Difference between revisions of "S15: Drone"
Proj user20 (talk | contribs) (→Brushless Motors) |
Proj user20 (talk | contribs) (→Brushless Motors) |
||
| Line 252: | Line 252: | ||
=== Brushless Motors === | === Brushless Motors === | ||
| − | [[S15_244_BrushlessandProp_drone. | + | [[File:S15_244_BrushlessandProp_drone.PNG|250px|thumb|right|Fig 1.Brushless Motors]] |
=== ESC(Electronic speed control) === | === ESC(Electronic speed control) === | ||
Revision as of 23:31, 23 May 2015
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Quadcopter
Abstract
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are gaining popularity in military operations as surveillance and weapons platforms, UAV's are being produced more than the conventional aircrafts. A recent rule in 2012, where an UAV less than a 55 pounds can be used for commercial purpose has brought lot of research in industries. A commonly used UAV is a quad-copter, which is used widely in commercial applications like delivering pizzas's, couriers,etc. Apart from commercial use, a quadcopter could can save someone's life by reaching the spot in emergency situations before an ambulance and deliver first aid kit.
Objectives & Introduction
Show list of your objectives. This section includes the high level details of your project. You can write about the various sensors or peripherals you used to get your project completed.
The goal of the project is to design an autonomous Quadcopter capable of self-sustained flight via wireless communications utilizing SJ-One board which is used as a flight control board. The Flight control board is the brain of the multirotor and it takes continuous measurements from the sensors and adjusts the speed of every motor inorder to be stable. The brushless motors are controlled by the AfroESC.
PID Brief Introduction:
PID (proportional-integral-derivative) is a closed-loop control system that try to get the actual result closer to the desired result by adjusting the input. Quadcopters or multicopters use PID controller to achieve stability.
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Bhushan Gopala Reddy
- Karthik Govindaswamy
- Rishikesh Nagare
- Mayur Salve
- Manuj Shinkar
Schedule
Show a simple table or figures that show your scheduled as planned before you started working on the project. Then in another table column, write down the actual schedule so that readers can see the planned vs. actual goals. The point of the schedule is for readers to assess how to pace themselves if they are doing a similar project.
| Sl.No | Start Date | End Date | Task | Status | Actual Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 03/17/2015 | 03/24/2015 | Ordered parts for quad-copter | Completed | 09/24/2015 |
| 2 | 03/25/2015 | 03/31/2015 | Assembled quad-copter and Tested it using pre-programmed board (KK 2.1.5). | Completed | 03/31/2015 |
| 3 | 04/01/2015 | 04/07/2015 | Interfaced Motors and RC to SJOne Board. | Completed | 04/07/2015 |
| 4 | 04/07/2015 | 04/14/2015 | Study quad-copters software framework provided by Preet | Ongoing | --/--/2015 |
| 5 | 04/14/2015 | 04/21/2015 | Interface and test 10-DOF IMU sensor by Adafruit. | Ongoing | --/--/2015 |
| 6 | 04/21/2015 | 05/05/2015 | Understanding and Tuning PID values. | --/--/2015 | |
| 7 | 05/05/2015 | 05/19/2015 | Final Testing. | --/--/2015 |
Parts List & Cost
Give a simple list of the cost of your project broken down by components. Do not write long stories here.
| Item# | Part Desciption | Vendor | Part Number | Qty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Motors and Propellers | tiger motors | 2 | $89.99 | |
| 2 | Afro ESC 30 Amp Speed Controller (SimonK Firmware) | Turnigy | 6 | $84 | |
| 3 | Turnigy 9X 9Ch Transmitter w/ Module & 8ch Receiver (Mode 2) (v2 Firmware) | Turnigy | 1 | $59.99 | |
| 4 | Turnigy nano-tech 4000mAh 3S1P 25-50C Lipo Pack | Turnigy | 1 | $26.90 | |
| 5 | Hobbyking SK450 Glass Fiber Quadcopter Frame 450mm | Hobbyking | 1 | $17.99 | |
| 6 | Landing Kit set | Hobbyking | 1 | $9.49 | |
| 7 | Hobbyking Quadcopter Power distribution board | Hobbyking | 1 | $3.39 | |
| 8 | Hobbyking Lipoly low voltage alarm | Hobbyking | 1 | $2.15 | |
| 9 | Turnigy Battery Strap | Hobbyking | 1 | $1.59 | |
| 10 | Mounting pad | Hobbyking | 1 | $1.99 | |
| 11 | 4mm bullet heads to connect battery to power distribution board | polymax | 1 | $2.83 | |
| 12 | Vibration damping balls | 1 | $9.10 | ||
| 13 | 3.5 mm bullet heads for power break distribution board | 1 | $1.83 | ||
| 14 | iMax B6 Battery Charger | 1 | $33.46 |
Design & Implementation
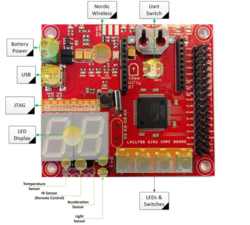
This section describes the hardware and software implementation. The quadcopter consist of the main frame, flight controller board (SJ-One Board), motors with ESC and the battery system. The Airframe used in this project is Hobbyking SK450 Glass Fiber Quadcopter Frame 450mm.
Hardware Design
Discuss your hardware design here. Show detailed schematics, and the interface here.
The quadcopters flight controller system is discussed in the block diagram shown below. The subsystem consists of following:
- SJ- One Board
- RX - Receiver Turnigy
- Adafruit 10-DOF IMU sensor
- Brushless Motors
- ESC(Electronic speed control)
The power is fed to the motors using the power distribution board. The power comes from 3S 11.2V LIPO battery Pack.
SJ-One Board
Brushless Motors
ESC(Electronic speed control)
Inertial Measurement Unit
The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an integrated sensor device which measures accleration and tilt by Accelerometer, angular velocity and orientation by Gyroscope and gravitational forces by Magnetometer. Inertial Measurement Unit by Adafruit provides 10 DOF(actually 11) i.e 3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis magnetometer barometric pressure sensor and temperature sensor. These values are sent to SJ-1 board over I2C, where the further processing is done by SJ-1 board to determine the angular position and orientation of the Quadcopter.
Remote Controller
Need to change according to our final setup
| Pin Number | Function |
| P0.0 | RC-Ch1 - Roll |
| P0.1 | RC-Ch2 - Pitch |
| P0.29 | RC-Ch3 - Throttle |
| P0.30 | RC-Ch4 - Yaw |
Hardware Interface
In this section, you can describe how your hardware communicates, such as which BUSes used. You can discuss your driver implementation here, such that the Software Design section is isolated to talk about high level workings rather than inner working of your project.
Software Design
Show your software design. For example, if you are designing an MP3 Player, show the tasks that you are using, and what they are doing at a high level. Do not show the details of the code. For example, do not show exact code, but you may show psuedocode and fragments of code. Keep in mind that you are showing DESIGN of your software, not the inner workings of it.
PID
PID (proportional-integral-derivative) is a closed-loop control system that try to get the actual result from the IMU sensors closer to the desired result from the RC transmitter by adjusting the input. Quadcopters use PID controller to achieve the stability.
There are 3 algorithms in a PID controller, they are P(Proportional), I(Integral), and D (Derivative) respectively. P depends on the present error, I on the accumulation of past errors, and D is a prediction of future errors, based on current rate of change of the Quadcopter.
To obtain the control and stability of the quadcopter we do the following, for example consider we are doing it for pitch axis, the user provides some input to the quadcopter which becomes the requested value, at the same time sensor outputs the present value for the pitch axis for the quadcopter. The three alogorithms P, I and D finds the difference between the requested and the present values which is calculated as an error and apply these values on the motor which are the applied values to reduce the error. Similarly it is done for other 2 axis i.e Roll and Yaw to obtain the overall stability of the Quadcopter.
Implementation
This section includes implementation, but again, not the details, just the high level. For example, you can list the steps it takes to communicate over a sensor, or the steps needed to write a page of memory onto SPI Flash. You can include sub-sections for each of your component implementation.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Describe the challenges of your project. What advise would you give yourself or someone else if your project can be started from scratch again? Make a smooth transition to testing section and described what it took to test your project.
Include sub-sections that list out a problem and solution, such as:
My Issue #1
Discuss the issue and resolution.
Conclusion
Conclude your project here. You can recap your testing and problems. You should address the "so what" part here to indicate what you ultimately learnt from this project. How has this project increased your knowledge?
Project Video
Upload a video of your project and post the link here.
Project Source Code
References
Preetpal Kang, Professor of CMPE 244, Computer Engineering, Charles W. Davidson College of Engineering, San Jose State University, Feb-May 2015.
Acknowledgement
Any acknowledgement that you may wish to provide can be included here.
References Used
List any references used in project.
Appendix
You can list the references you used.