Difference between revisions of "S13: Garage Parking Aid"
(→Hardware Interface) |
(→References Used) |
||
| Line 237: | Line 237: | ||
* https://www.sparkfun.com/products/158 | * https://www.sparkfun.com/products/158 | ||
| − | |||
* https://s3-ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/sain-amzn/20/20-019-100/HC-SR04.rar | * https://s3-ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/sain-amzn/20/20-019-100/HC-SR04.rar | ||
| + | * http://wiring.org.co/learning/tutorials/bluetooth/ | ||
| + | * http://www.lynxmotion.com/images/html/build117.htm | ||
=== Appendix === | === Appendix === | ||
You can list the references you used. | You can list the references you used. | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 22 May 2013
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Garage Parking Aid
Abstract
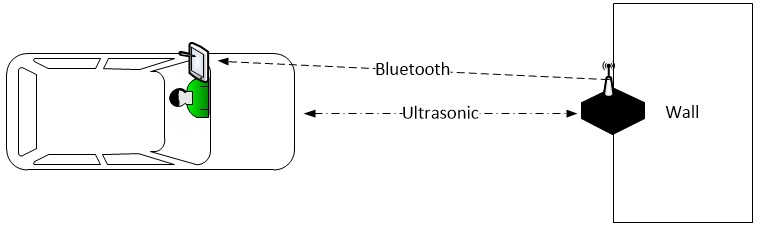
The purpose of this project is to aid when parking a car. This device will send to an Android phone the distance between the car and an obstacle.
Objectives & Introduction
The purpose of this project is to build a parking aid that will measure the distance between an object and a car and send the data to the user's Android phone. An ultrasonic transmitter/receiver is used to measure the distance and bluetooth is used to send data to the Andoid phone.
Objectives:
- Measure distance and display on computer screen
- Send data over bluetooth
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Elizabeth
- Create UART2 driver
- Wire peripherals
- Send messages with Bluetooth
- Tian
- Create Android app
- Assemble project into a box
- Configure ultrasonic distance meter
Schedule
| Week Number | Planned Items | Actual |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
Parts List & Cost
| Parts | Cost |
|---|---|
| SJ One Board | $65 |
| Bluetooth | $0 |
| 2.4 GHz Antenna | $5 |
| Ultrasonic transmitter and receiver | $10 |
| Blackbox | $0 |
| Wire | $10 |
| Batteries | $7 |
| Total: | $97 |
Design & Implementation
Hardware Design
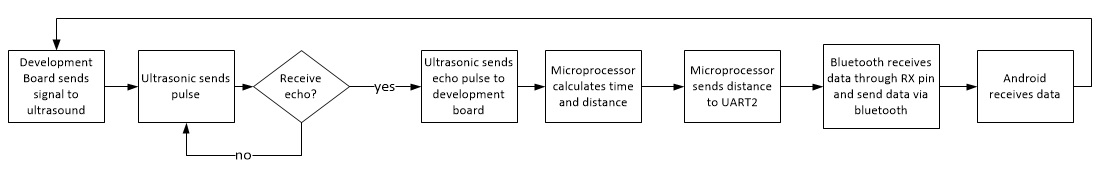
The following hardware components are all that we used for this project. The LPC1758 Processor on the SJSU_ONE Development Board, which is powered by the battery pack, controls everything through the board. It activates the ultrasonic module, gets the time reading from it, computes the readings into distance and then transfer the data to bluetooth module, then the bluetooth module will send the received data to the Android Application on a paired bluetooth Android Device through the 2.4Ghz Antenna.
Hardware Interface
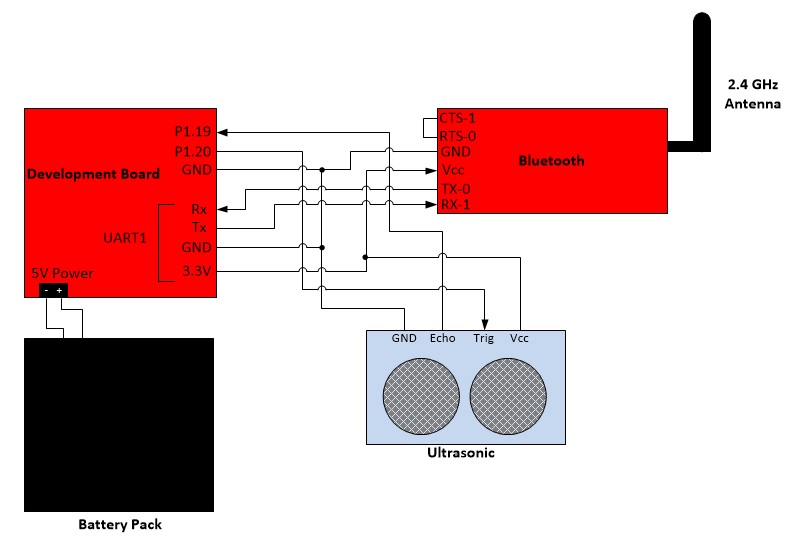
Hardware Communication: The development board is connected to the bluetooth chip and ultrasonic receiver/transmitter. The bluetooth receives data through pin RX-1, which is TX on the processor's end and transmits the data over bluetooth. The ultrasonic receives a trigger signal through the pin Trigger then sends an ultrasonic pulse. When the Echo pin is read back it will send an high signal back to the board for a brief period and that's the time sonic wave has been sent out and returned. The battery gives 5V power to development board and ultrasonic.
The Bluetooth device is connected to UART1 and the ultrasonic device is connected to GPIO. To communicate with the Bluetooth, the program sends data to UART1 and then is sent to bluetooth. To comunicate with the ultrasonic, the program sends and receives data from the board's pins P1.20 and P1.19, which are programmed to be output and input.
Another option to capture the time of the ultrasonic's pulse is to program the GPIO pins to be PWM and capture. The PWM pin will output a pulse to the ultrasonic and the ultrasonic will send an ultrasonic pulse. When it receives an echo of the pulse it will send a pulse to the caputure pin. When the capture pin receives a change in voltage, it will store the time into a designated register.
Software Design
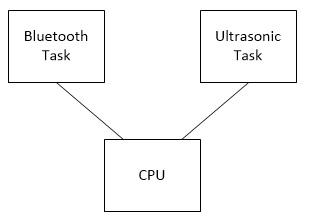
For Software Design, we have two Tasks dedicated for two components: bluetooth_task & ultrasonic_task. And we use queue for data transfer between two tasks.
Ultrasonic_task
This task takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to its private local variable. 2 Pins are initialized: Trigger as output, Echo as input. Then run the task, set Trigger Pin high for 20us and clear it. This will activate ultrasonic module to send 8 pulses of sound wave. Then monitor the Echo Pin, and once the Echo Pin goes high, start the timer and stop the timer when it falls back to low. This is the time for the soundwave to be sent out and echo back. Take this time and multiple by the speed of sound, then divided by two, That's the one way distance, which is what we want. ( Distance = ((Duration of high level)*(Sonic :340m/s))/2 ) After that, we use xQueueSend function to immediately send this distance value to the queue handler, and end this run. This task is designed to run every 2 sec.
Bluetooth_task
This task also takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to a private local variable; in addition, this task has another private variable that will get the instance of Uart2 Class, which controls ports connected to our bluetooth module, which is actually labeled as Uart1; and a third variable called distance, that will store the distance received from queue. The task first initializes the bluetooth module, then runs in a loop, checking if anything is on the queue, if yes, it immediately receives it and store it to local variable, distance, and output a message string containing the distance to the paired android device.
Main Function
The main function is really simple, it first creates a queue handle with xQueueCreate, then calls both tasks and pass the address of this handle to them.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
Wifi Connection Issues
Many wifi connection issues were encountered. To solve this problem, a dedicated task was created to re-connect to wifi if the connection was ever lost.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
Send me your zipped source code and I will upload this to SourceForge and link it for you.
References
Acknowledgement
- Preet Kang
- Dr. Haluk Ozemek
References Used
List any references used in project.
- https://www.sparkfun.com/products/158
- https://s3-ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/sain-amzn/20/20-019-100/HC-SR04.rar
- http://wiring.org.co/learning/tutorials/bluetooth/
- http://www.lynxmotion.com/images/html/build117.htm
Appendix
You can list the references you used.