path and then send the steer commands to be taken in order to to steer towards the destination.
MTK3339 Ultimate GPS
The MTK3339 Ultimate GPS module from Adafruit was chosen because it is a plug and play device and gives consistent GPS string The main purpose of the GPS module is to provide an accurate location of the car while the car navigates towards its destination. This is done by parsing NMEA sentences, which are transmitted by up to 66 satellites to pinpoint the current location of the module. There are various different types of NMEA sentences, such as $GPRMC and $GPGGA. The NMEA sentence that was used was $GPGGA, which provides only the recommended minimum. The module is interfaced via UART with a baud-rate set to 57600bps. The module also comes with a fix LED, which indicates if a GPS fix by blinking every 15 seconds, if not, it blinks every 1Hz. The module is powered by 3.3V from the SJOne board.
The $GPGGA sentence is separated by commas, which the user has to parse in order to get useful data out of the module. The most important data that the user want is the GPS coordinate, Latitude and Longitude.The parsing of data was done using the strstr() function which returns the pointer of the comma from the NMEA string to be parsed.
Below is an example of a parsed $GPGGA sentence:
Example: $GPGGA,123519,4807.038,N,01131.000,E,1,08,0.9,545.4,M,46.9,M,,*47
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
| Number | Raw form | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 123519 | Time of fix 12:35:19 UTC |
| 2 | A | Navigation receiver warning A = OK, V = warning |
| 3 | 4807.038 | Latitude 48 deg. 07.038 min |
| 4 | N | North |
| 5 | 01131.000 | Longitude 011 deg. 31.00 min |
| 6 | E | East |
| 7 | 1 | Fix Quality, 1 means GPS is fixed |
| 8 | 08 | Number of satellites being tracked |
| 9 | 0.9 | Horizontal dilution of position |
| 10 | 545.5,M | Altitude, Meters, above mean sea level |
| 11 | 46.9,M, | Height of geoid (mean sea level) above WGS84 |
| 12 | *68 | the checksum data, always begins with * |
CMPS12 - Tilt Compensated Magnetic Compass Module
The CMPS12 - Tilt Compensated Magnetic Compass module was chosen because it provides better performance than its predecessor CMPS12, the module also has a 3-axis magnetometer, a 3-axis gyro and a 3-axis accelerometer. The CMPS12 is a self calibrating module and is automatically calibrated by movement, there is no instigation required by the user.Register 30 can be checked to see the level to which the CMPS12 has been calibrated. The default mode of the compass was chosen to get the heading value. The compass needs to be calibrated initially by moving it around in 3 axis. The calibration profiles stays onto it until the power supply to compass module is taken off.
The compass module is placed away from all other components of the car to minimize any magnetic interference from the motor, servo, sensors, and microcontrollers. Placing it in an environment where there is magnetic interference will cause incorrect reading of the heading and the car will navigate towards the wrong direction. The compass and GPS module is placed on a higher mount on the car to avoid any interference to it.The compass module is interfaced via I2C. It is powered on by 5V, but 3.3V works also.
.
Software Implementation
GEO module sends the direction and heading values to the master controller.
| Sl. No | Message ID | Message name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 141 | DIRECTION_GPS | Send direction value to the master |
| 2 | 191 | HEADING | Send Heading value in degrees to the master |
Receiving and parsing GPS data
The first task was to interface the GPS module to the SJOne board (using UART3), and receive raw data over it. The module was configured to receive only GPGGA NMEA sentence at 9600 bps baud rate. The received NMEA data is a string, that has to be parsed to obtain current latitude and longitude values. This location data is continuously sent to the Master controller on the CAN bus at 10 Hz.
Heading Calculation
Heading of the car is the direction that the car is moving, with respect to true north. A compass gives heading with respect to magnetic north. T\
The CMPS12 is calibrated by tilting it around in 3 axis. The CMPS12 is connected to the SJONE board using the I2C connection.
Bearing calculation
Bearing is the direction that the car desires to travel along, i.e., the direction of the destination. It is calculated using the current location coordinates and the destination coordinates (or next checkpoint coordinates). The formula to calculate bearing is
X = cos(lat2) * sin(dLong) Y = cos(lat1) * sin(lat2) - sin(lat1) * cos(lat2) * cos(dLong) Bearing = atan2(X,Y) where, (lat1, long1) are the current location coordinates (lat2, long2) are the checkpoint coordinates dLong is (long2 - long1)
Distance calculation
The distance between the current location and the next checkpoint is calculated using the Haversine formula .
Haversine formula: a = sin²(Δφ/2) + cos φ1 ⋅ cos φ2 ⋅ sin²(Δλ/2) c = 2 ⋅ atan2( √a, √(1−a) ) d = R ⋅ c where φ is latitude, λ is longitude, R is earth’s radius (mean radius = 6,371km); note that angles need to be in radians to pass to trig functions!
A flag is set when the distance to the final checkpoint becomes zero, and sent to the Master controller, to indicate that the destination has been reached.
Technical Challenges
The following problems were faced and below are their resolutions:
- Problem 1: Calibration of CMPS 12 module was a major challenge in this module. The compass module needs calibration every time the power is taken off the compass module.
- Solution 1: We initially started by writing our own calibration profile into the registers of the CMPS12 module. After noticing that the calibration values were inconsistent we erased the profile that we wrote and used the default calibration profile. The module provided the accurate calibration modules with the default profile. The compass needs to be moved in all three axis for a while every time the board is powered to get the correct calibration.
- Problem 2: Path planning was done when the co ordinates were received from the bluetooth module in the 10Hz function which caused the 10Hz task to over run.
- Solution 2: We added flags in the received co ordinates function and the path planning function was moved to the 1Hz task.
Sensors Controller
Group Member
- Oliver Zhu
- Wen Yuen Chao
Hardware Design
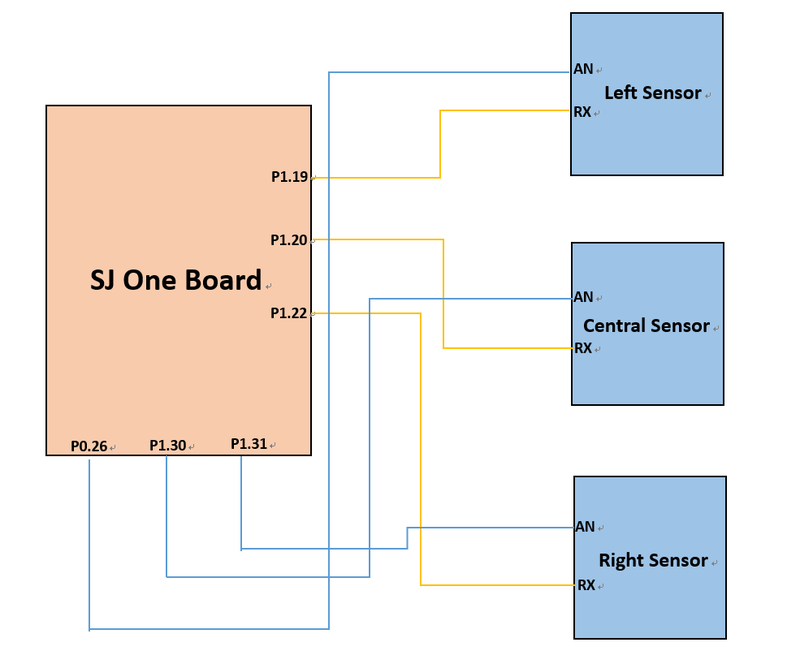
In this project, the sensor we use is LV-MAXSonar-EZ4, which is ultrasonic sensor. There are three sensors put in the front of our RC car and detect the left, middle and right side independently.
The feature of this sensor as follows:
1. 2.5V to 5.5V supply with 2mA typical current draw
2. Readings can occur up to every 50mS (20-Hz rate)
3. Serial, 0 to Vcc, 9600 Baud, 81N
4. Analog, (Vcc/512) / inch
5. Pulse width, (147uS/inch)
The benefit of the sensor as below:
1. Very low cost ultrasonic rangefinder
2. Very low power ranger, excellent for multiple sensor or battery-based systems
3. Quality beam characteristics
| Sl. No | Pin on SJOne Board | Pin on MaxSonar-EZ4 | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | PWM | AN | PWM pin from SJONE to MaxSonar-EZ4 |
| 4 | RX | RX | Recive data from SJONE to CMPS12 |
| 6 | 5V | VCC | 5V voltage supply |
| 7 | GND | GND | Ground |
Hardware Interface
CAN Bus
The CAN bus interface allows the sensor controller to send and receive data on the bus. For example, the sensor controller will send the data to the CAN bus and the master controller will take it and let the car to do the coordinate movement.
Software Design
1. Initialization sequence
In the Sensor init sequence is as follows:
- CAN Init
- Motor CAN is initialized on can1 with BAUD rate 100bps and TX/RX queue sizes of 100. Then the filter is setup for 100-150 MSG IDs.
- Sensor Init
2. Read Sensor
The relative functions is as follows:
- read_sensor
- After reading the data from sensor, we have to transfer the voltage to inch.
- read_sensor_left
- Read the data from left sensor.
- read_sensor_right
- Read the data from right sensor.
- read_sensor_center
- Read the data from center sensor.
3. Filter the value of sensor
The relative functions is as follows:
- filter_sensor
- Sometime we will get the outlier by noise, so we need to eliminate this abnormal value.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Problem 1: There is a unusual pulse when sensor sent the date to CAN bus.
Solution 1: When we meet the unusual value, we will adopt the previous value rather than the current value.
Testing
In the code of sensor part, we use API of CMock to test our code. There is a example we used as follows:
void test_sensor2chan(void)
{
TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(3, sensor2chan(sensor_left)); //0+3
TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(4, sensor2chan(sensor_center)); //1+3
TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(5, sensor2chan(sensor_right)); //2+3
TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(6, sensor2chan(sensor_back)); //3+3
}
void test_read_sensor(void)
{
uint16_t adc = 2;
enum sensor_dir sensor = sensor_left;
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, true, true);
adc0_get_reading_ExpectAndReturn(sensor2chan(sensor), adc);
sensor_delay_ms_Expect(1);
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, false, false);
sensor = sensor_center;
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, true, true);
adc0_get_reading_ExpectAndReturn(sensor2chan(sensor), adc);
sensor_delay_ms_Expect(1);
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, false, false);
sensor = sensor_right;
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, true, true);
adc0_get_reading_ExpectAndReturn(sensor2chan(sensor), adc);
sensor_delay_ms_Expect(1);
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, false, false);
sensor = sensor_back;
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, true, true);
adc0_get_reading_ExpectAndReturn(sensor2chan(sensor), adc);
sensor_delay_ms_Expect(1);
trigger_sensor_ExpectAndReturn(sensor, false, false);
sensor2type(sensor_left);
sensor2type(sensor_center);
sensor2type(sensor_right);
sensor2type(sensor_back);
TEST_ASSERT_EQUAL(3.15, read_sensor(sensor));
}
Android Application and Bridge
Group Members
Design
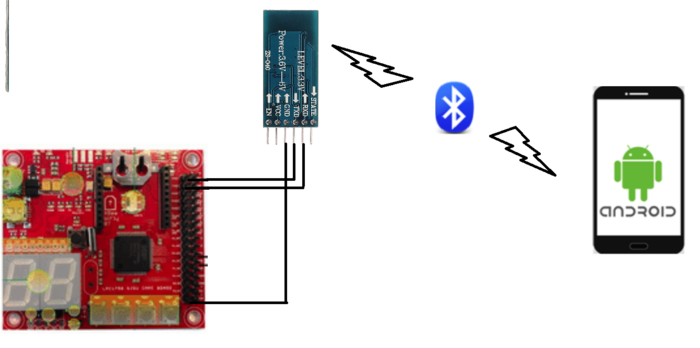
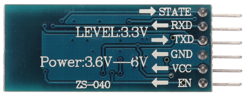
The bridge controller is responsible for establishing communication between the CAR and an Android Phone. This communication is achieved using Bluetooth technology and HC-05 bluetooth transceiver. The android app "ZeusApp" sends Co-ordinates as well as Start/Stop command to the car. Once the bridge ECU receives this data over UART, it transmits it to corresponding controllers using CAN bus. The HC-05 module communicates with SJONE over UART at 9600bps baud rate. The overall architecture of the system is given below:
Pin Configuration:
| Sl. No | Pin on SJOne Board | Pin on HC-05 | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TXD3 | RXD | Transmit using UART3(TXD3) to HC-05 |
| 2 | RXD3 | TXD | Receive using UART3(RXD3) from HC-05 |
| 3 | 3V3 | VCC | 3.3V voltage supply |
| 4 | GND | GND | Ground |
Hardware interface between the BLE ECU and The can bus is achieved using the CAN tranciever. P0.1 on the SJone board is connected to CAN Tx and P0.0 is connected to CAN Rx. The CAN bus section talks in more detail about how CAN is actually implemented.
Bluetooth Hardware Design
We decided to go with HC-05 as our bluetooth module HC-05 because of the vast amount of information on it on the internet. HC-05 is an easy to use Bluetooth SPP(Serial Port Protocol) module, designed for transparent wireless serial connection setup. Hc-05 also provides switching mode between master and slave mode. Given below are features of HC-05:
- -80dBm sensitivity
- Up to +4dBm transmit power
- Low Power operation
- UART interface with programmable baud rate.
- Integrated Antenna and edge connector.
- Supported Baud Rate: 9600,19200,38400,57600,115200,230400,460800.
- Auto-connect to the last device on power as default.
- Auto-pairing PINCODE:”0000” as default
- Auto-reconnect in 30 min when disconnected as a result of beyond the range of connection.
Bluetooth Software Design
The BLE ECU is responsible for receiving data over UART and then Packaging it in correct message format and sending it over the can bus. To achieve this a few messages were made in the DBC file. The Message IDs and info is given in the table below:
| Sl. No | Message ID | Message name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 181 | APP_DATA | Sends 2 bit start OR stop command |
| 2 | 182 | APP_DATA_LAT_LONG | Send Destination Latitude and Longitude to the ECU. |
Our BLE ECU is pretty simple and has one function as its core operation. This Function is given below.
void parse_data()
{
char coord[100]={0};
getstring(coord,100,0);
if(coord[0]==1)
{
printf("\nStart");
BLE_data.START_CAR=1;
c_LED_display_set_number(1);
memset(coord,0,sizeof(coord));
}
else if(coord[0]==2)
{
printf("\nStop");
BLE_data.START_CAR=2;
c_LED_display_set_number(0);
memset(coord,0,sizeof(coord));
}
else if(strlen(coord))
{
while(coord[i] != ',')
{
Latitude[i]=coord[i];
i++;
}
Latitude[i]='\0';
i++;
while(coord[i] != '@' )
{
Longitude[j]=coord[i];
i++;
j++;
}
Longitude[j]='\0';
i=0;
j=0;
float LAT1=atof(Latitude);
float LON1=atof(Longitude);
printf("\nLatitude: %.15f",LAT1);
printf("\nLongitude: %.15f",LON1);
gps_destination.DEST_LAT=LAT1;
gps_destination.DEST_LONG=LON1;
}
dbc_encode_and_send_APP_DATA(&BLE_data);
dbc_encode_and_send_APP_DATA_LAT_LONG(&gps_destination);
}
As seen in the code above, there are two DBC structures that are made, BLE_data to send start/stop command and gps_destination to send the destination co-ordinates. The android app sends a string over bluetooth to HC-05 which passes it on to SJone over UART. By parsing this string we can figure out which command was received from the App. If the 1st character of string is '1' the its a START command, if its '2' the it is STOP command and otherwise it parses the string to find Coordinates. Through the app i am sending coordinates in the format of LATITUDE,LONGITUDE so, in parse_data() function, two global character arrays were accessed. Until the iterator reaches the comma it puts everything in the Latitude array and after the till the end of string it puts everything in the Longitude array. Library function atof() was used to convert the character array to float to be able to send it over CAN.
The function parse_data() is periodically called at 1hz (so every one second). This means that the UART data is parsed and a can message is sent every second.
Android Application Design
Implementation
The main purpose of the android application is to provide the user with a way to interact with the Car using a smartphone. This app was built using Android Studio developed by Google and Jetbrains. You have the option of writing the code in either Java or Kotlin. For ZeusApp we decided to go with Java. One of the most important features that needed to be integrated into the app was Google Maps to show current position and the destination coordinates. A Google Maps API key is required to integrate Maps withing the application. This key can be acquired through the Google Developers Console. This key is mainly used to track activity of the app. Google uses the tracking to figure out charges (if any). Since our app is not a public app it doesnt cost anything for us. There are two main activities that form the app.
1. StartScreen.java is the first page that the user is greeted with its a basic home page that allows the user to go to the Map where he/she can interact with the car.
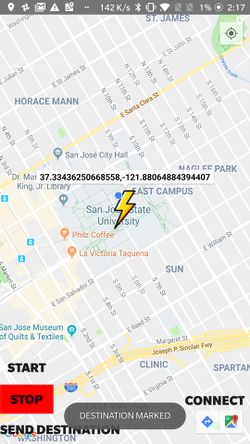
2. MapDemoActivity.java is the main activity where all the important work happens. This is the page which displays Google map fragment and all the controls associated with the car. The map fragment loads and updates the users location which he/she can see by clicking the recenter button. A pin can be dropped on the map by just touching the desired location on it. This activity also lets user connect to HC-05 bluetooth transceiver by simply clicking the Connect button. Once the app is connected to the car, user can then start the car using START button and similarly stop it using the STOP button. After marking the destination there is a button that lets the user send coordinates in the form of LATITUDE, LONGITUDE to the car.
Bluetooth - Android Side
The MapDemoActivity.java , besides UI for map. has one more integral purpose. It establishes a socket communication between the smartphone and HC-05 transceiver. For this a few things need to be done.
1. We need to specify certain permission in the AndroidManifest.xml. These permissions are given below
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
2. Import the following libraries
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter; import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice; import android.bluetooth.BluetoothSocket; import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream;
This lets us define variables that are needed for establishing communication over bluetooth. Input and Output stream classes lets us make buffers to write data to and read data from.
3. For basic communication we need need three things a Bluetooth Device, Bluetooth Adapter and a Bluetooth Socket. These are declared as follows:
BluetoothSocket mBTsocket = null; BluetoothDevice BoardSJONE = null; BluetoothAdapter ZeusAdapter;
Bluetooth adapter lets you represent local device(smartphone) bluetooth adapter and lets you perform bluetooth tasks such as device query, instantiate a BluetoothDevice using MAC ID or UUID and create a socket. The Bluetooth adapter itself can be initialized as follows:
ZeusAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
For this app we have initialized the adapter int the onStart function. This funtion is called when the activity becomes visible to the User, so, before anything can be done BluetoothAdapter is initialized.
4. Once the Adapter has been initialized and the device has been paired we now need to establish RF communication between the phone and HC-05. For that we use BluetoothSocket as below.
mBTsocket = BoardSJONE.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(BTMODULEUUID); mBTsocket.connect(); pairedDevice = BoardSJONE;
Here, BTMODULEUUID is the Universallu Unique Identifier which is a 128 bit ID of the smartphone. Now the Socket connection has been established.
5. For sending data, Output Stream can be used.
tOUTPUT = mBTsocket.getOutputStream(); tOUTPUT.write(string.getBytes()); tOUTPUT.flush();
The parameters inside write() function is the data you want to send over bluetooth. A coordinate string in our case.
The diagrams below show our App as its seen on an Android phone:
For starters, i developed the app just to establish Socket communication with HC-05 and Send 1 or 0. Sort of like a "hello World" code. It was a bit of a learning curve. After successful communication establishment, the Start and Stop buttons were added. These would just let the user choose wether to send "1" (start) or "2" (stop). I decided to not go with 0 as the stop command as in the BLE file, character receive array is initiated to ZERO every time parse_data() function is called. This is because the array is defined locally and not globally for the function. So now only when a "2" is received over UART the DBC struct variable is set to STOP.
The second major task was building the map screen. This was a bit difficult as it requires Google API key to instantiate a Map fragment. The features i had to add include Toast messages on every new activity, Destination Coordinate marker. User Location marker and Bluetooth Buttons. Once the map was successfully integrated adding the Custom Destination marker (lightning bolt) was pretty straight forward to add. A slight modification int the function that loads the map needs to be made. Given below is the code snippet for adding a marker.
map.setOnMapClickListener(new GoogleMap.OnMapClickListener() { //marker added :neel
@Override
public void onMapClick(LatLng point) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"DESTINATION MARKED",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
marker.position(point);
marker.title(point.latitude + "," + point.longitude); // point is an object of LatLng class , LAT and LON both are Doubles.
//marker.title("Destination");
marker.draggable(true);
marker.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.drawable.flash));
//Destination_location.setLatitude(point.latitude);
//Destination_location.setLongitude(point.longitude);
Dest_point=point;
map.clear();
map.addMarker(marker);
}
});
Dest_point in the above snippet is the private class variable that is used to send the destination over Bluetooth. It is a LatLng class object.
Testing and Technical Challenges
Issues
- With Zero experience of Java or Android Application development, it was very difficult fo me in the beginning to learn Java syntax and get accumulated with the Android SDK. This was made possible after spending a lot of time on Android Developer website and Android tutorial on Youtube. The website provides information on available APIs and their examples.
- Running background activity for bluetooth. So that we could have Start/Stop on home screen and Send Destination feature on the mapscreen, was very difficult since i could not understand multithread bluetooth architecture. In the end the best solution to this was have one main activity(in our case the MapActivity) and have all the bluetooth buttons on that page.
- On the BLE side, in the beginning we observed that unless Explicitly sending Start (1) from the app the BLE would by default put a Stop(0) command on the CAN bus. This was because the character array was getting initialized to 0 every function call. This was solved by simply sending a "2" from the app, and then sending a Stop command only when the first character in the string is 2.
- Another major issue was that i was unable to send correct LAT LONG on the can bus in float format. We needed to have atleast 6 decimal point precision and this could only be achieved using a factor of 0.0000001 in the DBC. But even after doing that we would get positive coordinate value only upto 4 decimal points and would get total garbage for negative coordinate value (Latitude in our case is in the range of -121). Preet gave us a great idea to just send the entire number as a uint32_t variable and then divide it by a million on the receiver side(GPS in our case). This solved the problem and we were able to send and receive correct and precise Coordinates on the can bus.
Testing
- We began testing the BLE Uart code first for this, after writing a very basic code that would just take a character from uart and display it on screen, we installed an app directly from the Play Store for android. There are several Apps available on the app store for HC-05. Once the data sent from app was successfully received and displayed, we could move on to the next stage.
- On the android side the Map Fragment testing was done using an Android Studio Virtual Device (API 27). This helped us in deciding the layout and functions of each activity without having to deploy it on the smartphone.
- IMPORTANT: It should be noted that to test the bluetooth features of the app, an actual compatible android phone is needed since the emulator does not take permissions from the laptop's bluetooth adapter. We realized this after the App kept crashing on the emulator every-time a button was pressed.
Master Controller
Hardware Design
Software Design
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
[1] Android Developers
Appendix
You can list the references you used.
Datasheets
[1] [Ultrasonic Sensor] [2] Bluetooth Module [3] [ LCD] [4] CAN Transceiver [5] GPS Module [6] Compass Module