F17: Rolling Thunder
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Rolling Thunder
Abstract
This section should be a couple lines to describe what your project does.
Objectives & Introduction
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Master Controller
- Akil Khan
- Jerry John
- Geographical Controller
- Abhilash Tuse
- Vishal Shrivastava
- Communication Bridge + Android Application
- Akinfemi Akin-Aluko
- Johnny Nigh
- Motor and I/O Controller
- Saurabh Ravindra Badenkal
- Joshua Skow
- Sensor Controller
- Sona Bhasin
- Thrishna Palissery
- QA Team
- Akil Khan
- Saurabh Ravindra Badenkal
Legend
| Color | Component |
|---|---|
|
Blue |
Sensor Controller |
|
Green |
Motor/IO Controller |
|
Red |
Geographical Controller |
|
Orange |
Central Controller |
|
Indigo |
Communication Bridge + Android Application |
|
Brown |
QA |
Schedule
| Start Date | End Date | Task | Status | Date of Completion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 09/20/2017 | 09/26/2017 |
|
Completed | 09/26/2017 |
| 2 | 09/27/2017 | 10/03/2017 |
|
Completed | 10/03/2017 |
| 3 | 10/04/2017 | 10/10/2017 |
|
Completed | 10/10/2017 |
| 10/10/2017 | Wiki Schedule | Completed | 10/10/2017 | ||
| 4 | 10/11/2017 | 10/17/2017 |
|
Completed | 10/17/2017 |
| 5 | 10/18/2017 | 10/24/2017 |
|
Completed | 10/24/2017 |
| 10/24/2017 | DBC File | Completed | 10/24/2017 | ||
| 10/24/2017 | DEMO: CAN communication between controllers | Completed | 10/24/2017 | ||
| 6 | 10/25/2017 | 11/28/2017 |
|
In progress | |
| 7 | 11/01/2017 | 11/07/2017 |
|
Completed | 11/07/2017 |
| 11/07/2017 | DEMO: Motors driven by wheel feedback and sensors, Basic obstacle avoidance
Final Wiki Schedule |
Completed | 11/07/2017 | ||
| 8 | 11/08/2017 | 11/14/2017 |
|
In progress | |
| 9 | 11/15/2017 | 11/21/2017 |
|
Not started | |
| 11/21/2017 | DEMO: GPS driving | Not started | |||
| 10 | 11/22/2017 | 11/28/2017 |
|
Not started | |
| 11
12 13 |
11/29/2017 | 12/19/2017 |
|
Not started | |
| 12/20/2017 | DEMO: Final Project
SUBMISSION: Final Project Wiki |
Not started | |||
Parts List & Cost
| Item # | Description | Distributor | Qty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SJOne Board | Provided by Preet | 5 | $400 |
| 2 | RC Car - Traxxas 1/10 Slash 2WD | Amazon | 1 | $189.95 |
| 3 | Bluetooth Bee BLE 4.0 Module | ebay | 1 | $15 |
| 4 | GPS Module | Amazon | 1 | $28.99 |
| 5 | Compass (CMPS11) | Acroname | 1 | $45.95 |
| 6 | Traxxas 6520 RPM Sensor | Amazon | 1 | $10.82 |
| 7 | Traxxas 2991 LiPo Battery and Charger | Amazon | 1 | $199.95 |
| 8 | Breadboard Jumper Wires | Amazon | 1 | $6.99 |
| 9 | MIFFLIN Acrylic Plexiglass Clear Plastic Sheet | Amazon | 1 | $9.89 |
| 10 | Printed Circuit Board | Amazon | 1 | $16.83 |
| 11 | PCB Mounting Feet Set | Amazon | 1 | $11.99 |
| 12 | Traxxas 6538 Telemetry Trigger Magnet Holder | Amazon | 1 | $4.63 |
| 13 | MB1240 XL-MaxSonar EZ4 Ultrasonic Sensor | Amazon | 2 | $73.90 |
| 14 | Parallax Ping Ultrasonic Range Sensor | Amazon | 2 | $69.98 |
| 15 | CAN Transceiver | Microchip | 10 | Free |
| 16 | 4D systems 32u LCD | 4D Systems | 1 | $85.00 |
| 17 | Miscellaneous Items | 1 | $100.00 |
Master Controller
Design & Implementation
The master controller acts as the brainpower of the car and processes the data from the rest of the nodes to achieve smooth navigation of the car to its destination. As the master controller is the central controller of the entire system, it has to handle plenty of CAN messages.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Sensor Controller
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Motor & I/O Controller
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Geographical Controller
Group Members
- Abhilash Tuse
- Vishal Shrivastava
Design & Implementation
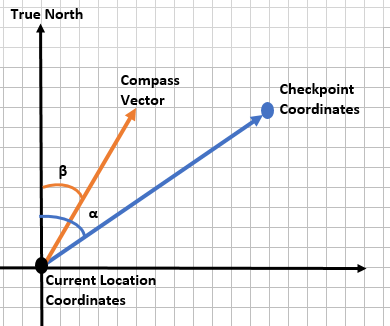
The Geographical Controller is in place for navigation purpose. It has two essential parts, namely GPS and compass. It provides direction to the car, by calculating the heading angle and the distance between the coordinates, based on GPS and compass readings. To calculate heading angle, we need compass bearing angle and angle between the line joining the two coordinates and the true north (bearing angle for GPS).
Bearing angle calculation between the line joining the two coordinates and the true north
With the reference to the figure, the bearing angle for GPS is the angle between the line joining the two coordinates and the true north. To calculate it graphically, draw a vector pointing towards the destination coordinates from the start point coordinate and measure the angle between the vector and the true north. Use the below formula to calculate the angle mathematically.
Bearing angle(α) = atan2(sin Δλ ⋅ cos φ2 , cos φ1 ⋅ sin φ2 − sin φ1 ⋅ cos φ2 ⋅ cos Δλ)
where,
φ1 = Latitude of 1st Coordinate
φ2 = Latitude of 2nd Coordinate
λ1 = Longitude of 1st Coordinate
λ2 = Longitude of 2nd Coordinate
Δλ = λ2 - λ1
Heading angle calculation
The heading angle is the angle between the compass vector and the vector drawn for calculating GPS bearing angle.
Heading angle(γ) = α – β
where,
α = Angle between the line joining the two coordinates and the true north
β = Angle between compass vector and the true north (Compass bearing angle)
If heading angle is positive the car turns right or else turns left.
Distance between the two coordinates calculation
The distance between the two coordinates can be calculated using the Haversine formula.
a = sin²(Δφ/2) + cos φ1 ⋅ cos φ2 ⋅ sin²(Δλ/2)
c = 2 ⋅ atan2(√a, √(1−a))
d = R ⋅ c
where,
φ1 = Latitude of 1st Coordinate
φ2 = Latitude of 2nd Coordinate
λ1 = Longitude of 1st Coordinate
λ2 = Longitude of 2nd Coordinate
Δφ = φ2 - φ1
Δλ = λ2 - λ1
d = distance between the two coordinates
R = earth’s radius (mean radius = 6,371km)
Note: All the angles should be in radians.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
GPS Module
Compass Module
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Android and Communication Bridge Controller
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
<Bug/issue name>
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.