Difference between revisions of "S13: Garage Parking Aid"
(→Hardware Design) |
(→Software Design) |
||
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
This task takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to its private local variable. 2 Pins are initialized: Trigger as output, Echo as input. Then run the task, set Trigger Pin high for 20us and clear it. This will activate ultrasonic module to send 8 pulses of sound wave. Then monitor the Echo Pin, and once the Echo Pin goes high, start the timer and stop the timer when it falls back to low. This is the time for the soundwave to be sent out and echo back. Take this time and multiple by the speed of sound, then divided by two, That's the one way distance, which is what we want. ( Distance = ((Duration of high level)*(Sonic :340m/s))/2 ) After that, we use xQueueSend function to immediately send this distance value to the queue handler, and end this run. This task is designed to run every 2 sec. | This task takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to its private local variable. 2 Pins are initialized: Trigger as output, Echo as input. Then run the task, set Trigger Pin high for 20us and clear it. This will activate ultrasonic module to send 8 pulses of sound wave. Then monitor the Echo Pin, and once the Echo Pin goes high, start the timer and stop the timer when it falls back to low. This is the time for the soundwave to be sent out and echo back. Take this time and multiple by the speed of sound, then divided by two, That's the one way distance, which is what we want. ( Distance = ((Duration of high level)*(Sonic :340m/s))/2 ) After that, we use xQueueSend function to immediately send this distance value to the queue handler, and end this run. This task is designed to run every 2 sec. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:CmpE146_S13_T3_Ultra_Code.jpg|center|frame|ultrasonic_task]] |
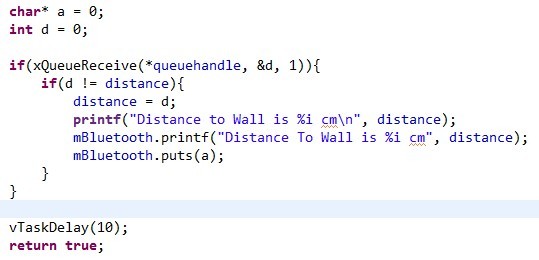
'''Bluetooth_task''' | '''Bluetooth_task''' | ||
| Line 203: | Line 203: | ||
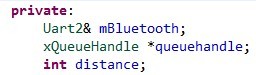
This task also takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to a private local variable; in addition, this task has another private variable that will get the instance of Uart2 Class, which controls ports connected to our bluetooth module, which is actually labeled as Uart1; and a third variable called distance, that will store the distance received from queue. | This task also takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to a private local variable; in addition, this task has another private variable that will get the instance of Uart2 Class, which controls ports connected to our bluetooth module, which is actually labeled as Uart1; and a third variable called distance, that will store the distance received from queue. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:CmpE146_S13_T3_Bluetooth_Local.jpg|center|frame|bluetooth_task local variable]] |
The task first initializes the bluetooth module, then runs in a loop, checking if anything is on the queue, if yes, it immediately receives it, if it is different from the stored value in distance from previous run, store it to local variable, distance, and output a message string containing the distance to the paired android device. | The task first initializes the bluetooth module, then runs in a loop, checking if anything is on the queue, if yes, it immediately receives it, if it is different from the stored value in distance from previous run, store it to local variable, distance, and output a message string containing the distance to the paired android device. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:CmpE146_S13_T3_Bluetooth_Code.jpg|center|frame|bluetooth_task]] |
'''Main Function''' | '''Main Function''' | ||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
The main function is really simple, it first creates a queue handle with xQueueCreate, then calls both tasks and pass the address of this handle to them. | The main function is really simple, it first creates a queue handle with xQueueCreate, then calls both tasks and pass the address of this handle to them. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:CmpE146_S13_T3_Main_Code.jpg|center|frame|main function]] |
=== Implementation === | === Implementation === | ||
Revision as of 05:27, 23 May 2013
Contents
Grading Criteria
- How well is Software & Hardware Design described?
- How well can this report be used to reproduce this project?
- Code Quality
- Overall Report Quality:
- Software Block Diagrams
- Hardware Block Diagrams
- Schematic Quality
- Quality of technical challenges and solutions adopted.
Garage Parking Aid
Abstract
The purpose of this project is to aid when parking a car. This device will send to an Android phone the distance between the car and an obstacle.
Objectives & Introduction
- Measure distance and display on computer screen
- Send data over bluetooth
- Combine bluetooth and ultrasonic
Team Members & Responsibilities
- Elizabeth
- Create UART2 driver
- Wire peripherals
- Send messages with Bluetooth
- Tian
- Create Android app
- Assemble project into a box
- Configure ultrasonic distance meter
Schedule
| Week Number | Planned Items | Actual |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
Parts List & Cost
| Parts | Cost |
|---|---|
| SJ One Board | $65 |
| Bluetooth | $0 |
| 2.4 GHz Antenna | $5 |
| Ultrasonic transmitter and receiver | $10 |
| Blackbox | $0 |
| Wire | $10 |
| Batteries | $7 |
| Total: | $97 |
Design & Implementation
Hardware Design
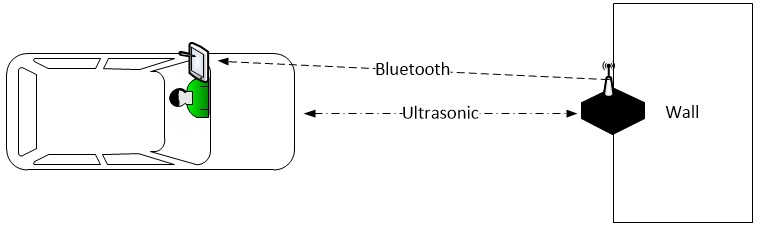
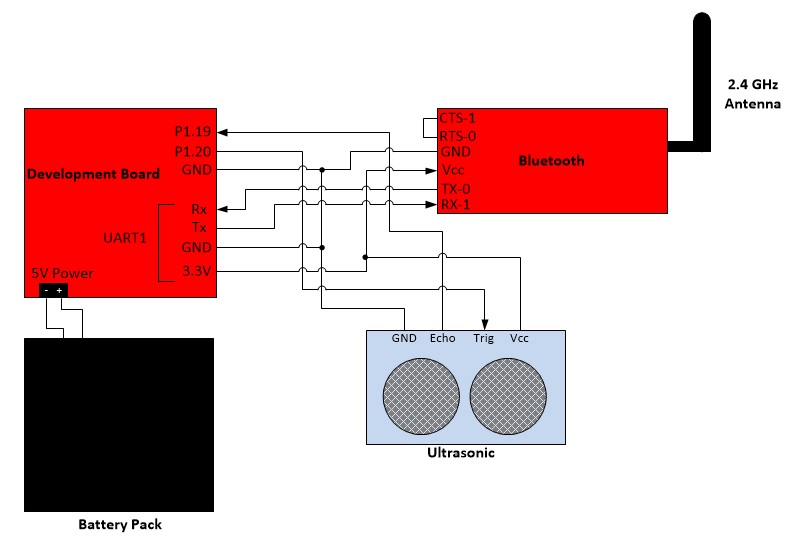
The following hardware components are all that we used for this project. The LPC1758 Processor on the SJSU_ONE Development Board, which is powered by the battery pack, controls everything through the board. It activates the ultrasonic module, gets the time reading from it, computes the readings into distance and then transfer the data to bluetooth module, then the bluetooth module will send the received data to the Android Application on a paired bluetooth Android Device through the 2.4Ghz Antenna.
Hardware Interface
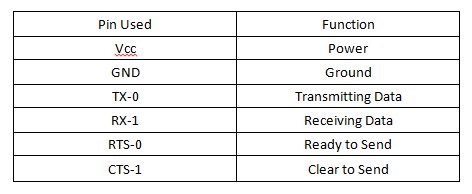
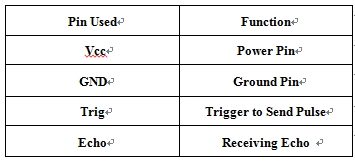
Hardware Communication: The development board is connected to the bluetooth chip and ultrasonic receiver/transmitter. The bluetooth receives data through pin RX-1, which is TX on the processor's end and transmits the data over bluetooth. The ultrasonic receives a trigger signal through the pin Trigger then sends an ultrasonic pulse. When the Echo pin is read back it will send an high signal back to the board for a brief period and that's the time sonic wave has been sent out and returned. The battery gives 5V power to development board and ultrasonic.
The Bluetooth device is connected to UART1 and the ultrasonic device is connected to GPIO. To communicate with the Bluetooth, the program sends data to UART1 and then is sent to bluetooth. To comunicate with the ultrasonic, the program sends and receives data from the board's pins P1.20 and P1.19, which are programmed to be output and input.
Another option to capture the time of the ultrasonic's pulse is to program the GPIO pins to be PWM and capture. The PWM pin will output a pulse to the ultrasonic and the ultrasonic will send an ultrasonic pulse. When it receives an echo of the pulse it will send a pulse to the caputure pin. When the capture pin receives a change in voltage, it will store the time into a designated register.
Software Design
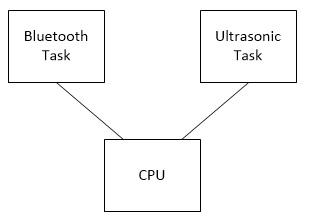
For Software Design, we have two Tasks dedicated for two components: bluetooth_task & ultrasonic_task. And we use queue for data transfer between two tasks.
Ultrasonic_task
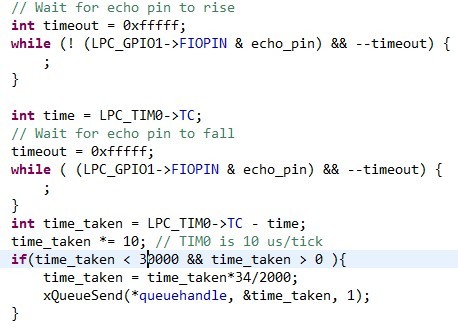
This task takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to its private local variable. 2 Pins are initialized: Trigger as output, Echo as input. Then run the task, set Trigger Pin high for 20us and clear it. This will activate ultrasonic module to send 8 pulses of sound wave. Then monitor the Echo Pin, and once the Echo Pin goes high, start the timer and stop the timer when it falls back to low. This is the time for the soundwave to be sent out and echo back. Take this time and multiple by the speed of sound, then divided by two, That's the one way distance, which is what we want. ( Distance = ((Duration of high level)*(Sonic :340m/s))/2 ) After that, we use xQueueSend function to immediately send this distance value to the queue handler, and end this run. This task is designed to run every 2 sec.
Bluetooth_task
This task also takes a queue handle pointer and stores it to a private local variable; in addition, this task has another private variable that will get the instance of Uart2 Class, which controls ports connected to our bluetooth module, which is actually labeled as Uart1; and a third variable called distance, that will store the distance received from queue.
The task first initializes the bluetooth module, then runs in a loop, checking if anything is on the queue, if yes, it immediately receives it, if it is different from the stored value in distance from previous run, store it to local variable, distance, and output a message string containing the distance to the paired android device.
Main Function
The main function is really simple, it first creates a queue handle with xQueueCreate, then calls both tasks and pass the address of this handle to them.
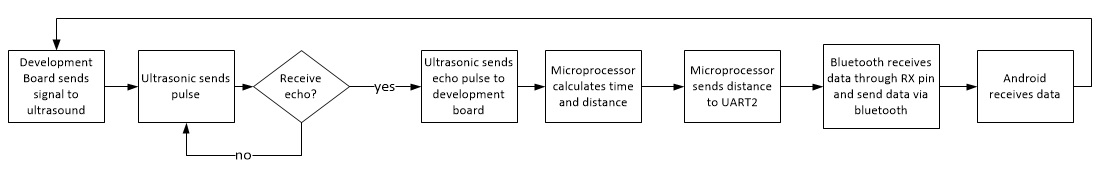
Implementation
The above flow chart is a clear view of the whole process of our project.
Get reading from Ultrasonic
1. Set Trigger Pin
2. Clear Trigger Pin
3. Wait for Echo Pin to go High
4. Measure the time duration that Echo Pin stays High
5. Echo Pin falls back to Low
6. Calculate distance: Distance = ((Duration of high level)*(Sonic :340m/s))/2
Send data through bluetooth
1.Receive data from queue and store it to a int temp variable
2.Compare temp with local private variable distance
3.if not equal, update temp to distance and send it through bluetooth
4.if equal, skip this data, and start new run and wait for the next avaiable data from queue
Testing & Technical Challenges
One major problem during testing is that whenever we point the ultrasonic module towards an object in a bad angle, where the exposed surface of the object is not sufficient, the ultrasonic reading gets stuck and the Echo Pin will keep staying Low. The solution to this problem is to add a timeout inside Ultrasonic_task to break out of the loop after reaching the timeout limit and check the timer to see if the time measured is greater than 0 and less than the time of maximum distance it could support. If the condition returns false, ignore this value and skip the queue process, and re-activated the trigger.
Conclusion
From this project, we gained a better understanding on how FreeRTOS and Uart communication works. We also learned how to build a simple Android Application associated with Bluetooth. Our project is pretty simple, but it is my (TIAN) first hardware/software hybrid project, where we had to start from the beginning, design, build and code, and finally test. We were stuck several times throughout the project, but with Preet's help, we came through. It is a good experience, and a reference to both of our future project.
Project Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Neq6_BrYMEc&feature=youtu.be
Project Source Code
Send me your zipped source code and I will upload this to SourceForge and link it for you.
References
Acknowledgement
- Preet Kang
- Dr. Haluk Ozemek
References Used
- https://www.sparkfun.com/products/158
- https://s3-ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/sain-amzn/20/20-019-100/HC-SR04.rar
- http://wiring.org.co/learning/tutorials/bluetooth/
- http://www.lynxmotion.com/images/html/build117.htm