Difference between revisions of "S18: Spybot"
Proj user1 (talk | contribs) (→Software Design) |
Proj user1 (talk | contribs) (→References Used) |
||
| (82 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[FILE:cmpe244 s18 spybot car.jpg|right|frame]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Project Title == | == Project Title == | ||
<center><h3> Spybot </h3></center> | <center><h3> Spybot </h3></center> | ||
| + | [[File: Cmpe244 s18 spybot ic_launcher.png|center|Eye C launcher]] | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| − | The team will develop a RC car driven remotely with an Android smartphone. The RC car will be equipped with a camera to provide real-time visual feedback to the smartphone. The camera will also be mounted on a servo to add the capability to change the camera angle. The SJOne will be used to drive the motor and servo of the car in addition to the camera’s servo. The Android smartphone will communicate with the SJOne using Bluetooth. The Android smartphone will be used to command the SJOne and drive the car and motorized camera. The RaspberryPi will stream visual data to the Android smartphone. | + | The team will develop a RC car driven remotely with an Android smartphone. The RC car will be equipped with a camera to provide real-time visual feedback to the smartphone. The camera will also be mounted on a servo to add the capability to change the camera angle. The SJOne will be used to drive the motor and servo of the car in addition to the camera’s servo. The Android smartphone will communicate with the SJOne using Bluetooth. The Android smartphone will be used to command the SJOne and drive the car and motorized camera. The RaspberryPi will stream visual data to the Android smartphone. Additionally, collision avoidance was added to prevent the RC car from colliding with objects in front. |
== Objectives & Introduction == | == Objectives & Introduction == | ||
| − | |||
=== Team Members & Responsibilities === | === Team Members & Responsibilities === | ||
| Line 24: | Line 14: | ||
** Android app & bluetooth communication | ** Android app & bluetooth communication | ||
* Jason Tran | * Jason Tran | ||
| − | ** PCB design & RC car firmware | + | ** PCB design & RC car firmware & Time-of-Flight sensor |
* Sophia Quan | * Sophia Quan | ||
** Servo camera mount and camera integration | ** Servo camera mount and camera integration | ||
| Line 117: | Line 107: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | $ | + | | $343.90 |
|} | |} | ||
== Design & Implementation == | == Design & Implementation == | ||
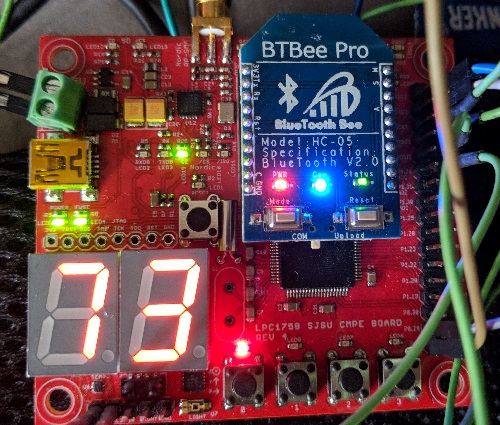
| − | The | + | The following image below shows the model of RC car used. The RC car is used as a base and the firmware of it was changed so that the SJone board is controlling the RC car. |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | The servo and motor of the Traxxas truck comes with a servo and a motor that is controlled via Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). There are 3 different color wires for both servo and motor. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''White''' wires should be connected to the SJone's PWM pin. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Black''' wires should be connected to ground. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Red''' wires should be connected together. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File: Cmpe244 s18 spybot traxxas.png|512px|traxxas]] | ||
| + | [[File: Cmpe244 s18 spybot traxxas servo motor.png|512px|traxxas servo motor]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
=== Hardware Design === | === Hardware Design === | ||
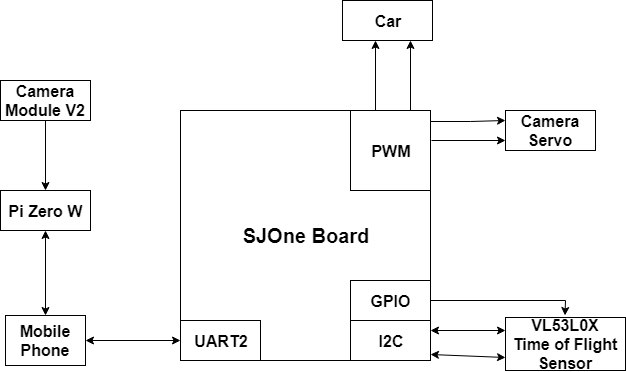
| − | + | [[File: Cmpe244 s18 spybot overallhardware.png|center|frame|Overall Hardware Architecture]] | |
There are various connections to the SJOne Board in the project. To deal with the steering of the car, two different PWM pins are connected to the car: one for the motor and one for the servo. The camera servo also requires two connections to the PWM pins of the SJOne Board: one for the tilt and one for the horizontal movements. The VL53L0X time of flight sensor sends data through the I2C bus to the SJOne Board and requires a connection for the data and another for the clock. The sensor also connects to a general purpose output pin for its shutdown pin. To connect to the mobile phone, an XBEE Bluetooth module was placed on the board and it communicates with the microprocessor via UART. Finally, the mobile phone connects to the Raspberry Pi Zero W and camera through a hotspot connection. | There are various connections to the SJOne Board in the project. To deal with the steering of the car, two different PWM pins are connected to the car: one for the motor and one for the servo. The camera servo also requires two connections to the PWM pins of the SJOne Board: one for the tilt and one for the horizontal movements. The VL53L0X time of flight sensor sends data through the I2C bus to the SJOne Board and requires a connection for the data and another for the clock. The sensor also connects to a general purpose output pin for its shutdown pin. To connect to the mobile phone, an XBEE Bluetooth module was placed on the board and it communicates with the microprocessor via UART. Finally, the mobile phone connects to the Raspberry Pi Zero W and camera through a hotspot connection. | ||
=== Hardware Interface === | === Hardware Interface === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 194: | Line 194: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope = "row"|8 | ! scope = "row"|8 | ||
| − | | | + | | UART |
| - | | - | ||
| Bidirectional | | Bidirectional | ||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
=== PWM === | === PWM === | ||
<p></p> | <p></p> | ||
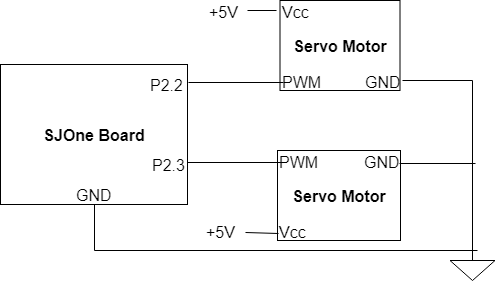
| − | + | <center>[[File:SpybotServo2.png|center|frame|Connections from the SJOne Board to the camera mount]]</center> | |
| + | |||
| + | The camera mount consists of two different servo motors. The top servo motor is connected to Port 2.2 and controls the tilt and allows the camera to pan up and down. The other servo motor is connected to Port 2.3 and controls the horizontal range and allows the camera to look left and right. Additionally, the SJOne Board can not supply a sufficient amount of voltage to the servos to allow them to run so an external power source supplies 5 volts. The servos move based on a varying duty cycle supplied to the motor from the SJOne Board. The duty cycle in the 50 Hz PWM Period ranges from 1 ms to 2 ms. Based on the duration that the duty cycle is active, the servo will assume a position with a 1.5 ms duty cycle being the middle position. | ||
| + | |||
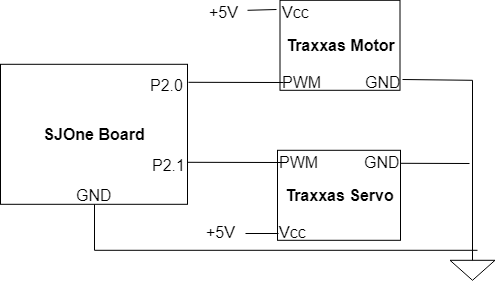
| + | <center>[[FILE: Cmpe244 s18 spybot carconnections.png |center|frame|Connections from the SJOne Board to the motors of the Traxxas car]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Traxxas car is controlled by two motors: one to control the speed and one to control the direction. Both of these connections utilize the PWM functionality of the SJOne Board. The motor controls the speed which increases based on the duty cycle of the wave. The servo motor operates similarly to that of the camera mount and will turn to different positions based on the duty cycle of the wave. | ||
=== I2C === | === I2C === | ||
<p></p> | <p></p> | ||
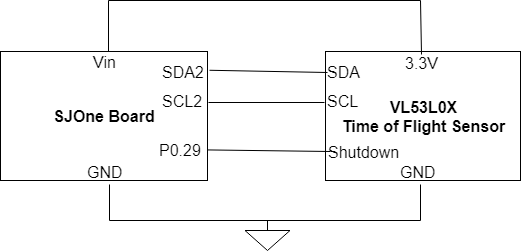
| − | <center>[[FILE: | + | <center>[[FILE: Cmpe244 s18 spybot i2csensor.png |center|frame|Connections from the SJOne Board to the VL53L0X time of flight sensor]]</center> |
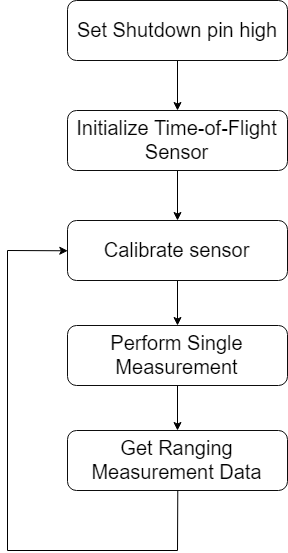
| − | The VL53L0X time of flight sensor connects to the SJOne Board through the I2C Bus. The SDA and SCL signals are connected to the SDA2 and SCL2 pins on the SJOne Board, respectively. In addition, the shutdown pin is connected to P0.29 which is used as an output with the GPIO functionality of the microprocessor. | + | The VL53L0X time of flight sensor connects to the SJOne Board through the I2C Bus. The SDA and SCL signals are connected to the SDA2 and SCL2 pins on the SJOne Board, respectively. In addition, the shutdown pin is connected to P0.29 which is used as an output with the GPIO functionality of the microprocessor to allow the sensor to reset. |
| − | === | + | === UART === |
<p></p> | <p></p> | ||
| − | + | The bluetooth module is connected to the SJOne Board through the XBee WiFly BT insert area. It communicates to a mobile phone via Bluetooth and sends information to the microprocessor through the UART 2 communication protocol. The XBee module acts as a receiver to the board as the phone sends motor and servo controls through an application. The board also transmit the distance sensor data to the phone every half a second. | |
| + | |||
| + | The bluetooth module receives data packets with the following detail | ||
| + | bluetooth data motor% car_servo% camera_vertical% car_servo_left/right forward/backward camera_left/right camera_up/down camera_horizontal% | ||
| + | |||
| + | A bluetooth API was built in order to create an easy interface to set/get the parsed packet value. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CMPE244_S18_Spybot_Firmware_btpro.jpg|center|frame|BTPro]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Raspberry Pi === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To accomplish the video streaming aspect of the project, the Raspberry Pi Zero W with a camera module was used. It provided the processing power to deal with video at 15 fps and could stream the video to the mobile application through Wi-Fi connection. Having a separate board deal with the video processing allowed more resources for the SJOne to deal with the steering, obstacle avoidance, and camera mount servo controlling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Raspberry Pi was flashed with MotionEyeOS. This gave us the flexibility to control various settings to optimize the streaming quality to the phone. The settings used allowed for video to be streamed at 15 fps with a half second delay. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[FILE: cmpe244 s18 spybot pi.jpg | center | frame | Raspberry Pi with camera module]] | ||
=== Software Design === | === Software Design === | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | The firmware architecture consists of 4 application-specific modules: | ||
| + | 1. Bluetooth interface | ||
| + | 2. Driver | ||
| + | 3. Proximity | ||
| + | 4. Camera mount controller | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Bluetooth interface is responsible for communication between the firmware and the controller software (Android application). The bluetooth interface exposes the following functionality: drive the RC car and control the camera mount tilt/pan. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The driver is responsible for translating parameters acquired from the Bluetooth interface to control the car's servo and motor as commanded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The proximity module is responsible for communicating with the time of flight sensor and provide an up-to-date frontal distance for proximity awareness. The driver uses the distance for collision avoidance by prohibiting the car from moving forward. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The camera mount controller is responsible for translating parameters acquired from the Bluetooth interface to control the camera mount's tilt servo and pan servo as commanded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:cmpe244 s18 spybot softwaredesign.jpg|center|frame|Firmware Architecture]] | ||
=== Implementation === | === Implementation === | ||
| − | |||
'''Servo Motor''' | '''Servo Motor''' | ||
The servo motor is used as a camera mount for the Raspberry Pi camera. It uses a PWM signal and the percentage of how much the servo should pan or tilt is supplied by the Android application | The servo motor is used as a camera mount for the Raspberry Pi camera. It uses a PWM signal and the percentage of how much the servo should pan or tilt is supplied by the Android application | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''VL53L0X time of flight sensor''' | ||
| + | [[File:cmpe244 s18 spybot time of flight flow.png|center|Time of Flight diagram]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' RC car control logic''' | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The RC car control logic is primarily controlled via the Android app. There are 2 flags that control the RC car's movement and direction. A forward/backward flag is used to control the RC car to move forward or backwards. A left/right flag is used to control the direction of where to steer. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | An addition feature added to the project was collision avoidance. | ||
| + | When the distance sensor is blocked and below a threshold, for example, 300 millimeters, the RC car will be unable to move forward even when the user increase the speed percentage to drive the motor. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:cmpe244 s18 spybot drive control logic.png|center|car control logic]] | ||
== Android Application == | == Android Application == | ||
| − | The main purpose of the Android application is to provide a simple user interface that allows the user to control the RC car. The user interface mimics what existing game consoles/controllers look like. | + | The main purpose of the Android application is to provide a simple user interface that allows the user to control the RC car via bluetooth. The user interface mimics what existing game consoles/controllers look like. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:SpybotUI.jpg|center|frame|Spybot UI]] |
| − | |||
'''The Android app will provide:''' | '''The Android app will provide:''' | ||
* Autoconnect Bluetooth to RC car | * Autoconnect Bluetooth to RC car | ||
| Line 262: | Line 310: | ||
compile 'io.github.controlwear:virtualjoystick:1.9.2' | compile 'io.github.controlwear:virtualjoystick:1.9.2' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | OnMoveListener is a callback function that is called every time the joystick position changes. The joysticks have a refresh rate of 50ms. | + | '''OnMoveListener''' is a callback function that is called every time the joystick position changes. The joysticks have a refresh rate of 50ms. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | MessageHandler is an intermediate layer which handles all receiving and transmitting requests. | + | '''MessageHandler''' is an intermediate layer which handles all receiving and transmitting requests. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | BluetoothService is the underlying layer after MessageHandler which assists with all high level Bluetooth functionality such as connect/disconnect and receiving/transmitting. It abstracts the detail of ConnectThread. In this layer, packets are also parsed so it can provide useful in the Fragment layer. This is also the layer where packets are built. | + | '''BluetoothService''' is the underlying layer after MessageHandler which assists with all high level Bluetooth functionality such as connect/disconnect and receiving/transmitting. It abstracts the detail of ConnectThread. In this layer, packets are also parsed so it can provide useful in the Fragment layer. This is also the layer where packets are built. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | ConnectThread is the final layer which does the low level initialization such as UUID and opening/closing sockets. This layer handles all incoming and outgoing messages. | + | '''ConnectThread''' is the final layer which does the low level initialization such as UUID and opening/closing sockets. This layer handles all incoming and outgoing messages. |
| + | |||
| + | === Use Cases === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Auto Connect === | ||
| + | When the app starts, auto connection to the RC car is initiated if it is in bluetooth range. It is able to auto connect by hardcoding the bluetooth MAC address in the app. | ||
| + | [[File:Cmpe244_S18_Spybot_auto_connect.png|center|frame|Spybot autoconnect]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Sending Data === | ||
| + | Packets of data is sent to the RC car periodically every 100ms when the '''On''' switch is toggled. | ||
| + | The packet includes: | ||
| + | * motor drive percentage from 0% to 100% | ||
| + | * car steer percentage from 0% to 100% | ||
| + | * camera tilt percentage from 0% to 100% | ||
| + | * camera pan percentage from 0% to 100% | ||
| + | * flag to determine left or right steering of car | ||
| + | * flag to determine car to drive forward or backwards | ||
| + | * flag to determine camera tilt up or down | ||
| + | * flag to determine camera pan left or right | ||
| + | |||
| + | Camera pan/tilt percentage will only change when the '''Camera''' switch is toggled on. When toggled off, car steering percentage will change, along with its associated flags. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The car will default to move forward when the '''Camera''' switch is toggled off. The car will move backwards when the steering joystick is moved below the lower half and forward when moved above the center. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Cmpe244_S18_Spybot_send_data.png|center|frame|Spybot Send Data]] | ||
== Testing & Technical Challenges == | == Testing & Technical Challenges == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Noise Interference === | |
| + | Noise was a huge issue when it came to steering the car. One of the issues occurred when the car was moving despite the duty cycle of the PWM connected to it was set to 0%. The solution we used to remedy this issue was to organize and rewire the car to minimize the effect of noise. Once this issue was fixed, the car was able to move and turn according to the requirements and specifications we initially set with the car and application. | ||
| + | <p> </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Raspberry Pi Camera Ribbon === | === Raspberry Pi Camera Ribbon === | ||
The ribbon used for the camera to communicate with the RPi is very sensitive. While testing out the camera and its settings, the video feed would cut out a lot when the ribbon was disturbed. There were times when the camera would not be detected at all. To remedy this issue, the connection was gently redone until the video feed returned. | The ribbon used for the camera to communicate with the RPi is very sensitive. While testing out the camera and its settings, the video feed would cut out a lot when the ribbon was disturbed. There were times when the camera would not be detected at all. To remedy this issue, the connection was gently redone until the video feed returned. | ||
| Line 284: | Line 353: | ||
=== Connecting to the Pi Zero W === | === Connecting to the Pi Zero W === | ||
| − | Initially, the group wanted to have the phone to connect to the Raspberry Pi through Wi-Fi. However, when setting up the Pi to be a Wi-Fi | + | Initially, the group wanted to have the phone to connect to the Raspberry Pi through Wi-Fi. However, when setting up the Pi to be a Wi-Fi access point, the phones could not discover the Pi, making communication impossible. Furthermore, it did not allow the Pi to initially boot up properly. To rectify this problem, the group decided to have the mobile phone with the application be a hotspot host. While this means that the Pi would have to be reconfigured every time it wants to connect to a new phone, the results would be consistent with the feed from the camera being able to broadcast to the host phone. |
| + | |||
| + | === VL53L0X Time of Flight Sensor === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Time of Flight sensor was very tricky to bring-up as little to no datasheet was provided. The sensor is from STMicroelectronics. The datasheet does not provide any register information, such as register address and register information. They expect you to use their pre-built API or their development kit, so the whole sensor was a black-box. Although a pre-built API was provided, the whole driver layer was written for Windows. Reverse engineering had to be done by swapping out the Window linkage to SJone's driver interface (I2C). | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Android Application === | ||
| + | Making the App was challenging because it was the first time developing an Android application. Basic concepts of Android programming had to be learnt quickly in the early development cycle of the project. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Every new feature of the App was tested rigorously so the App would not crash or stop working. | ||
| + | Since the app receives packets from the SJone board, packet parsing needed to be done in the App. There was NullExceptions occurring frequently causing the App to crash. To solve the issue, Android Studio's logger was used in order to print out every packet received. It turns out the App receives an extra byte of information at the beginning of the packet causing indexing-out-of-bound exceptions. The bug was fixed by taking into account that extra byte of information and removing it before the parsing process. | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
| − | + | In conclusion, the project worked to the requirements we had set up at its inception. Throughout the project, there were a lot of errors encountered such as the noise which made steering the car difficult to the utilization of the Raspberry Pi. Despite all of this, we were able to complete the project in time and demo a car that can be viewed and steered through the application. While the car was working and usable for the demo, there are still many improvements that we could have done. One of the biggest improvements would have been the implementation of a PCB which would have made testing as well as connected the pieces together much easier. Another improvement would have been to utilize the Raspberry Pi as a Wi-Fi access point to make the project more robust and portable. Despite some of these missing features, the Spybot is a project we are proud to call our own. | |
=== Project Video === | === Project Video === | ||
| − | + | [https://youtu.be/22DXwV99oBY Video Link] | |
=== Project Source Code === | === Project Source Code === | ||
| − | * [https:// | + | * [https://bitbucket.org/cmpe244heatsquared/spybot/src Firmware Git] |
| + | * [https://bitbucket.org/cmpe244heatsquared/spybot_app/src Software Git] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 303: | Line 383: | ||
=== References Used === | === References Used === | ||
| − | |||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
* [https://github.com/ccrisan/motioneyeos/wiki MotionEyeOS Source Code] | * [https://github.com/ccrisan/motioneyeos/wiki MotionEyeOS Source Code] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/controlwear/virtual-joystick-android JoystickView] | ||
| + | * [https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth#ManagingAConnection Bluetooth for Android] | ||
=== Appendix === | === Appendix === | ||
| − | + | None | |
Latest revision as of 08:39, 27 May 2018
Contents
Project Title
Spybot
Abstract
The team will develop a RC car driven remotely with an Android smartphone. The RC car will be equipped with a camera to provide real-time visual feedback to the smartphone. The camera will also be mounted on a servo to add the capability to change the camera angle. The SJOne will be used to drive the motor and servo of the car in addition to the camera’s servo. The Android smartphone will communicate with the SJOne using Bluetooth. The Android smartphone will be used to command the SJOne and drive the car and motorized camera. The RaspberryPi will stream visual data to the Android smartphone. Additionally, collision avoidance was added to prevent the RC car from colliding with objects in front.
Objectives & Introduction
Team Members & Responsibilities
- YuYu Chen
- Android app & bluetooth communication
- Jason Tran
- PCB design & RC car firmware & Time-of-Flight sensor
- Sophia Quan
- Servo camera mount and camera integration
- Andrew Javier
- Camera integration
- Jeremy Chau
- Camera integration
Schedule
| Week# | Date | Task | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 04/15/2018 | Able to communicate with Bluetooth module on MCU by end of the week | Completed |
| 2 | 04/22/2018 | Start on Android application and have UI finished by end of week
Research possible ways to display live video feed in Android application |
Completed |
| 3 | 04/29/2018 | Establish Bluetooth communication with Android App and MCU
Start PCB design Start on motor and servo(s) controller Install MotionEyeOS and get familiar with the UI |
Completed |
| 4 | 05/06/2018 | Test Android app communication with RC car
Test RPi Camera with MotionEyeOS on multiple devices Get camera servo up and running by end of week |
Completed |
| 5 | 05/13/2018 | System Integration and testing | Completed |
| 6 | 05/20/2018 | System testing | Completed |
Parts List & Cost
| Quantity | Vendor | Item | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | San Jose State University | SJ One Board | $80.00 |
| 1 | Adafruit | Raspberry Pi Zero W Camera Pack | $44.95 |
| 1 | Traxxas | Traxxas Stampede: Monster Truck | $199.95 |
| 1 | ITead | BTBee Pro | $12.50 |
| 1 | SparkFun | Servo Camera Mount | $6.50 |
| Total | $343.90 |
Design & Implementation
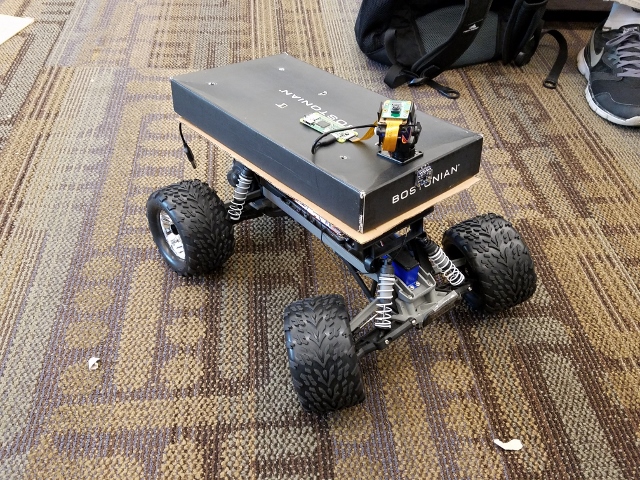
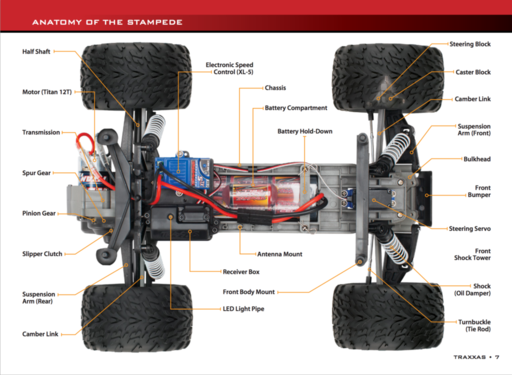
The following image below shows the model of RC car used. The RC car is used as a base and the firmware of it was changed so that the SJone board is controlling the RC car.
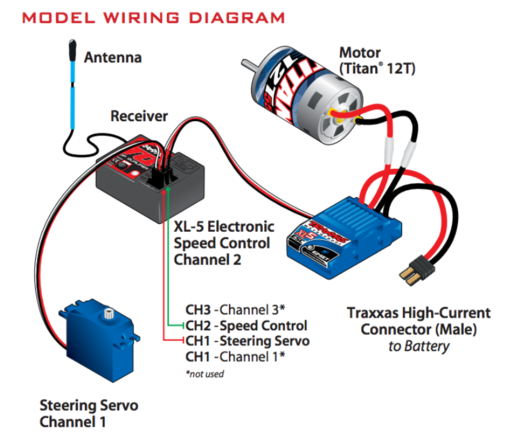
The servo and motor of the Traxxas truck comes with a servo and a motor that is controlled via Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). There are 3 different color wires for both servo and motor.
White wires should be connected to the SJone's PWM pin.
Black wires should be connected to ground.
Red wires should be connected together.
Hardware Design
There are various connections to the SJOne Board in the project. To deal with the steering of the car, two different PWM pins are connected to the car: one for the motor and one for the servo. The camera servo also requires two connections to the PWM pins of the SJOne Board: one for the tilt and one for the horizontal movements. The VL53L0X time of flight sensor sends data through the I2C bus to the SJOne Board and requires a connection for the data and another for the clock. The sensor also connects to a general purpose output pin for its shutdown pin. To connect to the mobile phone, an XBEE Bluetooth module was placed on the board and it communicates with the microprocessor via UART. Finally, the mobile phone connects to the Raspberry Pi Zero W and camera through a hotspot connection.
Hardware Interface
Pin Connectivity Table
| Item | Pin Usage | Port.Pin | Direction | Peripheral | Peripheral Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PWM | P2.0 | Output | SJ One Board | Car Motor |
| 2 | PWM | P2.1 | Output | SJ One Board | Car Servo |
| 3 | PWM | P2.2 | Output | SJ One Board | Camera Servo Tilt |
| 4 | PWM | P2.3 | Output | SJ One Board | Camera Servo Horizontal |
| 5 | I2C | SDA2 | Bidirectional | SJ One Board | VL53L0X SDA |
| 6 | I2C | SCL | Bidirectional | SJ One Board | VL53L0X SCL |
| 7 | GPIO | P0.29 | Output | SJ One Board | VL53L0X Shutdown |
| 8 | UART | - | Bidirectional | SJ One Board | XBEE Bluetooth |
PWM
The camera mount consists of two different servo motors. The top servo motor is connected to Port 2.2 and controls the tilt and allows the camera to pan up and down. The other servo motor is connected to Port 2.3 and controls the horizontal range and allows the camera to look left and right. Additionally, the SJOne Board can not supply a sufficient amount of voltage to the servos to allow them to run so an external power source supplies 5 volts. The servos move based on a varying duty cycle supplied to the motor from the SJOne Board. The duty cycle in the 50 Hz PWM Period ranges from 1 ms to 2 ms. Based on the duration that the duty cycle is active, the servo will assume a position with a 1.5 ms duty cycle being the middle position.
The Traxxas car is controlled by two motors: one to control the speed and one to control the direction. Both of these connections utilize the PWM functionality of the SJOne Board. The motor controls the speed which increases based on the duty cycle of the wave. The servo motor operates similarly to that of the camera mount and will turn to different positions based on the duty cycle of the wave.
I2C
The VL53L0X time of flight sensor connects to the SJOne Board through the I2C Bus. The SDA and SCL signals are connected to the SDA2 and SCL2 pins on the SJOne Board, respectively. In addition, the shutdown pin is connected to P0.29 which is used as an output with the GPIO functionality of the microprocessor to allow the sensor to reset.
UART
The bluetooth module is connected to the SJOne Board through the XBee WiFly BT insert area. It communicates to a mobile phone via Bluetooth and sends information to the microprocessor through the UART 2 communication protocol. The XBee module acts as a receiver to the board as the phone sends motor and servo controls through an application. The board also transmit the distance sensor data to the phone every half a second.
The bluetooth module receives data packets with the following detail
bluetooth data motor% car_servo% camera_vertical% car_servo_left/right forward/backward camera_left/right camera_up/down camera_horizontal%
A bluetooth API was built in order to create an easy interface to set/get the parsed packet value.
Raspberry Pi
To accomplish the video streaming aspect of the project, the Raspberry Pi Zero W with a camera module was used. It provided the processing power to deal with video at 15 fps and could stream the video to the mobile application through Wi-Fi connection. Having a separate board deal with the video processing allowed more resources for the SJOne to deal with the steering, obstacle avoidance, and camera mount servo controlling.
The Raspberry Pi was flashed with MotionEyeOS. This gave us the flexibility to control various settings to optimize the streaming quality to the phone. The settings used allowed for video to be streamed at 15 fps with a half second delay.
Software Design
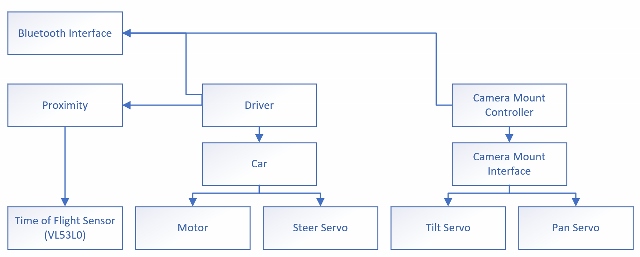
The firmware architecture consists of 4 application-specific modules: 1. Bluetooth interface 2. Driver 3. Proximity 4. Camera mount controller
The Bluetooth interface is responsible for communication between the firmware and the controller software (Android application). The bluetooth interface exposes the following functionality: drive the RC car and control the camera mount tilt/pan.
The driver is responsible for translating parameters acquired from the Bluetooth interface to control the car's servo and motor as commanded.
The proximity module is responsible for communicating with the time of flight sensor and provide an up-to-date frontal distance for proximity awareness. The driver uses the distance for collision avoidance by prohibiting the car from moving forward.
The camera mount controller is responsible for translating parameters acquired from the Bluetooth interface to control the camera mount's tilt servo and pan servo as commanded.
Implementation
Servo Motor
The servo motor is used as a camera mount for the Raspberry Pi camera. It uses a PWM signal and the percentage of how much the servo should pan or tilt is supplied by the Android application
VL53L0X time of flight sensor
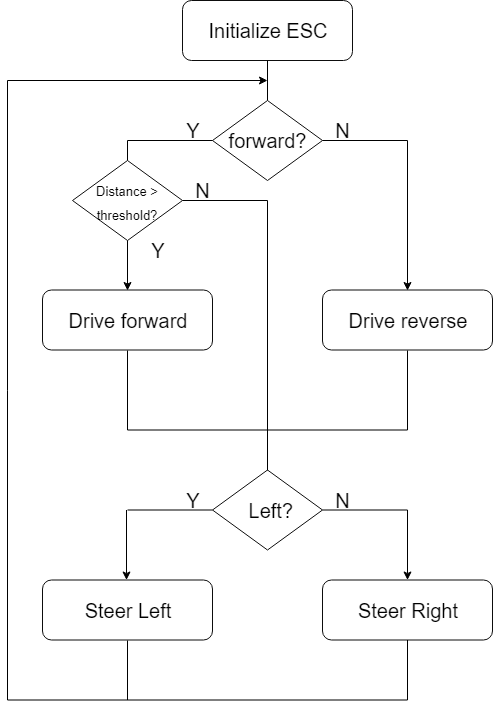
RC car control logic
The RC car control logic is primarily controlled via the Android app. There are 2 flags that control the RC car's movement and direction. A forward/backward flag is used to control the RC car to move forward or backwards. A left/right flag is used to control the direction of where to steer.
An addition feature added to the project was collision avoidance.
When the distance sensor is blocked and below a threshold, for example, 300 millimeters, the RC car will be unable to move forward even when the user increase the speed percentage to drive the motor.
Android Application
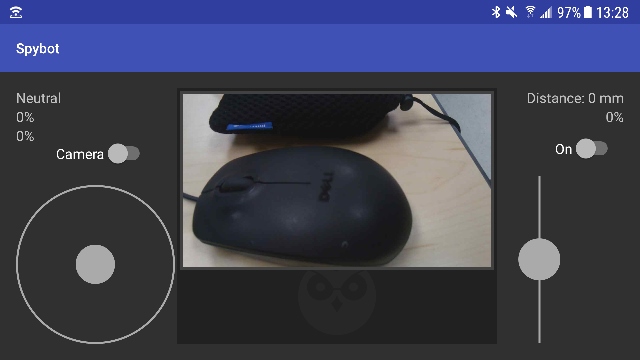
The main purpose of the Android application is to provide a simple user interface that allows the user to control the RC car via bluetooth. The user interface mimics what existing game consoles/controllers look like.
The Android app will provide:
- Autoconnect Bluetooth to RC car
- Steer the RC car left and right
- Drive the RC car forward and backwards
- Control servo tilt and pan orientation
The Android app will display:
- Live video feed from camera
- Current orientation of joystick
- Percentage of horizontal orientation
- Percentage of vertical orientation
- Speed of RC car in percentage
- Distance in millimeter from Time-of-Flight sensor
Software Design
High Level Architecture Design
The application is able to send and receive to/from the RC car via Bluetooth. With its simple UI, it is easy to control the RC car. The RC car will not receive any data until the On switch is toggled. Once toggled, the RC car will receive the data packets if it is within the vicinity. The left joystick is used to steer the RC car left or right depending on the position within the joystick circle. It is also used to determine if the RC car will drive forward or backward.
To steer the camera, the Camera switch needs to be toggled. The left joystick is used to pan left and right, and tilt up and down if Camera is toggled.
The right joystick is control the speed of the RC car. The range is between 0% to 100%.
The webView in the middle of the app allows the user to stream live-feed video from the camera on the RC car.
Implementation
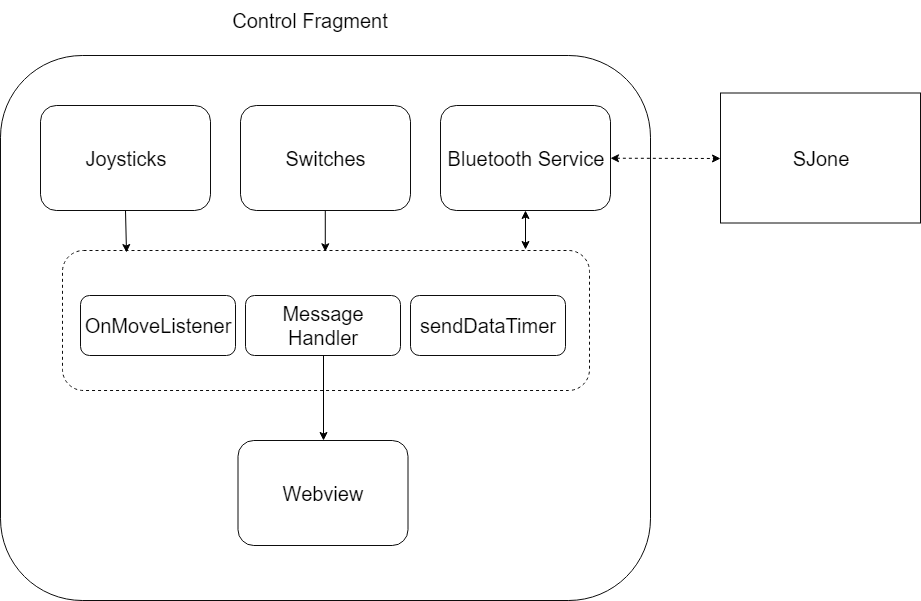
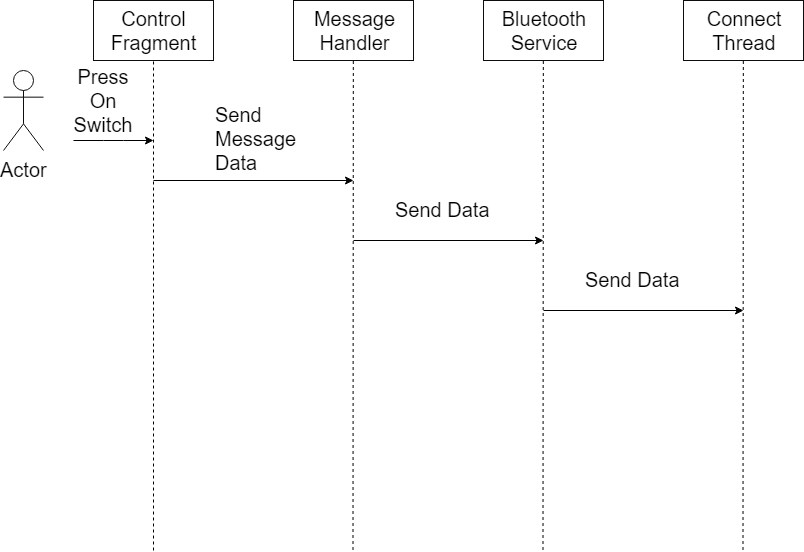
Control Fragment
The Control Fragment is the main fragment which contains all Views, such as textView, joystickView, and webView. This layer links the the message layer where different messages are handled. Joystick view is a custom view created by makowildcat. In order to download, the following needs to be added to the gradle script.
compile 'io.github.controlwear:virtualjoystick:1.9.2'
OnMoveListener is a callback function that is called every time the joystick position changes. The joysticks have a refresh rate of 50ms.
MessageHandler is an intermediate layer which handles all receiving and transmitting requests.
BluetoothService is the underlying layer after MessageHandler which assists with all high level Bluetooth functionality such as connect/disconnect and receiving/transmitting. It abstracts the detail of ConnectThread. In this layer, packets are also parsed so it can provide useful in the Fragment layer. This is also the layer where packets are built.
ConnectThread is the final layer which does the low level initialization such as UUID and opening/closing sockets. This layer handles all incoming and outgoing messages.
Use Cases
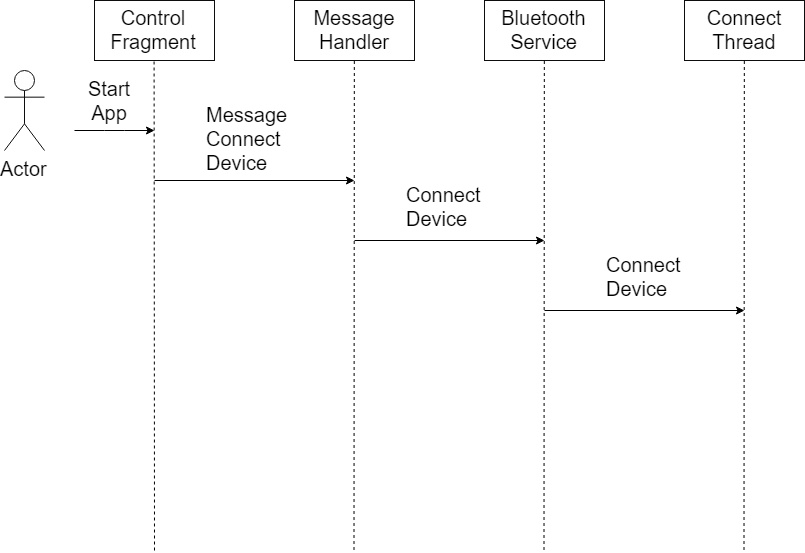
Auto Connect
When the app starts, auto connection to the RC car is initiated if it is in bluetooth range. It is able to auto connect by hardcoding the bluetooth MAC address in the app.
Sending Data
Packets of data is sent to the RC car periodically every 100ms when the On switch is toggled. The packet includes:
- motor drive percentage from 0% to 100%
- car steer percentage from 0% to 100%
- camera tilt percentage from 0% to 100%
- camera pan percentage from 0% to 100%
- flag to determine left or right steering of car
- flag to determine car to drive forward or backwards
- flag to determine camera tilt up or down
- flag to determine camera pan left or right
Camera pan/tilt percentage will only change when the Camera switch is toggled on. When toggled off, car steering percentage will change, along with its associated flags.
The car will default to move forward when the Camera switch is toggled off. The car will move backwards when the steering joystick is moved below the lower half and forward when moved above the center.
Testing & Technical Challenges
Noise Interference
Noise was a huge issue when it came to steering the car. One of the issues occurred when the car was moving despite the duty cycle of the PWM connected to it was set to 0%. The solution we used to remedy this issue was to organize and rewire the car to minimize the effect of noise. Once this issue was fixed, the car was able to move and turn according to the requirements and specifications we initially set with the car and application.
Raspberry Pi Camera Ribbon
The ribbon used for the camera to communicate with the RPi is very sensitive. While testing out the camera and its settings, the video feed would cut out a lot when the ribbon was disturbed. There were times when the camera would not be detected at all. To remedy this issue, the connection was gently redone until the video feed returned.
Connecting to the Pi Zero W
Initially, the group wanted to have the phone to connect to the Raspberry Pi through Wi-Fi. However, when setting up the Pi to be a Wi-Fi access point, the phones could not discover the Pi, making communication impossible. Furthermore, it did not allow the Pi to initially boot up properly. To rectify this problem, the group decided to have the mobile phone with the application be a hotspot host. While this means that the Pi would have to be reconfigured every time it wants to connect to a new phone, the results would be consistent with the feed from the camera being able to broadcast to the host phone.
VL53L0X Time of Flight Sensor
The Time of Flight sensor was very tricky to bring-up as little to no datasheet was provided. The sensor is from STMicroelectronics. The datasheet does not provide any register information, such as register address and register information. They expect you to use their pre-built API or their development kit, so the whole sensor was a black-box. Although a pre-built API was provided, the whole driver layer was written for Windows. Reverse engineering had to be done by swapping out the Window linkage to SJone's driver interface (I2C).
Android Application
Making the App was challenging because it was the first time developing an Android application. Basic concepts of Android programming had to be learnt quickly in the early development cycle of the project.
Every new feature of the App was tested rigorously so the App would not crash or stop working.
Since the app receives packets from the SJone board, packet parsing needed to be done in the App. There was NullExceptions occurring frequently causing the App to crash. To solve the issue, Android Studio's logger was used in order to print out every packet received. It turns out the App receives an extra byte of information at the beginning of the packet causing indexing-out-of-bound exceptions. The bug was fixed by taking into account that extra byte of information and removing it before the parsing process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the project worked to the requirements we had set up at its inception. Throughout the project, there were a lot of errors encountered such as the noise which made steering the car difficult to the utilization of the Raspberry Pi. Despite all of this, we were able to complete the project in time and demo a car that can be viewed and steered through the application. While the car was working and usable for the demo, there are still many improvements that we could have done. One of the biggest improvements would have been the implementation of a PCB which would have made testing as well as connected the pieces together much easier. Another improvement would have been to utilize the Raspberry Pi as a Wi-Fi access point to make the project more robust and portable. Despite some of these missing features, the Spybot is a project we are proud to call our own.
Project Video
Project Source Code
References
Acknowledgement
- Preetpal Kang
- Khalil Estell
References Used
Appendix
None