Difference between revisions of "S14: Anti-Crash Car"
Proj user22 (talk | contribs) (→Servo and Wheel motor Communication) |
Proj user22 (talk | contribs) (→Servo and Wheel motor Communication) |
||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation. | This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation. | ||
| − | ====Servo and Wheel motor Communication==== | + | ====Servo and Wheel motor ( PWM ) Communication==== |
| − | |||
Servo and Wheel motor communication is done by using PWM communication. Interface for PWM is already given by Professor Preet. | Servo and Wheel motor communication is done by using PWM communication. Interface for PWM is already given by Professor Preet. | ||
| − | |||
1. We must set the pin that we want to use with the waveform period | 1. We must set the pin that we want to use with the waveform period | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 22 May 2014
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
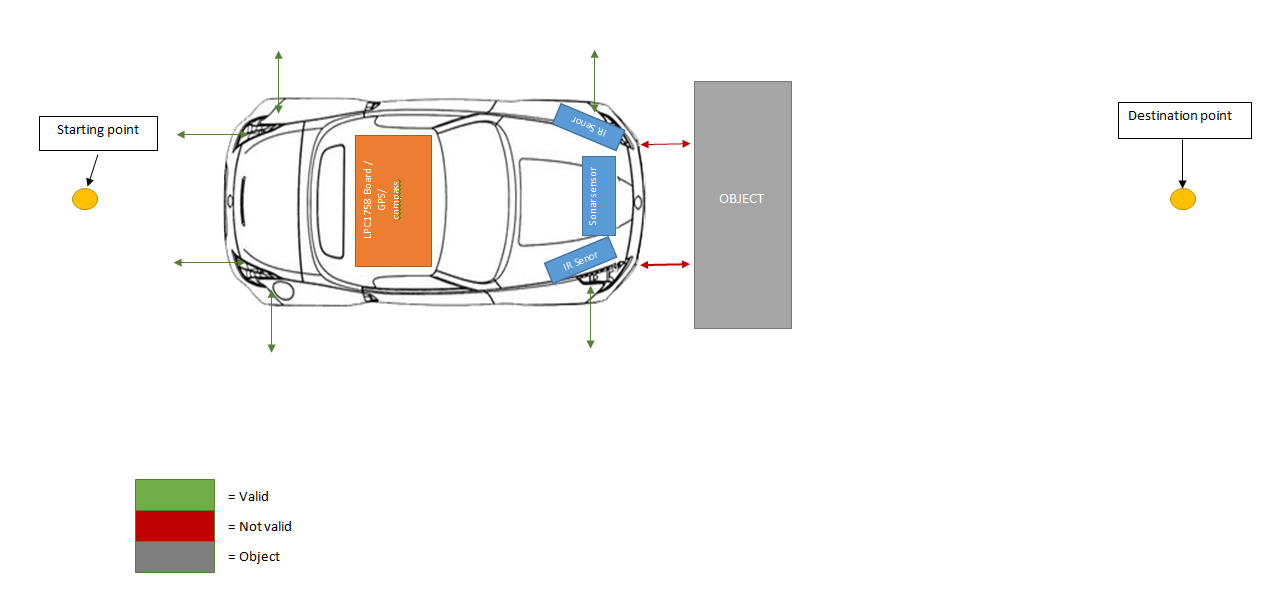
Anti-Crash Car
Abstract
The project involves a GPS controlled car that drives to a user determined destination and automatically stops or slows down when an obstacle is in its way in order to prevent itself from crashing. Any command that can potentially damage the car is disabled (e.g. moving forward when the obstacle is in front).
Objectives & Introduction
Show list of your objectives. This section includes the high level details of your project. You can write about the various sensors or peripherals you used to get your project completed.
NEED TO BE DONE
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Geff Lozano
- Infrared Sensor Module
- GPS Module
- Parser
- Information Processing
- System State Machine
- Koko Maung
- Car Kit Assembly
- Infrared Sensor Module
- Sonar Sensor Module
- Compass Module
- Servo / Wheels Motor
- State Machine
- Matthew Pham
- GPS Module
- UART Interface
- Parser
- Information Processing
- System State Machine
- GPS Module
Schedule
| Week# | Date | Task | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3/23 | Planning | Top-Level System Drafting |
| 2 | 3/30 | Top-Level System Design | Went through many drafts |
| 3 | 4/6 | Order Parts | Ordered GPS/compass unit, sonar sensor, IR sensor, and necessary accessories. |
| 4 | 4/13 | Assign peripheral responsibilities | Divided the work. |
| 5/6 | 4/20 | Peripheral Interfacing | GPS, Infrared, Sonar; No communication with GPS; Burned GPS; |
| 7 | 4/27 | System State Machine Implementation | Redrafted Original State Machine |
| 8 | 5/4 | Implementing | Started implementing State Machine with Peripheral devices together. Figured out that we purchased incorrect GPS / compass device. |
| 8 | 5/11 | Implementing | State machine and peripheral devices are working the we we predicted. Except compass. Order new compass |
| 8 | 5/18 | Implementing / Testing | Implementing State machine with compass. Did field testing. |
| 8 | 5/22 | Demo |
Parts List & Cost
| Qty | Part | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RC Rock Crawler | $200.86 |
| 1 | SRF08 Ultrasonic Range Finder | $54.30 |
| 4 | Sensor Housing MPSH-01 | $19.8 |
| 3 | GP2Y0A21YK0F IR Sensor - 10cm to 80cm | $59.4 |
| 3 | SIRC-01 Sensor Cable | $5.85 |
| 1 | 3DR GPS Module w/ Compass | $53.35 |
| 1 | Battery | $25.00 |
| 1 | FTDI Cable | $14.97 |
| 1 | GPS Receiver - LS20031 5Hz (66 Channel) | $59.95 |
| 1 | Compass Module 3-Axis HMC5883L | $15.99 |
| Total | $509.47 |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
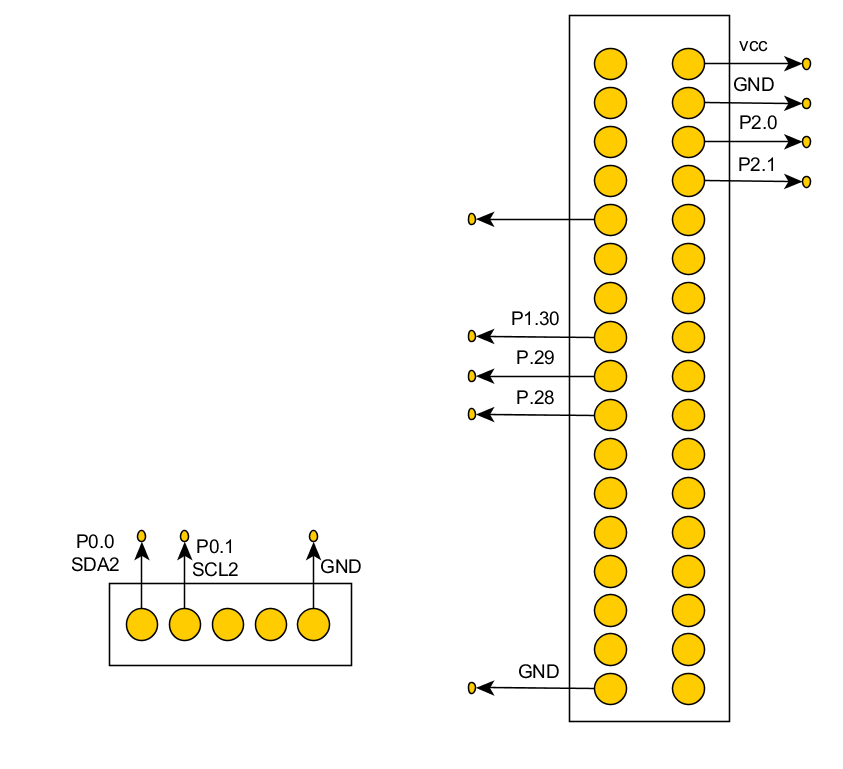
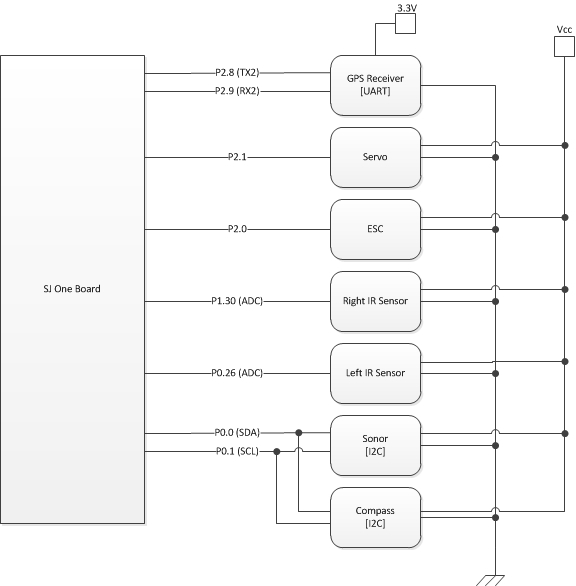
System Schematic
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
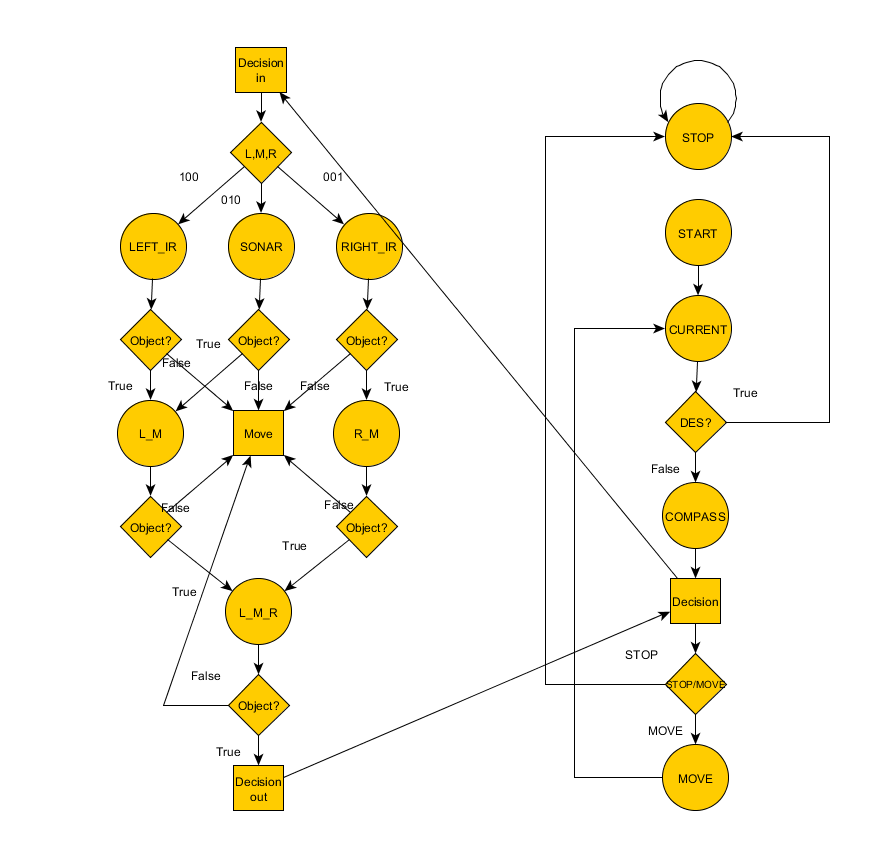
Design Flow
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Servo and Wheel motor ( PWM ) Communication
Servo and Wheel motor communication is done by using PWM communication. Interface for PWM is already given by Professor Preet.
1. We must set the pin that we want to use with the waveform period 2. set percentage of waveform to be stay at high.
eg.PWM pwm1(PWM::pwm1, 50); // pw1 = p0.0, period = 50
pwm1.set(10); // percent = 10 1/5 of the time signal gonna be high
GPS Communication
GPS Communication
GPS Communication
GPS Communication
UART
The GPS Receiver communicates with the SJ One board through UART via NMEA sentences.
Examples:
- The user can configure the update (baud) rate of the GPS module with the following example commands:
- 38400bps - $PMTK251,38400*27<CR><LF>
- 57600bps - $PMTK251,57600*2C<CR><LF>
- The user can filter out unwanted NMEA sentences with the following example commands:
- Only RMC at 1Hz - $PMTK314,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0*29<CR><LF>
- Only GGA at 1Hz - $PMTK314,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0*29<CR><LF>
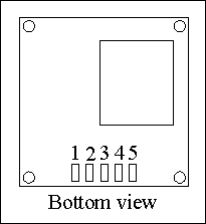
Pin Configuration
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power input |
| 2 | RX | Data input (TTL level) |
| 3 | TX | Data output (TTL level) |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
Test Phase 1: Individual Peripherals
Individual Peripherals
Test Phase 2: System State Cases
Checking state machine
Test Phase 3: State Cases with Peripherals
Test Phase 4: Field Testing
My Issue #1
PWMs : I found out PWMs for servo and wheels motor must run at 50Hz even though motor is capable of handling faster frequency. When we use other frequency, the hand shake between PWMs and motor will not sync correctly.
Solution : We end up using 50Hz and we had to operate motor at slower speed.
My Issue #2
Interrupt : When we had 2 interrupts and functional calls involve together, our code will not perform the way we expected. The system get crash or freeze time to time.
Solution : We end up putting sensor, gps, motor and state machine code in tasks.
My Issue #3
Sensors : We found out that if we try to read value too fast, we ended up getting zero.
Solution : We wrote a case when the value is zero, we keep the previous value for one time.
GPS Issues
Problems:
- The ordered GPS Receiver (LS20031) was not the one received (LS23060).
- There were no specific datasheets for the acquired model (LS23060).
- The datasheet for LS20031 was used instead. NOTE: Use LS20031 specifications with caution.
- The baud rate specified in the datasheet (57600bps) did not match the baud rate of the acquired GPS Receiver (38400bps).
- Communication between the GPS Receiver and the SJSU development board was not possible due to mismatched baud rates. The GPS Receiver baud rate cannot even be set to a desired baud rate through PTMK commands without being in sync with the command sender in the first place.
Solution:
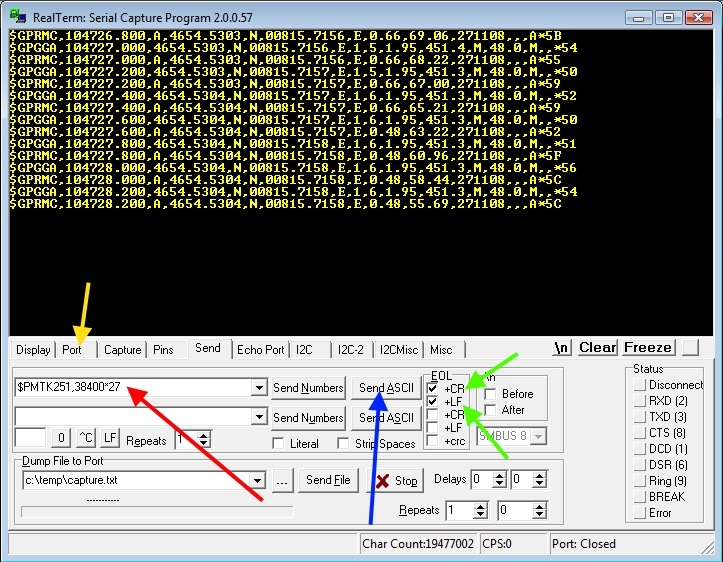
The solution was to use an FDTI cable (UART to USB) with Realterminal (http://realterm.sourceforge.net/index.html#downloads_Download) for synchronization.
- Using Realterminal, users can determine the baud rate of the GPS Receiver through trial and error--changing the port baud rate until NMEA sentences are displayed.
- e.g. $--GGA,hhmmss.ss,llll.ll,a,yyyyy.yy,a,x,xx,x.x,x.x,M,x.x,M,x.x,xxxx.
- See GPS - NMEA sentence information for more examples.
- Only until the Port is initially synced with the GPS Receiver, users cannot set the GPS Receiver to a desired baud rate. When the port is in sync, the following actions can be taken:
- With Realterminal open, click the Send Tab and check "+CR" and "+LF" flags.
- Send the string "$PMTK314,-1*04" as ASCII to reset the GPS to its default configuration. The baud rate will then be reset to 38400bps.
- Now the SJSU development board can communicate through PTMK commands at UART - 38400bps.
Car Response Time
Problem
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
Send me your zipped source code and I will upload this to SourceForge and link it for you.
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.