Difference between revisions of "F14: Collision Avoidance Car"
Proj user8 (talk | contribs) (→Abstract) |
Proj user8 (talk | contribs) (→Objective & Scope) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Objective & Scope== | ==Objective & Scope== | ||
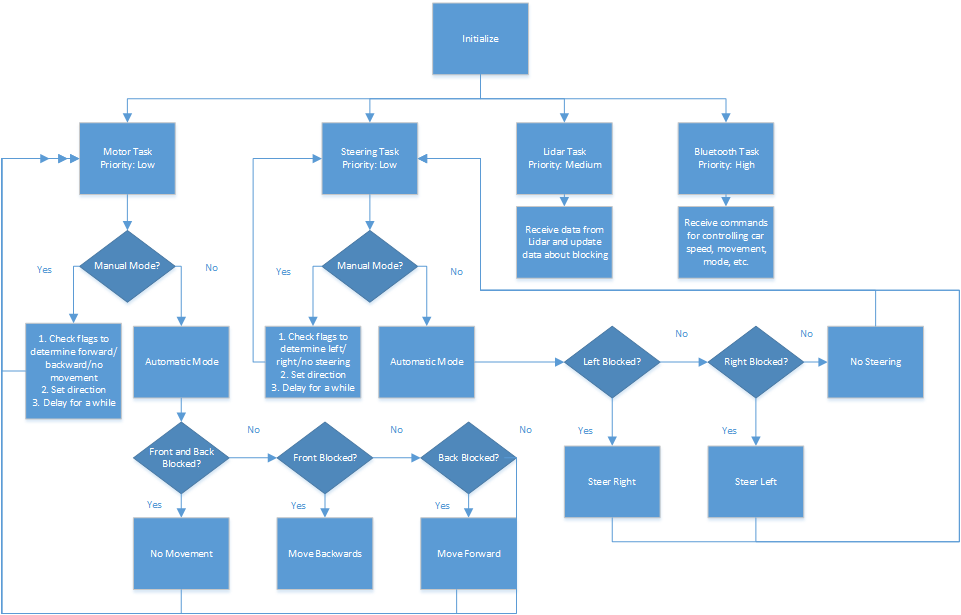
| + | The objective this project was to use a Lidar (laser-based equipment for measuring distance) to find obstacles around a moving toy car. Using this information, the car will change direction and prevent collisions. The car has two modes of operation: manual and automatic. In the manual mode, the car's movements can be controlled through a Bluetooth connection and a forward collision braking will prevent it from hitting obstacles. In the automatic mode, the car moves around autonomously while avoiding obstacles to the sides, in the front, and in the back either by stopping, steering or going forward or backward. | ||
| + | |||
==Team Members & Roles== | ==Team Members & Roles== | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Revision as of 00:01, 21 December 2014
Contents
Collision Avoidance Car
Abstract
The inspiration behind the Collision Avoidance Car comes from the state-of-the-art field of self-driving cars. All major automotive companies are investing heavily in autonomous car technology. One of the more prominent autonomous cars being developed is the Google Car, which features lidar and photo-imaging technology to implement autonomy. The goal of the self-driving car is to reduce gridlock, eliminate traffic fatalities, and most importantly, to eliminate the monotony of driving.
Objective & Scope
The objective this project was to use a Lidar (laser-based equipment for measuring distance) to find obstacles around a moving toy car. Using this information, the car will change direction and prevent collisions. The car has two modes of operation: manual and automatic. In the manual mode, the car's movements can be controlled through a Bluetooth connection and a forward collision braking will prevent it from hitting obstacles. In the automatic mode, the car moves around autonomously while avoiding obstacles to the sides, in the front, and in the back either by stopping, steering or going forward or backward.