Difference between revisions of "S17: Boom-Z Equalizer"
Proj user14 (talk | contribs) (→Equalizer) |
Proj user14 (talk | contribs) (→Equalizer) |
||
| Line 257: | Line 257: | ||
<p>Figure 3. Strobe Timing diagram | <p>Figure 3. Strobe Timing diagram | ||
[[File:CMPE244_S17_TZFORCE_strobe_timing_diagram.PNG]] | [[File:CMPE244_S17_TZFORCE_strobe_timing_diagram.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The code below shows the ADC reading implementation. As shown, the task loops for 7 times to read 7 different frequencies (for left and right outputs.) A <b>struc</b> was used to represent the frequency values and to make it easier to send to a queue. Take note that the reading only occurs when the strobe pins are driven <b>low</b>. In order to read the next frequency, the strobe pins need to be driven <b>high</b> and then <b>low</b> again. | ||
<pre>Code snippet | <pre>Code snippet | ||
Revision as of 00:44, 22 May 2017
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Project Title
Boom-Z Equalizer
Abstract
The purpose of this project is to allow the team to experiment with a sound reactive project. The team will use a specialized IC to convert the input audio signal into a digital signal that can be parsed by the SJSUone board. The team will also create the LED array grid that will be used to display the waveform/frequency representation of the audio signal. The final project should be able to take an input audio signal (using a regular audio cable/jack) and display some kind of frequency representation using the LED array grid.
Objectives & Introduction
Show list of your objectives. This section includes the high level details of your project. You can write about the various sensors or peripherals you used to get your project completed.
Introduction
The team split the project into two parts: The equalizer and the LED Matrix part. Thus, the team split into two sub-teams to tackle these two parts separately. The Equalizer task focuses on the conversion of audio input into an ADC output that can be parsed and create a data representation for the LED Matrix task. The LED Matrix task's main focus is to parse the converted data and drive the LEDs to display the appropriate representation of the signals.
Objectives
- design Equalizer hardware
- design Equalizer pcb
- design LED Matrix hardware
- design overall software architecture
- implement equalizer driver
- implement LED matrix driver
- integrate equalizer and LED matrix
- test overall system
Team Members & Responsibilities
- David Bui
- Equalizer Hardware Design
- Equalizer PCB Design
- Marvin Flores
- Overall software design
- Equalizer driver
- Adam Iglesias
- LED Matrix driver
- Mina Yi
- LED Matrix hardware design
Schedule
| Week# | Date | Task | Actual |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3/19 |
|
|
| 2 | 3/26 |
|
|
| 3 | 4/2 |
|
|
| 4 | 4/9 |
|
|
| 5 | 4/16 |
|
|
| 6 | 4/23 |
|
|
| 7 | 4/30 |
|
|
| 8 | 5/7 |
|
|
| 9 | 5/14 |
|
|
| 10 | 5/21 |
|
|
Parts List & Cost
Bill of Materials for Graphic Equalizer
| # | Name | Purchase Location | Description | Quantity | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MSGEQ7 | [1] | 7 Band Graphic Equalizer | 2 | $4.95 |
| 2 | capacitor | HSC Electronics | .1 uF capacitor | 7 | $0.35 |
| 3 | capacitor | HSC Electronics | 33 pF capacitor | 2 | $0.40 |
| 4 | capacitor | HSC Electronics | .33 uF capacitor | 1 | $0.35 |
| 5 | capacitor | HSC Electronics | 10 uF capacitor | 1 | $0.35 |
| 6 | capacitor | HSC Electronics | 100 nF capacitor | 1 | $0.35 |
| 7 | resistor | HSC Electronics | 200kΩ resistor | 2 | $0.05 |
| 8 | resistor | HSC Electronics | 22kΩ resistor | 2 | $0.05 |
| 9 | power jack | HSC Electronics | power jack | 1 | $0.45 |
| 10 | audio jack | HSC Electronics | audio jack | 1 | $0.45 |
| 11 | voltage regulator | HSC Electronics | 3V voltage regulator | 1 | $0.25 |
| 12 | voltage regulator | HSC Electronics | 5V voltage regulator | 1 | $0.25 |
| 13 | male header pins | HSC Electronics | male header pins | 1 | $0.95 |
Bill of Materials for LED Matrix
| # | Name | Purchase Location | Description | Quantity | Cost per item |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LED Strip | Amazon | APA102C LEDs | 1 | $29.88 |
| 2 | PCB | Bay Area Circuits | 9.6" x 5" | 1 | $30 |
| 3 | Shadowbox | Michaels | 10" x 10", 4.5" depth | 1 | $32.99 |
| 4 | Thin Plywood | Home Depot | 9.5" x 9.5" | 1 | Varies |
| 5 | Power Supply | Amazon | Mean Well 5v 5A power supply | 1 | $13.22 |
| 6 | 3 Pronged Power Cord | Home Depot | Husky 8ft 3 pronged power replacement cord | 1 | $9.97 |
Design & Implementation
The design section can go over your hardware and software design. Organize this section using sub-sections that go over your design and implementation.
Hardware Design
Graphic Equalizer
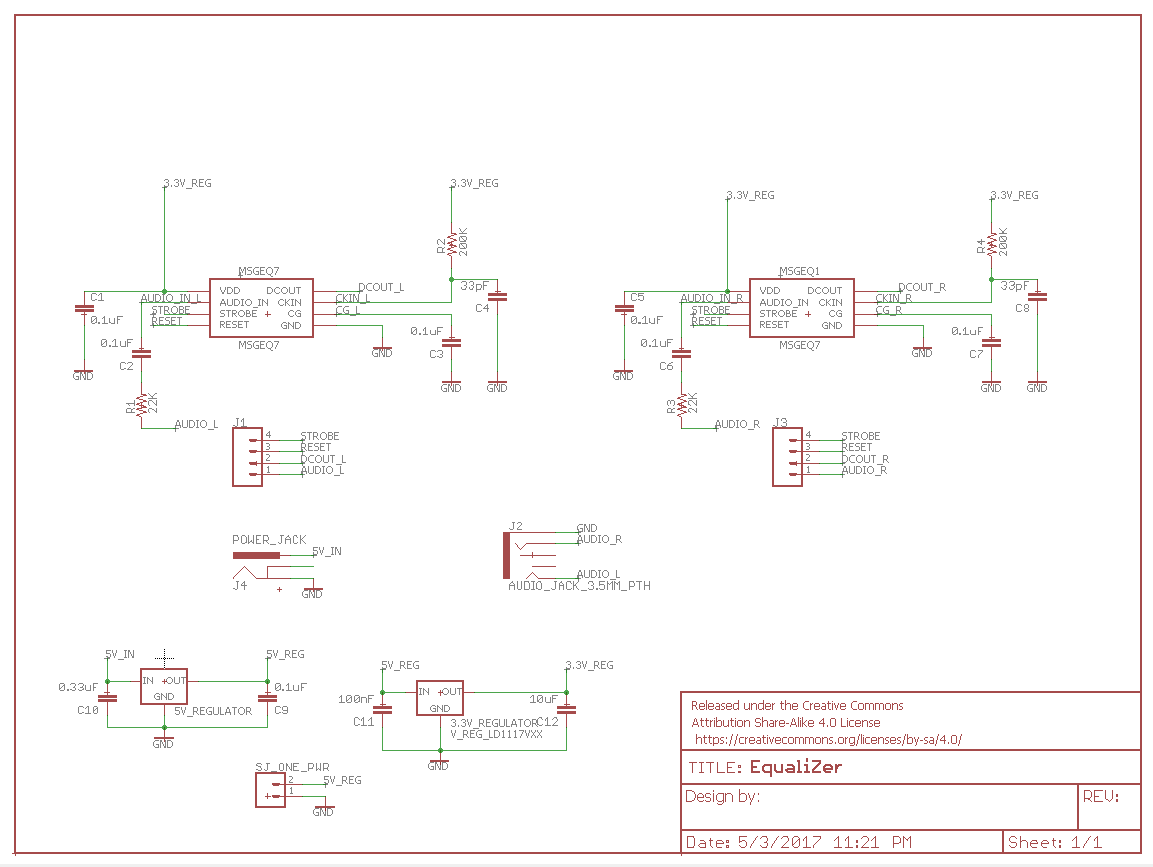
The main purpose of the graphic equalizer is to be able to take an audio input and generate an ADC output signal. The output values will be used to drive the LED Matrix values. The team decided to use MSGEQ7 chip for its simple design and ease of use. The MSGEQ7 Graphic equalizer can take an audio signal and 'split' it into 7 different frequencies. The team used two MSGEQ7 chips to separate left and right audio signal; this allowed the team to have more column of frequencies to display in the LED matrix.
The board design is very straight forward. The strobe and reset source are the same on both MSGEQ7 chip; left and right audio input are split to each designated MSGEQ7 chip. The output for both chips are fed into the ADC inputs of the SJSUOne board. Voltage regulators are added to power the equalizer system and the SJSUOne board using one DC adapter. The tricky part was to write the software driver to parse the frequency outputs which will be discussed in the software implementation below.
Figure 1. Equalizer Schematic
LED Matrix
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
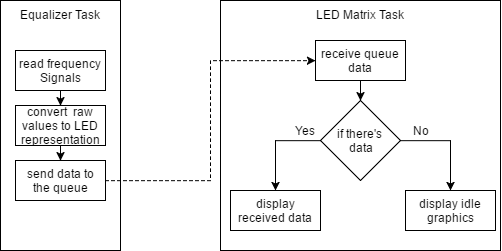
The Equalizer task reads ADC values from the Equalizer Board and converts them into LED Matrix representation values. The converted values are then sent to the queue which the Matrix LED driver task is listening. The Matrix LED driver interprets the data and drive the LEDs to display the appropriate signal representation.
Figure 2. Software diagram
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Equalizer
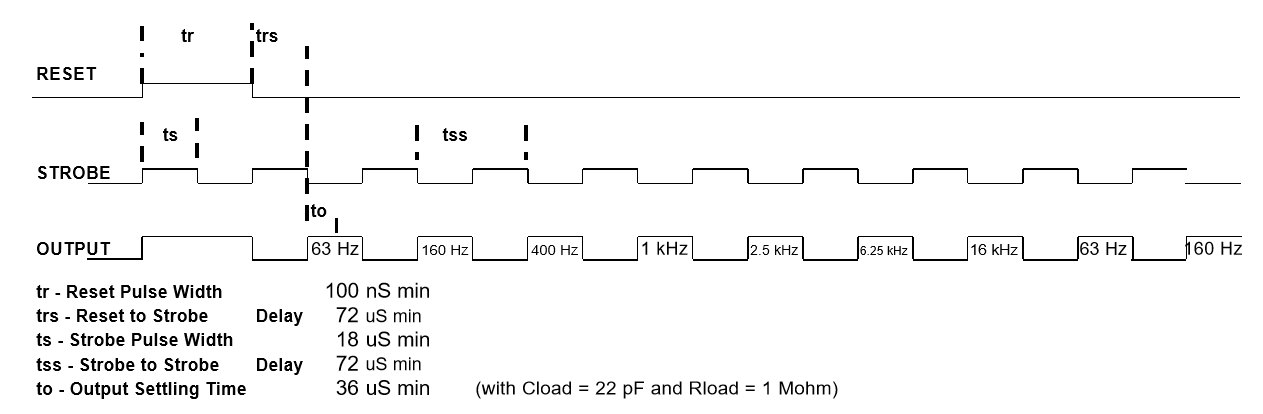
The MSGEQ7 chip has a unique way of outputting the analog signals (as shown in the strobe timing diagram below). The software needs to drive the GPIO pins to generate the strobe signal. The strobe signal is needed to be precisely controlled in order to read the analog outputs properly. Fortunately, the chip doesn't have a very strict timing and only has minimum values signal widths.
Figure 3. Strobe Timing diagram
Code snippet
for(int i = 0; i<7; i++) {
clear_pin(STROBE_PIN_LEFT); //Clear Strobe_Pin 2.0
clear_pin(STROBE_PIN_RIGHT); //Clear Strobe_Pin 2.2
current_time_us = sys_get_uptime_us() + 36;
while(sys_get_uptime_us() < current_time_us);
uint16_t leftRawValue = readPinValueP026();
uint16_t rightRawValue = readPinValueP131();
frequencyData.left[i] = convertSignalToMatrixReadable(leftRawValue);
frequencyData.right[i] = convertSignalToMatrixReadable(rightRawValue);
set_pin(STROBE_PIN_LEFT); //Set Strobe_Pin 2.0
set_pin(STROBE_PIN_RIGHT); //Set Strobe_Pin 2.2
current_time_us = sys_get_uptime_us() + 36;
while(sys_get_uptime_us() < current_time_us);
}
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
LED Matrix Design
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.