Difference between revisions of "F13: Remote Control Car"
Proj user2 (talk | contribs) (→Testing) |
(→Project Source Code) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Remote Control Car == | == Remote Control Car == | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| − | The goal of this project is to use 2 SJSU Development boards to control a remote control car. The first board will act as the controller using motion for control (throttle and steering). The second board will be mounted on the car and control the servo and motor controller. | + | The goal of this project is to use 2 SJSU Development boards to control a remote control car. The first board will act as the controller using motion for control (throttle and steering). The second board will be mounted on the car and control the servo and motor controller with a front proximity sensor. |
== Objectives & Introduction == | == Objectives & Introduction == | ||
| Line 56: | Line 44: | ||
! scope="col"| Week# | ! scope="col"| Week# | ||
! scope="col"| Task | ! scope="col"| Task | ||
| − | ! scope="col"| | + | ! scope="col"| Planned |
| + | Date | ||
! scope="col"| Completion | ! scope="col"| Completion | ||
Date | Date | ||
| Line 97: | Line 86: | ||
Integrate & Test system with simulated R/C Car | Integrate & Test system with simulated R/C Car | ||
| 11/12 | | 11/12 | ||
| − | | | + | | 11/05 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| 7 | ! scope="row"| 7 | ||
| Line 172: | Line 161: | ||
== Design & Implementation == | == Design & Implementation == | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Hardware Design === | === Hardware Design === | ||
| Line 180: | Line 169: | ||
=== Hardware Interface === | === Hardware Interface === | ||
| − | |||
The TX board used the following interfaces: | The TX board used the following interfaces: | ||
| − | * Accelerometer sensor for steering and throttle control | + | * I2C Bus |
| − | * Nordic wireless interface for transmitting control packets | + | ** Accelerometer sensor for steering and throttle control |
| − | * Switches for Enable/Disable of Control and Sensor (GPIO) | + | ** LED number display for throttle position |
| − | + | * SPI Bus | |
| + | ** Nordic wireless interface for transmitting control packets | ||
| + | * GPIO | ||
| + | ** Switches for Enable/Disable of Control and Sensor (GPIO) | ||
| + | |||
The RX board used the following interfaces: | The RX board used the following interfaces: | ||
| − | * Nordic wireless interface for receiving control packets ( | + | * I2C Bus |
| − | * PWM interface to steering servo (50Hz | + | ** Accelerometer sensor to detect upside or flipping of car |
| − | * PWM interface to electronic speed control (50Hz | + | ** LED Display (numbers) for error codes |
| − | * Analog to Digital Converter from proximity sensor (LPC1758) | + | * SPI Bus |
| − | * | + | ** Nordic wireless interface for receiving control packets |
| − | * Switches for Car Enable/Disable | + | * Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) |
| − | * Discrete LEDs for status such Car and Proximity Sensor Enable/Disable | + | ** PWM interface to steering servo (50Hz) |
| − | + | ** PWM interface to electronic speed control (50Hz) | |
| + | * A/D Converter | ||
| + | ** Analog to Digital Converter from proximity sensor (LPC1758, 12-bit) | ||
| + | * GPIO | ||
| + | ** Switches for Car Enable/Disable | ||
| + | ** Discrete LEDs for status such Car and Proximity Sensor Enable/Disable | ||
=== Software Design === | === Software Design === | ||
| − | |||
| − | RX Board Software Diagram | + | '''RX Board Software Diagram''' |
[[File:CmpE240_F13_RCCAR_RxBoardSw.jpg]] | [[File:CmpE240_F13_RCCAR_RxBoardSw.jpg]] | ||
| − | TX Board Software Diagram | + | '''TX Board Software Diagram''' |
[[File:CmpE240_F13_RCCAR_rxsoftware.jpg]] | [[File:CmpE240_F13_RCCAR_rxsoftware.jpg]] | ||
=== Implementation === | === Implementation === | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Switch De-bounce Timer | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
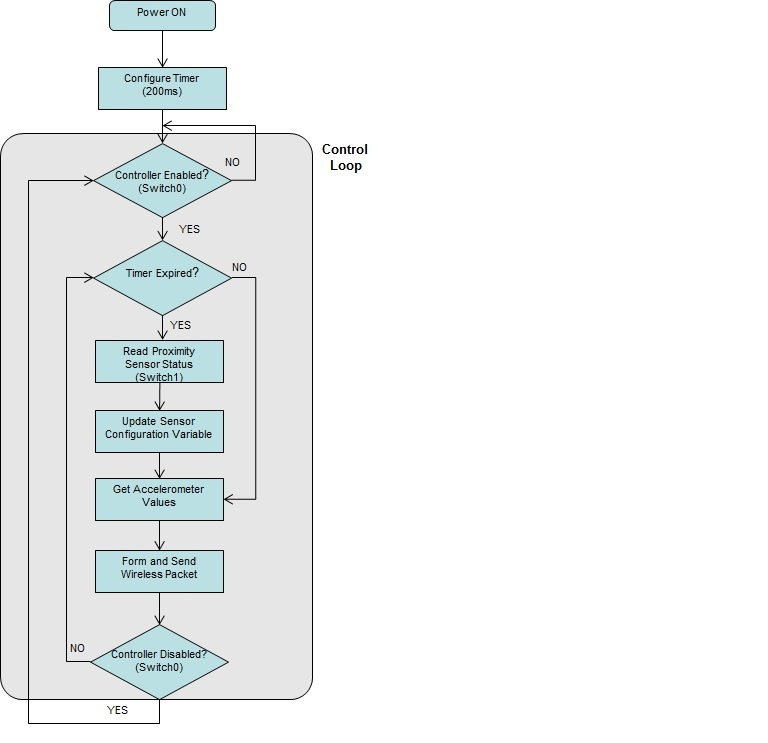
* A 200ms software timer is used to set the sensor configuration variable. At the beginning of the control loop, if the timer has expired then the switch status is read and the configuration is updated. This is to "de-bounce" the switch. | * A 200ms software timer is used to set the sensor configuration variable. At the beginning of the control loop, if the timer has expired then the switch status is read and the configuration is updated. This is to "de-bounce" the switch. | ||
| Line 227: | Line 220: | ||
=== Steering and Throttle Resolution === | === Steering and Throttle Resolution === | ||
| − | The initial design used 10 steps in each direction for direction and throttle. As a result, the steering was | + | The initial design used 10 steps in each direction for direction and throttle. As a result, the steering was incredibly jittery and acceleration of the car was difficult to control. After testing several settings, we settled on 100 steps. This allowed for smoother control with full range of steering motion. |
=== Proximity Sensor Detection === | === Proximity Sensor Detection === | ||
| Line 234: | Line 227: | ||
== Testing == | == Testing == | ||
| − | The TX board software and RX board software were tested independently prior to integration. Then the integration of the TX and RX board was performed in steps up to the final integrated configuration. | + | The TX board software and RX board software were tested independently prior to integration. |
| + | Then the integration of the TX and RX board was performed in steps up to the final integrated configuration. | ||
'''TX Board''' | '''TX Board''' | ||
| Line 251: | Line 245: | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
| − | + | The RC Control car was a fun project that also demonstrated that the simplest software solution to control hardware is usually the best. Integrating software and hardware with the knowledge of the hardware devices being controlled made integrated levels of degrees easier. The testing philosophy of verifying drivers as they are developed, rather than at final integration, proved successful. Since TX and RX boards software was tested by modules, individually, and finally integrated, the project came together smoothly. The UART interface was vital in the development as challenges encountered were quickly overcome. | |
| + | |||
| + | We did have some thoughts for future expansion on this project such as: | ||
| + | * Add GPS features to command the car to a location | ||
| + | * Add small video camera to utilize the SD card memory as a recorder | ||
| + | * Replace the electronic speed control to include reverse (current one only had forward and brake) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | All in all, the experience gave us good practical applications of standard interfaces such as I2C, UART, ADC and SPI to control multiple devices in a practical manner. | ||
=== Project Video === | === Project Video === | ||
| − | + | [http://youtu.be/JgZC1rasnzs Youtube Video Link] | |
=== Project Source Code === | === Project Source Code === | ||
| − | + | [https://sourceforge.net/projects/sjsu/files/CmpE240_LM_F2013/ Sourceforge Source Code] | |
== References == | == References == | ||
=== Acknowledgement === | === Acknowledgement === | ||
| − | Thank you Professor Kang for expanding our project with the supplied proximity sensor. | + | Thank you Professor Kang for expanding our project with the supplied proximity sensor and provided guidance. |
=== References Used === | === References Used === | ||
Latest revision as of 03:56, 8 December 2013
Contents
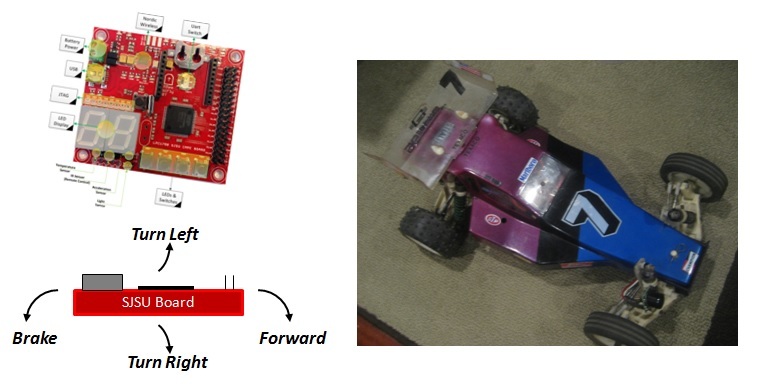
Remote Control Car
Abstract
The goal of this project is to use 2 SJSU Development boards to control a remote control car. The first board will act as the controller using motion for control (throttle and steering). The second board will be mounted on the car and control the servo and motor controller with a front proximity sensor.
Objectives & Introduction
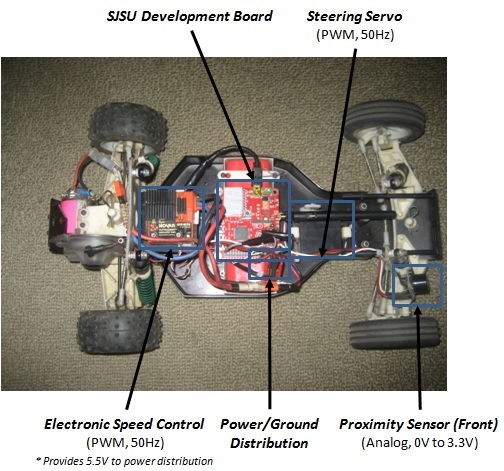
RX Board Overview
The RX board provides:
- Receives wireless commands from transmitter board
- Control for steering servo and speed throttle control
- Car On/Off button
- Proximity Sensor for front obstacle avoidance
- Stability control to self-correct if starting to flip over
TX Board Overview
The TX board provides:
- Wireless control of R/C using tilt detection (2-channel)
- Car On/Off button
- Front Proximity Sensor On/Off button
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Alan Wang
- TX Board software development including:
- Develop driver for Acceleration Sensor (throttle and steering)
- Develop Wireless message protocol between boards
- Develop TX board software to transmit commands
- TX Board software development including:
- Curtis Woodworth
- RX Board software/hardware development including:
- Integrate hardware onto R/C Car (board, power, cable)
- Develop RX board software to control RC car
- Develop front proximity sensor detection software
- RX Board software/hardware development including:
Schedule
| Week# | Task | Planned
Date |
Completion
Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify R/C Car usage and ensure operation
Identify & Order parts needed Complete Project Proposal document |
10/8 | 10/8 |
| 2 | Setup & build R/C Car
Test R/C operation with nominal controller Develop pin list for I/O use & types |
10/15 | 10/15 |
| 3 | Develop Accelerometer software driver
Develop Servo control software driver |
10/22 | 10/15 |
| 4 | Develop Transmitter data protocol
Develop Transmitter software driver Develop Proximity sensor software driver |
10/29 | 10/15 |
| 5 | Integrate accelerometer and transmitter drivers program
Integrate servo and proximity drivers into program |
11/5 | 10/29 |
| 6 | Integrate TX and RX development boards communications
Integrate & Test system with simulated R/C Car |
11/12 | 11/05 |
| 7 | Integrate & Test system with actual R/C Car | 11/19 | 11/18 |
| 8 | Demo Project
Finish report |
12/3 | 12/3 |
Parts List & Cost
| Part Number | Description | Price ($) | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| SJSUONE | SJSU-One Development Board | 75.00 | 2 |
| - | AA Battery Pack | 6.00 | 1 |
| RC10 | Associated RC10 Car | 305.00 | 1 |
| 410-MXc | Novak Electronic Speed Control | 90.00 | 1 |
| Stock | Pocket Rocket Motor | 25.00 | 1 |
| - | Sanyo 1400mA 7.2V Battery | 20.00 | 1 |
| S9302 | Futaba HS Steering Servo | 40.00 | 1 |
| MB1010 | LV-MaxSonar EZ1 | 30.00 | 1 |
| - | Misc Hardware | 8.00 | 1 |
| Total | 674.00 |
Design & Implementation
Hardware Design
The hardware development mostly consisted of integrated the R/C car and SJSU-one development board. The custom made cables and power distribution header required planning and custom soldering. The SJSJ-one board was mounted on the R/C car using screws with plastic spacers.
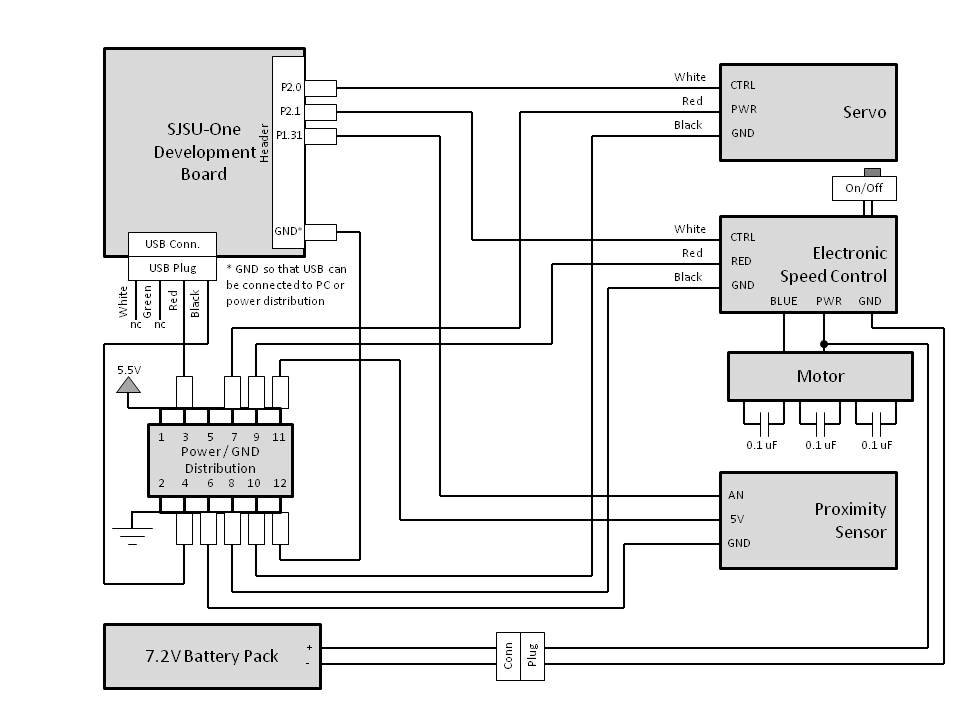
Hardware Interface
The TX board used the following interfaces:
- I2C Bus
- Accelerometer sensor for steering and throttle control
- LED number display for throttle position
- SPI Bus
- Nordic wireless interface for transmitting control packets
- GPIO
- Switches for Enable/Disable of Control and Sensor (GPIO)
The RX board used the following interfaces:
- I2C Bus
- Accelerometer sensor to detect upside or flipping of car
- LED Display (numbers) for error codes
- SPI Bus
- Nordic wireless interface for receiving control packets
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- PWM interface to steering servo (50Hz)
- PWM interface to electronic speed control (50Hz)
- A/D Converter
- Analog to Digital Converter from proximity sensor (LPC1758, 12-bit)
- GPIO
- Switches for Car Enable/Disable
- Discrete LEDs for status such Car and Proximity Sensor Enable/Disable
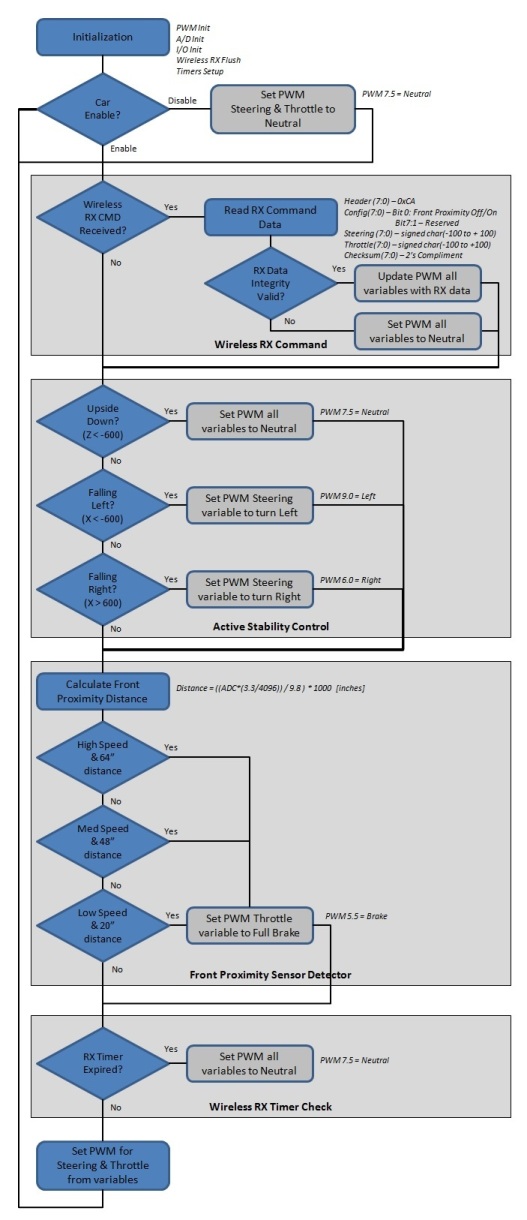
Software Design
RX Board Software Diagram
TX Board Software Diagram
Implementation
Switch De-bounce Timer
- A 200ms software timer is used to set the sensor configuration variable. At the beginning of the control loop, if the timer has expired then the switch status is read and the configuration is updated. This is to "de-bounce" the switch.
Steering and Throttle Resolution
- The 16-bit value read from the accelerometer is translated to an 8-bit value. The 8-bit value (capped at +/- 100) is then transmitted to the RX Board, to control steering and throttle. 100 steps in each direction provided smoother control and acceleration of the car.
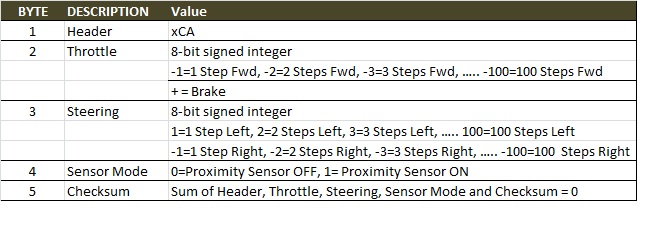
Wireless Command Format
- A header field and checksum was included with the control data to form the command packet. The format is shown below
Technical Challenges
Steering and Throttle Resolution
The initial design used 10 steps in each direction for direction and throttle. As a result, the steering was incredibly jittery and acceleration of the car was difficult to control. After testing several settings, we settled on 100 steps. This allowed for smoother control with full range of steering motion.
Proximity Sensor Detection
The proximity sensor was first mounted to the front bumper of the car. When it was disabled, control of the car was normal. When enabled the car became very erratic. We later learned that the field-of-view of the sensor was cone shaped and the ground was most likely in view of the sensor. The sensor also has a minimum range detection of 6". We mounted the sensor higher and farther back on the car which gave us the control expected.
Testing
The TX board software and RX board software were tested independently prior to integration. Then the integration of the TX and RX board was performed in steps up to the final integrated configuration.
TX Board
The TX board software testing consisted of printing wireless commands to the serial window to verify the accelerometer function. Although this did not mimic the timing of the actual system, since the serial port print slows the processor, it provided a baseline of the command data to be transmitted and gave the ability to develop the accelerometer value conversions.
RX Board
The RX board software testing consisted of using switches rather than receiving wireless commands, controlled by #define, to control the car. Some timers were used to de-bounce the switches. Also, an oscilloscope was used to verify the PWM frequency and pulse widths required by the servo and speed controller. The serial port was also used to test the features of the upside detection and tilt over detection logic.
Integrated Testing
Once both the TX and RX board were tested independently, the first integration test was to have the TX board transmit the wireless commands and have the RX board print the value to the serial port. Next, with the car sitting on a stand we determined the stability of the TX and RX boards to control the car. When it was proven that the car was reliable and stable, we drove the car in a controlled environment.
We operated the the car in different environments, outside and inside, to ensure its reliability. We also tested the distance that the car could travel from the TX board and it found it to be around 40 feet.
Conclusion
The RC Control car was a fun project that also demonstrated that the simplest software solution to control hardware is usually the best. Integrating software and hardware with the knowledge of the hardware devices being controlled made integrated levels of degrees easier. The testing philosophy of verifying drivers as they are developed, rather than at final integration, proved successful. Since TX and RX boards software was tested by modules, individually, and finally integrated, the project came together smoothly. The UART interface was vital in the development as challenges encountered were quickly overcome.
We did have some thoughts for future expansion on this project such as:
- Add GPS features to command the car to a location
- Add small video camera to utilize the SD card memory as a recorder
- Replace the electronic speed control to include reverse (current one only had forward and brake)
All in all, the experience gave us good practical applications of standard interfaces such as I2C, UART, ADC and SPI to control multiple devices in a practical manner.
Project Video
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
Thank you Professor Kang for expanding our project with the supplied proximity sensor and provided guidance.
References Used
None